Support for Solaris Zones on Sun Cluster Nodes
Solaris zones provide a means of creating virtualized operating system environments within an instance of the Solaris 10 OS. Solaris zones enable one or more applications to run in isolation from other activity on your system. The Solaris zones facility is described in Part II, Zones, in System Administration Guide: Solaris Containers-Resource Management and Solaris Zones.
When you run Sun Cluster software on the Solaris 10 OS, you can create any number of zones on a physical node.
You can use Sun Cluster software to manage the availability and scalability of applications that are running in Solaris non-global zones on cluster nodes. Sun Cluster software provides support for applications that are running in non-global zones as follows:
-
Directly through the RGM
-
Through the Sun Cluster HA for Solaris Containers data service
Support for Solaris Zones on Sun Cluster Nodes Directly Through the RGM
On a cluster where the Solaris 10 OS is running, you can configure a resource group to run in the global zone or in non-global zones. The RGM manages each zone as a switchover target. If a non-global zone is specified in the node list of a resource group, the RGM brings the resource group online in the specified zone on the node.
Figure 3–8 illustrates the failover of resource groups between zones on Sun Cluster nodes in a two-node cluster. In this example, identical zones are configured on each node to simplify the administration of the cluster.
Figure 3–8 Failover of Resource Groups Between Zones on Sun Cluster Nodes
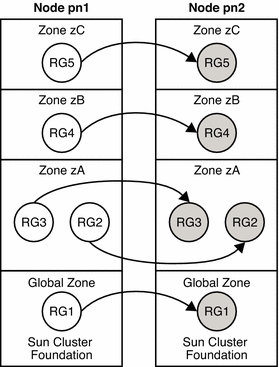
A failover resource group can fail over to a zone on another node or on the same node. However, if the node fails, the failing over of this resource group to a zone on the same node does not provide high availability. Nonetheless, you might find this failing over of a resource group to a zone on the same node useful in testing or prototyping.
You can configure a scalable resource group (which uses network load balancing) to run in a non-global zone as well. However, do not configure a scalable resource group to run in multiple zones on the same node.
In Sun Cluster commands, you specify a zone by appending the name of the zone to the name of the physical node, and separating them with a colon, for example:
phys-schost-1:zoneA
You can specify a zone with several Sun Cluster commands, for example:
Criteria for Using Support for Solaris Zones Directly Through the RGM
Use support for Solaris zones directly through the RGM if any of following criteria is met:
-
Your application cannot tolerate the additional failover time that is required to boot a zone.
-
You require minimum downtime during maintenance.
-
You require dual-partition software upgrade.
-
You are configuring a data service that uses a shared address resource for network load balancing.
Requirements for Using Support for Solaris Zones Directly Through the RGM
If you plan to use support for Solaris zones directly through the RGM for an application, ensure that the following requirements are met:
-
The application is supported to run in non-global zones.
-
The data service for the application is supported to run in non-global zones.
If you use support for Solaris zones directly through the RGM, configure resources and resource groups as follows:
-
Ensure that resource groups that are related by an affinity are configured to run in the same zone. An affinity between resource groups that are configured to run in different zones on the same node has no effect.
-
Configure every application in the non-global zone as a resource.
Additional Information About Support for Solaris Zones Directly Through the RGM
For information about how to configure support for Solaris zones directly through the RGM, see the following documentation:
-
Zone Names in Sun Cluster Software Installation Guide for Solaris OS
-
Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS
-
Individual data service guides
Support for Solaris Zones on Sun Cluster Nodes Through Sun Cluster HA for Solaris Containers
The Sun Cluster HA for Solaris Containers data service manages each zone as a resource that is controlled by the RGM.
Criteria for Using Sun Cluster HA for Solaris Containers
Use the Sun Cluster HA for Solaris Containers data service if any of following criteria is met:
-
You require delegated root access.
-
The application is not supported in a cluster.
-
You require affinities between resource groups that are to run in different zones on the same node.
Requirements for Using Sun Cluster HA for Solaris Containers
If you plan to use the Sun Cluster HA for Solaris Containers data service for an application, ensure that the following requirements are met:
-
The application is supported to run in non-global zones.
-
The application is integrated with the Solaris OS through a script, a run-level script, or a Solaris Service Management Facility (SMF) manifest.
-
The additional failover time that is required to boot a zone is acceptable.
-
Some downtime during maintenance is acceptable.
Additional Information About Sun Cluster HA for Solaris Containers
For information about how to use the Sun Cluster HA for Solaris Containers data service, see Sun Cluster Data Service for Solaris Containers Guide.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
