Implementing Dual-Stack
The term dual-stack normally refers to a complete duplication of all levels in the protocol stack from applications to the network layer. An example of complete duplication is the OSI and TCP/IP protocols that run on the same system. However, in the context of IPv6 transition, dual-stack means a protocol stack that contains both IPv4 and IPv6. The remainder of the stack is identical. Consequently, the same transport protocols, TCP, UDP, and so on, can run over both IPv4 and IPv6. Also, the same applications can run over both IPv4 and IPv6.
The following figure illustrates dual-stack protocols through the OSI layers.
Figure 4–1 Dual-Stack Protocols
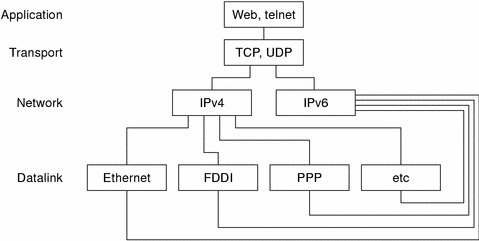
In the dual-stack method, subsets of both hosts and routers are upgraded to support IPv6, in addition to IPv4. The dual-stack approach ensures that the upgraded nodes can always interoperate with IPv4-only nodes by using IPv4.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
