Viewing SunScreen SKIP Statistics
SunScreen SKIP provides two methods of viewing statistics: skiptool and skipstat. skiptool is the GUI. skipstat is the command-line interface for viewing SKIP statistics and is discussed in Chapter 4. The method you choose is a matter of personal preference since both interfaces provide the same data. The GUI display has a yellow label with the word "UPDATED" in front of fields whose values have changed since the last "sampling." This feature is not available through skipstat.
The following statistics are available in SunScreen SKIP:
-
Network Interface Statistics
-
SKIP Header Statistics
-
Key Statistics
-
Encryption Statistics (for Versions 1 and 2)
-
Authentication Statistics
The Statistics Window
You can view the Network Interface, SKIP Header, Key, Encryption (Versions 1 and 2), and Authentication statistics in real-time by selecting SKIP Statistics from the File menu (File --> SKIP Statistics) on the skiptool main window (Figure 3-13).
Figure 3-13 Bringing Up a Statistics Window
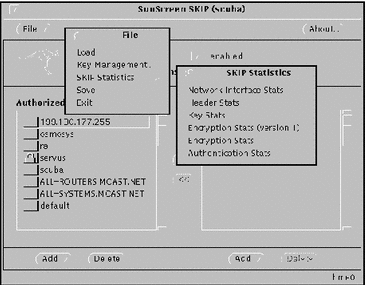
Each of the statistics available for SunScreen SKIP is described on the following pages. Sample data with field descriptions illustrate the information available for monitoring SunScreen SKIP's performance. The fields on the statistics screens are updated approximately every 3 seconds. A status change is indicated by a yellow label with the word "UPDATED" next to the fieldname.
SKIP Statistics
SKIP Interface StatisticsSelecting File --> SKIP Statistics --> Network Interface Stats displays the SKIP Interface Statistics window ().
Figure 3-14 SKIP Interface Statistics Window
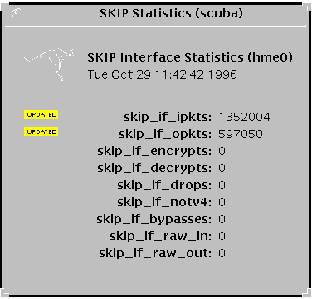
A brief description of each field is given below:
|
skip_if_ipkts |
Packets received by the interface. |
|
skip_if_opkts |
Packets sent by the interface. |
|
skip_if_encrypts |
Packets encrypted. |
|
skip_if_decrypts |
Packets decrypted. |
|
skip_if_drops |
Packets dropped. |
|
skip_if_notv4 |
Packets that are not IPv4 packets. |
|
skip_if_bypasses |
The number of certificate packets. |
|
skip_if_raw_in |
Raw AH and ESP packets received by the interface. |
|
skip_if_raw_out |
Raw AH and ESP packets sent by the interface. |
SKIP Header Statistics
Selecting File --> SKIP Statistics --> Header Stats displays the Header Statistics window (Figure 3-15). In the field descriptions below, V1 refers to SKIP Version 1.
Figure 3-15 SKIP Header Statistics Window
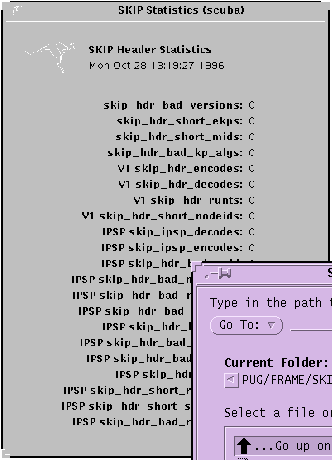
A brief description of each field in SKIP Header Statistics window is given below:
|
skip_hdr_bad_versions |
The number of headers with invalid protocol versions. |
|
skip_hdr_short_ekps |
The number of headers with short eKp fields. |
|
skip_hdr_short_mids |
The number of headers with short MID fields. |
|
skip_hdr_bad_kp_algs |
The number of headers with unknown cryptographic algorithms. |
|
V1 skip_hdr_encodes |
The number of SKIP V1 headers encoded. |
|
V1 skip_hdr_decodes |
The number of SKIP V1 headers decoded. |
|
V1 skip_hdr_runts |
The number of headers with short SKIP V1 packets. |
|
V1 skip_hdr_short_nodeids |
The number of headers with short SKIP V1 key ID. |
|
IPSP skip_ipsp_decodes |
The number of SKIP headers decoded. |
|
IPSP skip_ipsp_encodes |
The number of SKIP headers encoded. |
|
IPSP skip_hdr_bad_nsid |
The number of headers with a bad SKIP name- space ID. |
|
IPSP skip_hdr_bad_mac_algs |
The number of headers with unknown or bad authentication algorithms. |
|
IPSP skip_hdr_bad_mac_size |
The number of headers with an authentication error in the MAC size. |
|
IPSP skip_hdr_bad_mac_val |
The number of headers with an authentication error in the MAC value. |
|
IPSP skip_hdr_bad_next |
The number of headers with a bad SKIP next protocol field. |
|
IPSP skip_hdr_bad_esp_spi |
The number of headers with a bad SKIP SPI field. |
|
IPSP skip_hdr_bad_ah_spi_ |
The number of bad AH/SPI headers (manual keying). |
|
IPSP skip_hdr_bad_iv |
The number of headers with a bad SKIP initialization vector. |
|
IPSP skip_hdr_short_r_mkeyid |
The number of headers with a short SKIP receiver key ID. |
|
IPSP skip_hdr_short_s_mkeyid |
The number of headers with a short SKIP sender key ID. |
|
IPSP skip_hdr_bad_r_mkeyid |
The number of headers with a bad SKIP receiver key ID. |
SKIP Key Statistics
Selecting File --> SKIP Statistics --> Key Stats displays the Key Statistics window (Figure 3-16).
Figure 3-16 SKIP Key Statistics Window
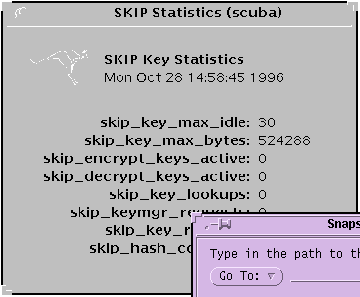
A brief description of each field on the Key Statistics window is given below:
|
skip_key_max_idle |
The time, in seconds, until an unused key is reclaimed. |
|
skip_key_max_bytes |
Maximum number of bytes to encrypt before discarding a key. |
|
skip_encrypt_keys_active |
Number of encryption keys in the cache. |
|
skip_decrypt_keys_active |
Number of decryption keys in the cache. |
|
skip_key_lookups |
The total number of key cache lookups. |
|
skip_keymgr_requests |
The total number of key cache misses (key not found). |
|
skip_key_reclaims |
The total number of key entries reclaimed. |
|
skip_hash_collisions |
The total number of table collisions. |
SKIP (Version 1) Algorithm Statistics
Selecting File --> SKIP Statistics --> Encryption Stats (Version 1) displays the Algorithm Statistics window for SKIP Version 1 (Figure 3-17).
Figure 3-17 Encryption Statistics Window--SKIP Version 1
SKIP Algorithm Statistics
Selecting File --> SKIP Statistics --> Encryption Stats displays the Algorithm Statistics window shown in Figure 3-18.
Figure 3-18 Encryption Statistics Window
One set of statistics is displayed for each different traffic and key encryption module. A brief description of each field is give below:
|
Crypto Module Name |
The name of the cryptographic module for which the statistics are being displayed. |
|
encrypts |
Number of successful encryptions. |
|
encrypterrs |
Number of failed encryptions. |
|
decrypts |
Number of successful decryptions. |
|
decrypterrs |
Number of failed decryptions. |
SKIP Authentication Statistics
Selecting File --> SKIP Statistics --> Authentication Stats displays the Authentication Statistics window (Figure 3-19), which provides information on MACs (Message Authentication Code).
Figure 3-19 Authentication Statistics Window
A brief description of each field on the Authentication Stats window is given below:
|
MAC_Module_Name |
MAC method used for authentication. |
|
in_mac |
Number of received MAC calculations that succeeded. |
|
in_mac_errs |
Number of received MAC calculations that failed. |
|
out_mac |
Number of sent MAC calculations that succeeded. |
|
out_mac_errs |
Number of sent MAC calculations that failed. |
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
