2 Developing Adapters
Adapters are Java programs that enable you to integrate Oracle Identity Manager with other software solutions. This chapter describes how to create adapters using the Adapter Factory form. It contains these sections:
2.1 Introduction to Adapters
To be effective, it must be possible to integrate an access rights management application, such as Oracle Identity Manager, with other software solutions. This is necessary not only because there are many resources, but also because there is no single integration standard for connecting to these resources.
The traditional way to tackle this challenge is by using the common functionality that is supported by all the integrations. To do this, you need developers who can write this code. In addition, every time an existing software resource is modified, or a new one is added, you must write more code.
The Adapter Factory is a code-generation tool provided by Oracle Identity Manager. It helps you create Java classes, known as adapters, that simplify the integration challenge.
Note:
Oracle Identity Manager can connect to external systems such as databases and directory servers by using Java APIs for JDBC and LDAP. In addition, for all other APIs, such as C, C++, VB, and COM/DCOM, you can create a Java wrapper so that Oracle Identity Manager can communicate with the API directly.
A resource has an associated provisioning process, which in turn has various tasks associated with it. Each task in turn has an adapter associated to it, which in turn can connect to the target resource to carry out the required operations.
An adapter provides the following benefits:
-
It extends the internal logic and functionality of Oracle Identity Manager.
-
It interfaces with any software resource, by connecting to that resource by using the API of the resource.
-
It enables the integration between Oracle Identity Manager and an external system.
-
It can be generated without manually writing code. However, Oracle Identity Manager does not restrict you from writing your own code for creating adapters.
-
It is lightweight and specific to your needs.
-
It can be maintained easily because all of the definitions for the adapter are stored in a repository. This repository can be edited through a GUI.
-
One Oracle Identity Manager user can retain the domain knowledge about the integration, while another user can maintain the adapter.
-
It can be modified and upgraded efficiently.
Adapters can be developed for a range of tasks:
-
A process task adapter, which allows Oracle Identity Manager to automate the completion of a process task.
-
A task assignment adapter, which enables Oracle Identity Manager to automate the assignment of a process task to a user or group.
-
A rule generator, which incorporates business rules to the fields of either an Oracle Identity Manager form or a user-defined form (created by using the Form Designer form), so these fields can be populated automatically and saved to the Oracle Identity Manager database.
Note:
For more information about the Form Designer form, see "Form Designer Form".
-
A pre-populate adapter, which is a specific type of rule generator adapter that can be attached to a user-created form field. The data generated by this type of adapter can appear either automatically or manually. In addition, it uses criteria that enable Oracle Identity Manager to determine which pre-populate adapter will be applied to the designated form field. It populates the designated form field without saving this information to the Oracle Identity Manager database.
-
An entity adapter, which is attached to an Oracle Identity Manager or user-created form field. Oracle Identity Manager triggers an entity adapter on preinsert, preupdate, predelete, postinsert, postupdate, or postdelete. After this occurs, the field to which the adapter is attached is populated automatically and saved to the Oracle Identity Manager database.
Note:
Oracle Identity Manager 11g Release 1 (11.1.1) also allows you to create postprocessing handlers on entities, such as user, role, and organization.
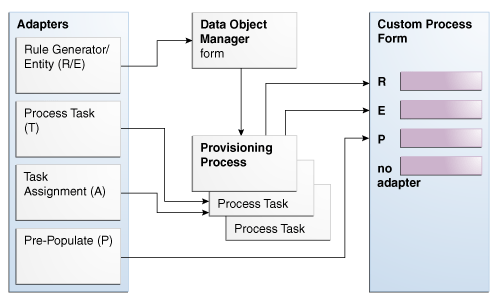
Figure 2-1 illustrates the functionality of five different types of adapters.
2.2 Types of Adapters
This section provides additional details about the five adapter types.
Certain business rules must be applied to perform field validations and enter default values into the forms which either come packaged with Oracle Identity Manager or are created by Oracle Identity Manager users. For example, for the Users form, you might want Oracle Identity Manager to generate the User ID automatically by concatenating the user's first name and last name.
To do this, you must create a specific type of adapter, which is designed to modify the field value in a form. This type of adapter, which can generate, modify, or verify the value of a form field automatically, is called a rule generator. Oracle Identity Manager triggers a rule generator on preinsert and preupdate.
After you create this adapter and attach it to a form, Oracle Identity Manager automatically updates the field value for all records of that form, and saves this information to the Oracle Identity Manager database.
If you create a rule generator that contains adapter variables, you must map these adapter variables to their proper locations. Otherwise, the adapter will not be functional.
You can also attach this type of adapter to a provisioning process. Once the process is provisioned to a target user or organization, Oracle Identity Manager will trigger the associated rule generator.
On occasion, a rule generator which has been assigned to a provisioning process might no longer be needed to complete the process. If this happens, you can remove the rule generator from the provisioning process. Similarly, after you attach one rule generator to a form field, you can connect a different rule generator to that form field. When this occurs, you must first remove the rule generator currently attached to the form field.
Similar to rule generator adapters, entity adapters are also responsible for generating, modifying, or verifying the value of a form field automatically, and saving this information to the Oracle Identity Manager database.
Some differences between rule generators and entity adapters are:
-
Execution schedule. Entity adapters can be triggered by Oracle Identity Manager on preinsert, preupdate, predelete, postinsert, postupdate, and postdelete. A rule generator adapter can be executed only on preinsert and preupdate.
-
Manual field value modification. The adapter populates the form field to which an entity adapter is attached. An Oracle Identity Manager user should not edit this value because the entity adapter will overwrite this modification. As a result, the modification will not be saved to the database.
Similarly, the adapter also populates the form field to which a rule generator adapter is attached. However, an Oracle Identity Manager user can edit this value because this modification will take precedence over the value that the rule generator adapter generates. Because of this, the modification will be saved to the database.
-
Background color of form field. If a rule generator is attached to a form field, the field will appear in a particular background color such as pink. This is a visual indicator that the field has a rule generator attached to it. On the other hand, when an entity adapter is attached to a form field, the field will not have a distinct background color.
For a process task that must be completed manually, you can configure Oracle Identity Manager to automate the assignment of the task to either a specific user or a user who belongs to a particular role. This is achieved through the use of a task assignment adapter. Task assignment adapters are used only for assigning a task to a particular user or role.
When a task that is associated with specific provisioning process is created using the Tasks tab in the Process Definition form of the Design Console, you can choose the rule that decides if adapter will be picked up for execution. Note that this rule is defined in the Rule Definition form of the Design Console. An example of a rule is "Target User's Org name is XYZ. If this rule is satisfied, then the corresponding task assignment is picked up. However, you can have multiple rules defined and used while deciding task assignment. For multiple rules, Oracle Identity Manager associates priority with the task assignment functionality to decide the order in which the rule determination must occur. When the rule is determined, corresponding task assignment is run.
Note:
In other words, the task assignment rule allows Oracle Identity Manager to decide whether to assign a process task to a user or role. The task assignment adapter enables Oracle Identity Manager to determine which user or role will be the recipient of the process task.
For this example, Oracle Identity Manager will trigger the Associate Adapter with User rule first (because it has the highest priority). If the condition of this rule is TRUE, it is successful. As a result, Oracle Identity Manager will associate the related task assignment adapter (the Assign Task to User adapter) with the process task.
On the other hand, when the condition of a rule is FALSE, the rule has failed. Oracle Identity Manager triggers the rule with the next highest priority. If this rule is successful, then Oracle Identity Manager assigns the designated adapter to the target process task.
So, in this example, if the Associate Adapter with User rule fails, then Oracle Identity Manager triggers the Associate Adapter with Role rule. If this rule is successful, then Oracle Identity Manager associates the related task assignment adapter (the Assign Task to Role adapter) to the process task.
After assigning a rule to a task assignment adapter, if this type of adapter contains adapter variables, you must map these variables to their proper locations. Otherwise, the adapter will not be functional.
Finally, when a task assignment adapter becomes invalid, or is no longer necessary for Oracle Identity Manager to allocate the process task to a user or group, you must remove the adapter from the task.
Sometimes a user-created form contains both fields that can be populated by Oracle Identity Manager and fields into which an Oracle Identity Manager user must enter data. When the information that the user types into a field is contingent upon the data that appears in a system-generated field, Oracle Identity Manager must first populate this field. When the form is displayed, the user can view the system-generated data to enter information into the appropriate fields.
This is achieved by creating a type of rule generator known as a prepopulate adapter. By attaching it to a field designated to be system-generated, you enable Oracle Identity Manager to automatically populate this field with the appropriate information, without saving this information to the Oracle Identity Manager database.
The data generated by a prepopulate adapter can appear automatically or it can be manually entered. Oracle Identity Manager displays this information automatically when the Auto-prepopulate check box is selected for a provisioning process. When this check box is cleared, an Oracle Identity Manager user must manually generate the displaying of the data that is generated by the prepopulate adapter. To do this, click the prepopulate button on the form section of the Direct Provisioning wizard in the Web client, while provisioning the form to a user.
You can use the same prepopulate adapter for different form fields. In addition, you can designate multiple prepopulate adapters to be associated with a particular field. As a result, Oracle Identity Manager must know which prepopulate adapter it must select for the form field. This requires the use of prepopulate rules. These rules enable Oracle Identity Manager to select one prepopulate adapter, which is associated with a form field, when this prepopulate adapter is assigned to the field.
Each prepopulate adapter has a prepopulate rule associated with it. In addition every rule has a priority number which indicates the order in which Oracle Identity Manager triggers it.
For example, Oracle Identity Manager can trigger the Rule for Uppercase User ID rule first because it has the highest priority. If the condition of this rule is TRUE, it is successful. As a result, Oracle Identity Manager will attach the related prepopulate adapter (the Display Uppercase Letters for User ID adapter) to the User ID field.
On the other hand, when the condition of a rule is FALSE, the rule has failed. Oracle Identity Manager will trigger the rule with the next highest priority. If this rule is successful, Oracle Identity Manager will attach the associated adapter to the designated field.
So, in this example, if the Rule for Uppercase User ID rule fails, Oracle Identity Manager will trigger the Rule for Lowercase User ID rule. If this rule is successful, Oracle Identity Manager will attach the related prepopulate adapter (the Display Lowercase Letters for User ID adapter) to the User ID field.
After assigning a rule to a prepopulate adapter, if this type of adapter contains adapter variables, you must map these adapter variables to their proper locations. Otherwise, the adapter will not be functional.
Finally, when a prepopulate adapter associated with a field is no longer valid, you must remove the adapter from the field.
A process task adapter enables Oracle Identity Manager to automatically execute process tasks in provisioning processes.
Each process and process task has a status, which indicates the stage of its completion. The statuses for a process or process task are listed in the following table in order of importance.
| Task Status | Description |
|---|---|
|
C |
Completed: This process/process task has been completed successfully. |
|
MC |
Manually Completed: This process task has been completed successfully by an Oracle Identity Manager user (that is, manually). |
|
P |
Pending: This process/process task is in the process of being completed. All preceding tasks and processes, respectively, have been completed. |
|
PX |
Pending Cancellation: This process task will be canceled, but this task has to be completed first before it can be canceled. |
|
R |
Rejected: This process/process task has not been completed successfully or has not been approved. The status of rejected process tasks can only be changed to Canceled or Unsuccessfully Completed. |
|
S |
Suspended: This process/process task has been put on hold temporarily. |
|
UC |
Unsuccessfully Completed: This process task has been set to Completed. However, it had been rejected before. |
|
W |
Waiting: This process/process task cannot be completed until all preceding process tasks or processes are completed. |
|
X |
This process/process task has been stopped. Its status cannot change anymore |
The status level of a process represents the most important status level of its process tasks, which must be completed for the process to be completed. Suppose a process has three process tasks, each process task has a different status level (Completed, Waiting, and Rejected), and all three process tasks must be completed for the process to complete. Because the highest task status level is Rejected, the status level of the process is also Rejected.
A process task can be managed in these ways:
-
It can be handled manually by using the Object Process Console tab of the Organizations or Users forms, or the Oracle Identity Manager Web Application.
-
An Oracle Identity Manager process can be configured so that one (or more) of its tasks is triggered automatically once it achieves a status of Pending.
2.3 Adapter Environment and Tools
This section contains these topics:
2.3.1 Configuring the Adapter Environment
To construct adapter tasks, ensure that Oracle Identity Manager has access to the target API JAR files and third-party applications to which you want to connect.
When your adapter uses Java tasks, you must configure Oracle Identity Manager to find the appropriate Java APIs. To do this, you must place the .jar files that contain these APIs into the Meta Data Store (MDS).
See Also:
Chapter 33, "MDS Utilities and User Modifiable Metadata Files" for information about utilities to modify Oracle Identity Manager metadata
Then, you can access the Java classes associated with these Java APIs and use them in the Java task you are creating.
To configure Oracle Identity Manager to reference JAR and class files:
-
Open the JavaTasks subdirectory, which can be found within the
OIM_HOME/directory path. For example,C:\oracle\Xellerate\JavaTasks. -
Place the JAR file or files into this subdirectory. You can use these files to create Java tasks within an adapter without restarting the server.
2.3.2 Remote Manager
Sometimes, instead of directly communicating with the third-party system, Oracle Identity Manager must use an Oracle Identity Manager component that acts like a proxy. This component is known as Remote Manager.
The Remote Manager is used for:
-
Invoking nonremotable APIs through Oracle Identity Manager
-
Invoking APIs that do not support Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) over secure connections
To configure the Remote Manager, follow the instructions described in Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation Guide for Oracle Identity Management.
2.3.3 The Adapter Factory
As stated earlier, an adapter is a Java class created by an Oracle Identity Manager user through the Adapter Factory, which is accessed through the Design Console.
Adapters extend the internal logic and functionality of Oracle Identity Manager. In addition, they interact with any IT resource by connecting to that resource's API.
The Adapter Factory is a code-generation tool provided by Oracle Identity Manager that enables a user to create Java classes, known as adapters. Figure 2-2 shows the Adapter Factory Form in the Design Console.
2.3.4 Compiling Adapters
Oracle Identity Manager provides various options for compilation, including:
-
compile individual adapters one at a time
-
compile a set of adapters at once
-
compile all adapters that exist in the Oracle Identity Manager database with a single click
2.3.4.1 Automatic Compilation of Adapters
Adapters are compiled automatically when you import connector files by using the Deployment Manager. The compiled adapter class files are stored in the Oracle Identity Manager database, as opposed to the file system, from where they are loaded at run time. The following two APIs are available to compile adapters programmatically:
-
public void compileAdapter (String adapterName): This API compiles a single adapter and stores the compiled classfile in the database. It takes the name of the adapter as a parameter. If the adapter is not found or if there are any errors, the API throws an appropriate exception. -
public void compileAll: This API compiles all adapters in a system. If it encounters any errors during compilation, it throws an exception of the typetcBulkException. This exception comprises all the individual errors that the API encounters during compilation.
You can modify the adapters manually if you make any changes.
Note:
You must set the path of the JDK directory in the XL.CompilerPath system property. Otherwise, an error is encountered during the adapter compilation stage when you import an XML file using the Deployment Manager.
Refer to the "System Properties in Oracle Identity Manager" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware System Administrator's Guide for Oracle Identity Manager for information about setting values of system properties.
2.3.4.2 Compiling Adapters Manually
The Adapter Manager form is located in the Development Tools folder. You use it to compile multiple adapters simultaneously.
To manually compile multiple adapters, perform these steps:
-
Open the Adapter Manager form.
The Adapter Manager form is in the Development Tools folder. It is used to compile multiple adapters simultaneously, as shown in Figure 2-3.
-
To compile every adapter that resides within the Oracle Identity Manager database, select the Compile All option.
To compile multiple adapters, select the adapters you want to compile. Then, select the Compile Selected option.
To compile all adapters that do not have an OK status, select the Compile Previously Failed option.
-
Click the Start button.
Oracle Identity Manager will compile the adapters that match the criteria you specified in Step 2.
Tip:
Oracle Identity Manager lets you review the record of any adapter that appears within the Adapter Manager form to see detailed information about the adapter.
To view an adapter's record, select the desired adapter and either double-click its row header, or right-click the adapter, and select the Launch Adapter command from the menu that appears.
2.4 Defining Adapters
To define an adapter:
-
Log in to Oracle Identity Manager Design Console.
-
Open the Adapter Factory form. This form is in the Development Tools folder in the Design Console.
-
In the Adapter Name field, enter the name of the adapter, for example,
Create Solaris User.Note:
Although the adapter name can contain special characters, Oracle recommends that you do not use them because there might be run-time errors.
-
Double-click the Adapter Type lookup field.
The Lookup window is displayed, displaying the five types of Oracle Identity Manager adapters. These are:
-
Process Task
-
Rule Generator
-
Pre-populate Rule Generator
-
Entity
-
Task Assignment
-
-
To enable the adapter to automate a process task, select Process Task (T).
To incorporate business rules into an Oracle Identity Manager or user-defined form field, select Rule Generator (R). For example, for the User ID field of a form, you can configure Oracle Identity Manager to concatenate the initial letter of the user's first name with the user's last name.
You can attach a type of rule generator adapter to a user-created form field, so that it can:
-
Display the data, which is generated by the adapter, automatically or manually.
-
Use criteria that enable Oracle Identity Manager to determine which adapter is applied to the designated form field.
To attach the adapter to an Oracle Identity Manager or user-defined form field, and have Oracle Identity Manager trigger the adapter on preinsert, preupdate, predelete, postinsert, postupdate, or postdelete, select Entity (E).
To allow the adapter to automate the allocation of a process task to a user or group, select Task Assignment (A).
Tip:
If you create an entity adapter, then an error might be generated while compiling the adapter on computers with less file limits. To avoid this problem, change the file limits in the /etc/security/limits.conf file to the following:
soft nofile 4096
hard nofile 4096
Then, restart Oracle Identity Manager.
-
-
Select the type of adapter you want, for example, Process Task (T). Then, click OK.
See Also:
"Form Designer Form" for more information about the Form Designer form
-
In the Description field, type a description for the adapter, for example,
This adapter is used to create a new user for the Solaris environment. -
From the toolbar, click Save.
The adapter is now stored in the Oracle Identity Manager database.
2.5 Tabs of the Adapter Factory Form
The Adapter Factory form in the Design Console contains the following tabs:
2.5.1 Adapter Tasks
In the Adapter Tasks tab, you can create and manage the atomic function calls of an adapter. These function calls are known as adapter tasks.
The sequence of calls is vital because these calls in turn gets converted into Java statements. In other words, if you put an Else call before an If call, then the adapter is not compiled. In addition, you must understand the logical flow of java program while creating adapter. Analogically, this is like writing an algorithm instead of a program with Java syntax.
2.5.2 Execution Schedule
The Execution Schedule tab lets you specify when you want Oracle Identity Manager to trigger a rule generator or an entity adapter. You can schedule Oracle Identity Manager to run a rule generator (Adapter Type R) on preinsert and/or preupdate. You can also configure Oracle Identity Manager to execute an entity adapter (Adapter Type E) on preinsert, preupdate, predelete, postinsert, postupdate, or postdelete.
Caution:
Process task adapters and task assignment adapters, which are attached to process tasks, are triggered once the process task's status becomes Pending. Therefore, you do not specify when Oracle Identity Manager will trigger these types of adapters, Oracle Identity Manager disables the Execution Schedule tab for them.
Also, because Oracle Identity Manager always triggers pre-populate adapters on preinsert, Oracle Identity Manager disables the check boxes of this tab for pre-populate adapters.
2.5.3 Resources
From the Resources tab, you can:
-
Click the Java APIs subtab to see the Java APIs that are being used by the adapter.
-
Click the Other subtab to document a non-Java API file to the adapter, if necessary.
Note:
This Resources tab does not represent resource objects.
2.5.4 Variable List
For prepopulation adapters, the data is passed to adapter input variables and are processed by using adapter logic. The adapter returns output variable, which is then assigned to process form field.
From the Variable List tab, you can:
-
Create, modify, and delete adapter variables.
-
Set the data type and provide a description for each variable.
-
Map an adapter variable to a literal or an adapter reference. You can also postpone the mapping until it is attached to a process task or a form field.
You also can resolve the value of the adapter variable at run time, when it is attached to a process task and the process task is run. As a result, process-specific data is available to map to this variable.
2.5.5 Usage Lookup
For a process task or task assignment adapter, the Usage Lookup tab displays the process task to which the adapter is attached, as well as the process of which this process task is a member.
For a rule generator or entity adapter, this tab shows the Oracle Identity Manager form and associated data object to which the adapter is attached. In addition, it displays the execution schedule of the adapter, along with a sequence number that represents the order in which Oracle Identity Manager will trigger the adapter.
For a pre-populate adapter, this tab displays the user-defined form and form field to which the adapter is attached. Also, it shows the pre-populate rule that is associated with the adapter.
2.5.6 Responses
The Responses tab is used for defining meaningful responses to the process task. These responses depend on the execution result of the adapter. The various error messages returned by the external system can be mapped to these responses in a way that they make sense in the context of the process task. On attaching the adapter to a process task, the status bucket, which consists of Pending, Completed, and Rejected, of the process task (and subsequently the Object status) can be set, based on the adapter response code.
Tip:
Oracle Identity Manager enables the Responses tab only for process task adapters. If an adapter is a task assignment, rule generator, pre-populate, or entity adapter, Oracle Identity Manager disables this tab.
2.6 Disabling and Re-enabling Adapters
To disable an adapter so that it cannot be used with a process task or form field, select the Disable Adapter option, and save the adapter.
To re-enable it, clear the Disable Adapter option, and save the adapter.
2.7 About Adapter Variables
For a newly-created adapter to work, you can map data to the parameters of the adapter tasks. For this reason, you create placeholders, also known as adapter variables, to map the data at run time.
Note:
An adapter variable can be reused for all adapter tasks.
Once an adapter variable is not needed for the adapter to run, you can remove it from the adapter. After you have deleted the adapter variable, ensure to recompile the adapter.
2.7.1 Creating an Adapter Variable
To create an adapter variable:
-
Select the adapter to which you wish to add an adapter variable, for example, the
Create Solaris Useradapter. -
Select the Variable List tab.
-
Click Add.
The Add a Variable window is displayed.
-
When you do not want Oracle Identity Manager to be able to change the adapter variable value after it is activated, select Final.
-
In the Variable Name field, enter the name of the adapter variable, for example,
SolarisUserID.Caution:
The adapter variable name cannot contain spaces.
-
From the Type menu, select the classification type of the adapter variable, such as String. The available items are:
-
Object
-
IT Resource
-
String
-
Boolean
-
Character
-
Byte
-
Date
-
Integer
-
Float
-
Long
-
Short
-
Double
-
-
Within the Description text area, you can enter explanatory information about the adapter variable.
-
From the Map To menu, you can map your adapter variable to one of the items listed in Table 2-1.
Table 2-1 Items on the Map To Menu
Name Description Literal
This adapter variable is mapped to a constant (or literal).
Resolve at Run time
This adapter variable's mapping occurs later, at run time. Selecting this option increases the reusability of the adapter.
Adapter References
This adapter variable gives access to an Oracle Identity Manager database reference or an Oracle Identity Manager data object reference.
System Date
When this adapter variable is triggered by Oracle Identity Manager, it is mapped to the current date and time of the Server.
Note: This option appears only when you select the Date type.
Note:
When you select the object type, a Qualifier menu is displayed within the Add a Variable window. From this menu, you can select either of the following:
-
Database Reference. If you select this item, the adapter variable is mapped to the reference of the database that the Oracle Identity Manager is currently running against.
-
Data Object Reference. If you select this item, the adapter variable is mapped to an Oracle Identity Manager data object.
Note:
If you select the IT Resource type, a Resource Type menu is displayed within the Add a Variable window. From this menu, you can select one of the IT resource types that have been created by using the IT Resource Type Definition form. By doing so, you can map the adapter variable to a parameter of this IT resource type.
-
-
On the toolbar in the Add a Variable window, click Save. The information for your adapter variable is stored in the Oracle Identity Manager database.
Close the Add a Variable window to activate the main screen. The name, classification type, mapping selection, and description of the adapter variable you created appear in the child table of the Variable List tab.
This adapter variable now belongs to the adapter in the Adapter Factory form. It is saved to the Oracle Identity Manager database, and the adapter variable is ready to use.
2.7.2 Modifying an Adapter Variable
To modify an adapter variable:
-
Select the adapter that contains the adapter variable you want to edit, for example, the
Create Solaris Useradapter. -
Click the Variable List tab and double-click the row header of the adapter variable you want to modify. The Edit a Variable window is displayed, showing information about the adapter variable.
-
Make the necessary edits, for example, changing the adapter variable's data type from String to Character.
-
On the Edit a Variable toolbar, click Save. The modified information about the adapter variable is stored in the Oracle Identity Manager database.
-
Close the Edit a Variable window to activate the main screen. The adapter variable you modified appears within the child table of the Adapter Factory form.
Note:
Ensure that you check your data mappings and recompile the adapter, especially if you change the adapter variable's data type.
2.7.3 Deleting an Adapter Variable
When an adapter variable is no longer necessary for the adapter to run, you can remove it from the adapter. To do this:
-
Select the adapter that contains an adapter variable you want to remove, for example, the
Create Solaris Useradapter. -
Select the Variable List tab.
-
From the list of this tab, select the adapter variable you want to delete.
-
Click Delete.
-
Recompile the adapter after deleting any variable.
The adapter variable disappears from the child table. The adapter variable has been deleted.
2.8 Creating Adapter Tasks
After you construct the adapter and create its variables, you can create the atomic function calls of an adapter. These function calls are known as adapter tasks.
This section explains adapter tasks and how to create tasks:
2.8.1 Types of Adapter Tasks
Oracle Identity Manager allows you to create the following adapter tasks:
-
A Java task, which allows an adapter to communicate with an external source by invoking Java API.
-
A remote task, which enables an adapter to call a method on an API. This API resides on a computer that is external to Oracle Identity Manager.
This type of task is used mostly with integrations of third-party APIs that are not network-enabled. A remote manager executes the remote API method, which is located on a remote computer. In addition, if the third-party API does not use SSL, you can use the remote manager to invoke third-party APIs over SSL-protected communication. Remote tasks can also be used with integrations of third-party APIs, which are network-enabled, but are not located on the Oracle Identity Manager server for scalability purposes. The remote API method is still executed by a remote manager. However, because the third-party API is network-enabled, the remote manager does not have to reside on the target system.
-
A stored procedure task, which allows Oracle Identity Manager to map to and execute SQL programs located within a particular database schema. These programs are known as stored procedures. They contain information, such as SQL statements, which are pre-compiled for greater efficiency.
By incorporating a stored procedure task into an adapter, and attaching this adapter to a process task, Oracle Identity Manager can incorporate stored procedures on any Oracle Database or Microsoft SQL Server database that is accessible on its network. This includes retrieving primitive values from stored procedures.
-
A utility task, which enables you to populate an adapter with methods and APIs that come packaged with Oracle Identity Manager. In addition, this type of task provides you with access to the Java Standard Library APIs.
-
An Oracle Identity Manager API task, which enables access to Oracle Identity Manager published APIs from adapter tasks. This allows for enhanced portability of adapter code.
-
A set variable task, which allows you to set a variable within an adapter.
-
An error handler task, which lets you display any errors associated with an adapter that occur at run time. In addition, you can see the reasons for the errors, along with possible solutions.
-
A logic task, which lets you build a conditional statement within an adapter.
You can create the following types of logic tasks:
-
FOR loops
-
WHILE loops
-
IF statements
-
ELSE statements
-
ELSE IF statements
-
BREAK statements
-
RETURN statements
-
CONTINUE statements
-
SET VARIABLE statements
-
Handle Error statements
See Also:
Section 2.8.9, "Creating a Logic Task" for more information about the types of logic tasks you can build
For classification purposes, Oracle Identity Manager represents each type of adapter task by an icon. The icon, which precedes the task name, is a visual indicator of the type of task it is. For example, "J" represents a Java task, and "LT" represents a logic task.
To see a list of these icons, select the Adapter Tasks tab, and click Legend. The Legend window appears, displaying the following list of icons:
-
Functional Task
-
Java
-
Remote
-
Stored Procedure
-
-
Utility Task
-
Utility
-
Oracle Identity Manager API
-
-
Logical Task
2.8.2 Creating a Java Task
Oracle Identity Manager can handshake with an external source through a Java API. To make this happen, you must add a task to an adapter which, when triggered by Oracle Identity Manager, initiates communications with the external source. This type of task is called a Java task.
To create a Java task:
-
Select the adapter to which you want to add a Java task, for example, the Update Solaris Password adapter.
-
Select the Adapter Tasks tab.
-
Click Add.
After the Adapter Task Selection window is displayed, select the Functional Task option.
-
From the display area to the right of this option, select the Java item, and click Continue.
The Object Instance Selection window is displayed.
Table 2-2 explains the options in the Object Instance Selection window.
Table 2-2 Options in the Object Instance Selection Window
Option Description New Object Instance
When you click this option, you are creating a new Java object instance.
Persistent Instance
You can call the method on a persistent object by clicking this option, clicking the adjacent combo box, and selecting an object instance from the drop-down menu.
Task Return Value Instance
You can call this method on an object returned by an adapter task defined earlier by clicking this option, clicking the combo box, and selecting an adapter task from the drop down list.
Note:
When the Persistent Instance option is grayed out, it indicates that you have not defined any persistent objects for your adapter. Similarly, if the Task Return Value Instance option is grayed out, none of the tasks have Java Object return values associated with them.
-
Click an option—for example, New Object Instance—and click Continue. The Add an Adapter Factory Task window is displayed.
Table 2-3 lists and describes the various regions of the Add an Adapter Factory Task window:
Table 2-3 Regions of the Add an Adapter Factory Task Window
Name Description Task Name
This field displays the name of the Java task.
Persistent Instance
If this Java object is to be used again, the check box is selected, and the name of the task instance is entered in the adjacent field.
API Source
This combo box contains a list of all JAR and class files to which you have access.
Application API
This combo box contains a list of all class files to which you have access, and which belong to the JAR file that has been selected from the API Source list.
Constructors
This text area displays all the constructors, which are available for the Java object.
Methods
This text area shows a list of all the methods, which are available for the Java object.
Application Method Parameters
This area contains the parameters of the selected constructor and method. These parameters are mapped to the adapter variables and Oracle Identity Manager components.
-
In the Task Name field, enter the name of the task you are creating, for example,
Update Password. -
(Optional.) To make your Java object reusable, select Persistent Instance, type the name of the instance of this task in the text field located to the right of the check box.
Caution:
Ensure that name of the instance contains no spaces.
Note:
To reference a session with the target resource multiple times during the life of the adapter, and not just once, select Persistent Instance.
Tip:
By setting the Java object to be persistent, the next time you create a Java object, it appears in the Persistent Instance list of the Object Instance Selection window. In addition, you do not have to map the constructor to all adapter tasks of the same Java object.
-
Select the API Source. The JAR files appear, which Oracle Identity Manager references from the JavaTasks subdirectory of the
OIM_HOME/directory path—for example,C:\oracle\Xellerate\JavaTasks.See Also:
Section 2.3.1, "Configuring the Adapter Environment" for instructions on how to enable Oracle Identity Manager to use third-party JAR files with a Java task
-
Select the Application API. The class files, which belong to the JAR file you selected in the API Source, appear.
-
From the Constructors area, select the method to be used to initialize the Java class you selected.
-
From the Methods area, select the method that will be used with your Java task.
-
From the toolbar, click Save.
The information pertaining to the Java task is stored in the Oracle Identity Manager database. You can now access the parameters of your Java task's constructors and methods. These parameters appear in the Application Method Parameters region of the Add an Adapter Factory Task window.
-
To display the Java class constructors and methods for which you must set mappings, click the plus icons displayed to the left of the Constructor and Method icons.
-
Select the parameter of the constructor or method for which you must set a mapping.
-
In the Description text area, you can enter a description for this mapping.
-
Click the Map to combo box, and select an item that you can map to the parameter of the constructor or method, for example, Adapter Variables.
-
Set the appropriate mappings.
See Also:
"Adapter Mapping Information" for more information about which mappings to set
-
Click Set.
The parameter of the selected constructor or method now appears in blue. This signifies that it has been mapped.
Tip:
To remove a parameter mapping, right-click the appropriate parameter, and select Un-Map Parameter from the popup menu that appears.
-
Repeat steps 15 through 18 for all parameters of the constructors and methods that appear in the Application Method Parameters region.
-
On the Add an Adapter Factory Task window toolbar, click Save. The information pertaining to the Java task is stored in the Oracle Identity Manager database.
-
On the toolbar, click Close. The Add an Adapter Factory Task window disappears, and the main screen is active once again. The Java task that you created—for example, Update Password—appears within the Adapter Factory form.
-
(Optional.) To create additional Java tasks for the adapter, repeat steps 3-21.
Tip:
You can create different types of adapter tasks, and add them to the adapter.
If the adapter is logically complete, and all variables on the adapter tasks are mapped, you can compile it to use with a process task or form field.
-
To compile the adapter, click Build.
The text in the Compile Status field changes from Recompile to OK. This indicates that Oracle Identity Manager compiled the adapter and found no errors. You can now attach the adapter to a process task or form field.
-
(Optional.) To see the code that Oracle Identity Manager generates, from the toolbar, click Notes.
The Notes window is displayed, containing the code that Oracle Identity Manager generated.
Note:
If, after clicking Build, CODE GEN ERROR appears in the Compile Status field, it means that Oracle Identity Manager encountered one of two types of errors while validating and compiling the adapter:
-
Validation Error
While Oracle Identity Manager is checking the adapter to verify that it is valid, an error is found. This error can result from a parameter of an adapter task not being mapped, a parameter being mapped improperly, or an adapter task being placed out of order.
Because Oracle Identity Manager generates code for an adapter only after it is validated, if Oracle Identity Manager encounters a validation error, it does not create any code.
-
Java Compilation Error
Oracle Identity Manager has verified that the adapter is valid. However, while Oracle Identity Manager is compiling the adapter, an error is found. This error can result from assigning an incorrect data type to an adapter task parameter.
Because Oracle Identity Manager has validated the adapter, it generates code. However, Oracle Identity Manager stops building code at the point of the compilation where it encounters the error.
Tip:
Once you create a Java task, and add it to an adapter, you can see the following information by accessing the Resources tab of the Adapter Factory form:
-
The JAR and class files used to create the Java task.
-
The name, which represents the directory path that contains these JAR and class files.
-
2.8.3 Creating a Remote Task
A remote task enables an adapter to invoke an API method by using the Remote Manager. This API resides on a computer that is external to Oracle Identity Manager. This section explains how to create a remote task.
Note:
Before creating a remote task, ensure that you define an adapter variable with a classification type of IT Resource, as well as select one of the IT resources that have been created by using the IT Resource Type Definition form.
-
Select the adapter to which you wish to add a remote task.
-
Click the Adapter Tasks tab.
-
Click Add.
The Adapter Task Selection window is displayed.
-
Select the Functional Task option.
-
From the display area to the right of the button, select the Remote item to create a remote task. Then, click Continue.
The Object Instance Selection window is displayed.
Note:
To learn more about the choices of this window, refer to Section 2.8.2, "Creating a Java Task".
-
Click Continue.
The Add an Adapter Factory Task window is displayed.
-
In the Task Name field, enter the name of the remote task you are creating.
-
(Optional.) If you want your remote task to be reusable, select the Persistent Instance option. Then, type the name of the instance of this task in the text field, located to the right of the check box.
Caution:
Ensure that the name of the instance contains no spaces.
See Also:
Section 2.8.2, "Creating a Java Task" for more information about the regions of the Add an Adapter Factory Task window
Section 2.3.1, "Configuring the Adapter Environment" for information about how to enable Oracle Identity Manager to use third-party JAR files with a Java task -
From the Add an Adapter Factory Task window, select a JAR file, class file, constructor, and method. Then, set the mappings for the parameters of the constructor and method.
Note:
One of the input parameters will have a classification type of IT Resource. You must associate this parameter with an adapter variable of type IT Resource.
See Also:
"Adapter Mapping Information" for more information about which mappings to select
-
From the Add an Adapter Factory Task window toolbar, click Save.
The information pertaining to the remote task is stored in the Oracle Identity Manager database.
-
From this window toolbar, click Close.
The Add an Adapter Factory Task window disappears, and the main screen is active once again. The remote task that you created appears within the Adapter Factory form.
-
(Optional.) To create additional remote tasks for the adapter, repeat Steps 3 through 11.
You are now ready to compile the adapter, so it can be used with a process task or form field.
-
To compile the adapter, click Build.
The text in the Compile Status field changes from Recompile to OK. This indicates that Oracle Identity Manager compiled the adapter and did not find any errors. You can now attach the adapter to a process task or form field, so Oracle Identity Manager can communicate with the external API.
2.8.4 Creating a Stored Procedure Task
Through Oracle Identity Manager, you can map to and execute SQL programs that are located within a particular database schema. These SQL programs are known as stored procedures. Stored procedures contain information, such as SQL statements, which are precompiled for greater efficiency.
For this to occur, you must add a stored procedure task to an adapter. When triggered by Oracle Identity Manager, this task incorporates stored procedures on any Oracle Database or Microsoft SQL Server database that is accessible on its network. This includes retrieving primitive values from stored procedures.
Take these steps to create a stored procedure task:
Note:
The parameter values and server type for the database schema are set within the IT Resources form.
The server type of the schema must be set to Database. Otherwise, Oracle Identity Manager cannot reference the database schema during the creation of a stored procedure task, the execution of a stored procedure task, or both.
In addition, Oracle Identity Manager uses values, which are represented by parameters—for example, Database Name or URL—to connect to the schema. As a result, the stored procedures contained within the schema, can be executed.
-
For Oracle Identity Manager Installations that use Oracle Database, copy the ojdbc14.jar file from the
OIM_HOME/ext/directory to theOIM_DC_HOME/xlclient/extdirectory.For Oracle Identity Manager Installations that use Microsoft SQL Server, you must obtain the following files from Microsoft and copy them to the
OIM_DC_HOME/xlclient/extdirectory:-
msbase.jar -
mssqlserver.jar -
msutil.jar
-
-
Select the adapter to which you wish to add a stored procedure task, for example, the Update User ID adapter.
-
Click the Adapter Tasks tab.
-
Click Add.
The Adapter Task Selection window is displayed.
-
Select the Functional Task option.
-
From the display area to the right of the option, select Stored Procedure, and click Continue. The Add an Adapter Factory Task window is displayed.
The following table lists and describes the regions of the Add an Adapter Factory Task window.
Table 2-4 Regions of the Add an Adapter Factory Task Window
Name Description Task Name
Displays the name of the stored procedure task.
Description
Displays explanatory information about the stored procedure task.
Database
Lists the databases defined in the IT Resources form.
Important: Only those IT resources with a server type of Database appear in the Database list.
Schema
Lists the schemas, which are associated with the database that appears in the Database list.
Procedure
Lists the stored procedures, which reside within the database schema that is displayed in the Schema list.
Connection Status
Displays the status of the connection between Oracle Identity Manager and the database that contains the target stored procedure.
When Oracle Identity Manager can connect to the database, Connection Established is displayed in the Connection Status region.
Note: If Oracle Identity Manager cannot connect, Connection Failed appears in the display area. In addition, the Notes button of the Add an Adapter Factory Task window is enabled. Clicking this button shows you why a connection could not be established, for example:
Exception Type:java.lang.ClassNotFoundExceptionMessage:java.lang.ClassNotFoundException:oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriverIn this example, Oracle Identity Manager could not connect to the designated database because it could not find a particular Java class.
Parameters
Contains parameters that can be mapped to the stored procedure. These parameters appear after you select a database, schema, and stored procedure and save this information to the Oracle Identity Manager database.
-
In the Task Name field, enter the name of the stored procedure task you are creating (for example, Update ID).
-
In the Description text area, you can enter a description for this stored procedure task.
-
Click the Database list. The databases, which are defined in the IT Resources form, appear.
Note:
If Oracle Identity Manager cannot connect to the database you selected, Connection Failed appears in the display area. In addition, the Notes button of the Add an Adapter Factory Task window is enabled. Clicking this button shows you why a connection could not be established.
Tip:
Schemas and stored procedures appear only after you select a database to which Oracle Identity Manager can connect. Based on this selection, related schemas and stored procedures appear in the corresponding combo boxes.
-
Click the Schema list. The schemas appear, which are associated with the database you selected.
-
Click the Procedure list. The stored procedures, which reside within the database schema that you selected from the Schema combo box, appear.
-
From the Add an Adapter Factory Task window's toolbar, click Save. The information pertaining to the stored procedure task is saved into the Oracle Identity Manager database.
You can now set the mappings for the parameter(s) of the stored procedure. These parameters appear in the Parameters region of the Add an Adapter Factory Task window.
Note:
Oracle Identity Manager automatically maps the database and schema of the selected stored procedure. However, Oracle Identity Manager enables you to override these mappings.
See Also:
"Adapter Mapping Information" for more information about which mappings to select
-
From the Add an Adapter Factory Task window's toolbar, click Save. The mappings that you have set for the parameter(s) of the stored procedure task are stored in the Oracle Identity Manager database.
-
From this window's toolbar, click Close.
The Add an Adapter Factory Task window disappears, and the main screen is active once again. The stored procedure task you created (for example, Update ID) appears within the Adapter Factory form.
-
(Optional.) Repeat steps 3 through 13 to create additional stored procedure tasks for the adapter.
-
To compile the adapter, click Build.
The text in the Compile Status field changes from Recompile to OK. This indicates that Oracle Identity Manager compiled the adapter and did not find any errors. You can now attach the adapter to a process task or form field, so Oracle Identity Manager can map to and execute the stored procedure you selected.
2.8.5 Creating a Utility Task
The Adapter Factory is shipped with a library of utility classes and methods, which increase the efficiency of developing adapters.
These utility classes and methods are contained within the xlUtils.jar, xlIntegration.jar, and rt.jar files. A Java task you create by using a class or method from one of these JAR files is called a utility task.
See Also:
Oracle Fusion Middleware Java API Reference for Oracle Identity Manager for more information about the class files that contains the xlUtils.jar, xlAPI.jar, xlIntegration.jar, and rt.jar files
-
Select the adapter to which you wish to add a utility task, for example, the Update Solaris User Group adapter.
-
Click the Adapter Tasks tab.
-
Click Add.
The Adapter Task Selection window is displayed.
-
Select the Utility Task option.
-
From the display area to the right of the option, select Utility, and click Continue. The Object Instance Selection window is displayed.
See Also:
"Creating a Java Task" to learn more about the choices of this window
-
Click Continue. The Add an Adapter Factory Task window is displayed
-
In the Task Name field, enter the name of the utility task you are creating, for example, Update User Group.
-
(Optional.) If you want your utility task to be reusable, select Persistent Instance, type the name of the instance of this task in the text field to the right of the check box.
Caution:
Ensure that name of the instance does not contain any spaces.
See Also:
"Creating a Java Task" for more information about the regions of the Add an Adapter Factory Task window
"Configuring the Adapter Environment" -
Click the Application API list. The class files appear, which belong to the
xlUtils.jar,xlIntegration.jar, andrt.jarfiles.Note:
The xlUtils.jar, xlIntegration.jar, and rt.jar files contain all of the class files that you can use for a utility task. Therefore, you do not have to access the API Source list.
-
From the Add an Adapter Factory Task window, select a constructor and method. Then, set the mappings for the parameters of the constructor and method.
See Also:
"Adapter Mapping Information" for more information about which mappings to select
-
From the Add an Adapter Factory Task window's toolbar, click Save. The information pertaining to the utility task is stored in the Oracle Identity Manager database.
-
From this window's toolbar, click Close.
The Add an Adapter Factory Task window disappears, and the main screen is active once again. The utility task that you created (for example, Update User Group) appears within the Adapter Factory form.
-
(Optional.) Repeat steps 3 through 12 to create additional utility tasks for the adapter.
You are now ready to compile the adapter, so it can be used with a process task or form field.
-
To compile the adapter, click Build.
The text in the Compile Status field changes from Recompile to OK. This indicates that Oracle Identity Manager compiled the adapter and did not find any errors. You can now attach the adapter to a process task or form field.
2.8.6 To Create an Oracle Identity Manager API Task
For greater portability of the adapter code, an Oracle Identity Manager API task enables Adapter tasks to call APIs published by Oracle Identity Manager. This is better than accessing Oracle Identity Manager data directly through hardcoded SQL statements.
The Adapter Factory is shipped with a library of utility classes and methods, which increase the efficiency of developing adapters that contain Oracle Identity Manager API tasks. These utility classes and methods are contained within the xlAPI.jar file.
See Also:
Oracle Fusion Middleware Java API Reference for Oracle Identity Manager for more information about the class files that contain the xlUtils.jar, xlAPI.jar, xlIntegration.jar, and rt.jar files
To create this type of adapter task:
-
Select the adapter to which you wish to add an Oracle Identity Manager API task, for example, the Get User's Password adapter.
-
Click the Adapter Tasks tab.
-
Click Add.
The Adapter Task Selection window is displayed.
-
Select the Utility Task option.
-
From the display area to the right of the option, select Xellerate API, and click Continue. The Object Instance Selection window is displayed.
See Also:
"Creating a Java Task" to learn more about this window
-
Click Continue. The Add an Adapter Factory Task window is displayed.
-
In the Task Name field, enter the name of the Oracle Identity Manager API task you are creating, for example, Retrieve Password).
-
(Optional.) If you want your Oracle Identity Manager API task to be reusable, select Persistent Instance. Then, type the name of the instance of this task in the text field to the right of the check box.
Tip:
Ensure that name of the instance contains no spaces.
See Also:
"Creating a Java Task" for more information about the regions of the Add an Adapter Factory Task window
"Configuring the Adapter Environment" to learn how to enable Oracle Identity Manager to use third-party JAR files with a Java task -
Click the Application API list. The class files appear, which belong to the
xlAPI.jarfile.Note:
The xlAPI.jarfile contains all of the class files that you can use for an Oracle Identity Manager API task. Therefore, you do not have to access the API Source list. -
From the Add an Adapter Factory Task window, select a class file, constructor, and method. Then, set the mappings for the parameters of the constructor and method.
See Also:
"Adapter Mapping Information" for more information about which mappings to select
-
From the Add an Adapter Factory Task window's toolbar, click Save. The information pertaining to the Oracle Identity Manager API task is stored in the Oracle Identity Manager database.
-
Close the Add an Adapter Factory window to activate the main screen. The Oracle Identity Manager API task that you created—for example, Retrieve Password—appears within the Adapter Factory form.
-
(Optional.) To create additional Oracle Identity Manager API tasks for the adapter, repeat steps 3 through 12.
You are now ready to compile the adapter, so it can be used with a process task or form field.
-
To compile the adapter, click Build.
The text in the Compile Status field changes from Recompile to OK. This indicates that Oracle Identity Manager compiled the adapter and did not find any errors. You can now attach the adapter to a process task or form field, so Oracle Identity Manager can communicate with a third-party application.
2.8.7 Reassigning the Value of an Adapter Variable
Sometimes, for an adapter to accomplish its required objective, you must reassign the value of one adapter variable to another adapter variable, a different type of adapter task, or a constant (or literal). The task that enables you to reallocate an adapter variable value is known as a set variable task.
See Also:
"About Adapter Variables" for information about adapter variables
For example, you can create a set variable task to set the adapter variable return value to equal the output of an adapter task (UserName) if the User ID length is fewer than 11 characters.
To create a set variable task:
-
Select the adapter to which you wish to add a set variable task (for example, the Check the Solaris User ID adapter).
-
Click the Adapter Tasks tab.
-
Click Add. The Adapter Task Selection window is displayed.
-
Select the Logic Task option.
-
From the display area, select SET VARIABLE, and click Continue. The Add Set Variable Task Parameters window is displayed.
-
From the Variable Name list, select the adapter variable that has a value you want to reassign—for example, Adapter return value.
-
From the Operand Type list, select the type of operand that will provide the value for the variable.
Tip:
You can reassign an adapter variable's value to another adapter variable, a different type of adapter task, or a literal.
Use Table 2-5 to understand the various types of operands.
Operand Name Description Variable
If you select this operand type, adapter variables appear in the Operand Qualifier list. From this list, select the specific adapter variable that will provide the reassigned value.
Note: The only adapter variables that will appear in the Operand Qualifier combo box will be those variables that have the same data type as the adapter variable that is displayed within the Variable Name combo box.
Adapter Task
By selecting this operand type, adapter tasks are displayed in the Operand Qualifier combo box. From this combo box, select the particular adapter task that will provide the reallocated value.
Note: The only adapter tasks that will appear in the Operand Qualifier combo box will be those tasks that have the same data type as the adapter variable that is displayed within the Variable Name combo box.
Literal
When you select this operand type, types of literals appear in the Operand Qualifier combo box. From this combo box, select the type of literal that will provide the reallocated value. Then, type the specific literal into the field that appears underneath the combo box.
The following task sets the adapter variable's return value to be equal to the UserName adapter variable.
-
On the toolbar in the Add Set Variable Task Parameters window, click Save. The set variable task you created is stored in the Oracle Identity Manager database.
-
On the Add Set Variable Task Parameters window toolbar, click Close. The Add Set Variable Task Parameters window disappears, and the main screen is active once again. The set variable task that you created, for example,
Set Adapter return value = UserName, appears in the Adapter Factory form. -
(Optional.) Repeat Steps 3-9 to create additional set variable tasks for the adapter.
You are now ready to compile the adapter, so it can be used with a process task or form field.
-
To compile the adapter, click Build. The text in the Compile Status field changes from Recompile to OK. Oracle Identity Manager compiled the adapter and found no errors. You can attach the adapter to a process task or form field.
2.8.8 Adding an Error Handler Task
To add an error handler task:
-
An adapter task can return errors. When this occurs, the process task or form field to which the adapter is attached gets rejected.
You can attach your own customizable error messages, which will be displayed to the user. These messages are known as error handler tasks.
For example, you can attach an error handler task to an adapter that will display an error message when the length of a User ID is greater than 10 characters.
-
Select the adapter to which you wish to add an error handler task (for example, the Check the Solaris User ID adapter).
-
Click the Adapter Tasks tab.
-
Click Add.
The Adapter Task Selection window is displayed.
-
Select the Logic Task option.
-
From the display area, select Handle Error, and click Continue. The Add an Adapter Factory Task window is displayed.
-
Double-click this window's lookup field. The Lookup window is displayed, displaying the error handler tasks you can add to the adapter.
Note:
The only error handler tasks that appear in this Lookup window are the ones that begin with ADAPTER—such as ADAPTER.USERIDLENERR).
If you do not see the error handler task that you want to incorporate into the adapter, you can create one by accessing the Error Message Definition form. Refer to "Creating an Error Message".
-
Select the error handler task you want, for example, ADAPTER.USERIDLENERR.
-
Click OK. The Lookup window disappears, and the Add an Adapter Factory Task window is active. In addition, the error handler task you selected appears in the field of this window.
-
From the Add an Adapter Factory Task window toolbar, click Save. The error handler task you incorporated into the adapter is stored in the Oracle Identity Manager database.
-
From this window's toolbar, click Close.
The Add an Adapter Factory Task window disappears, and the main screen is active once again. The error handler task you added, for example,
Handle Error.ADAPTER.USERIDLENERR, appears within the child table of the Adapter Factory form. -
(Optional.) Repeat Steps 3-10 to create additional error handler tasks for the adapter.
If the adapter is logically complete and all variables on the adapter tasks are mapped, you can compile it to use with a process task or form field.
-
To compile the adapter, click Build.
The text in the Compile Status field changes from Recompile to OK. This indicates that Oracle Identity Manager compiled the adapter and did not find any errors. You can now attach the adapter to a process task or form field.
See Also:
"Creating an Error Message" for information about creating error messages by using the Error Message Definition form
2.8.9 Creating a Logic Task
While defining the adapter, you can add conditional statements to the adapter to control its logic flow. These conditional statements are known as logic tasks. For example, you can create a logic task that will trigger an action if the length of a User ID is greater than 10 characters.
To create a logic task:
-
Select the adapter to which you wish to add a logic task (for example, the Check the Solaris User ID adapter).
-
Click the Adapter Tasks tab.
-
Click Add. The Adapter Task Selection window is displayed.
-
Select the Logic Task option.
-
From the display area, select the type of logic task you want to create. Then, click Continue.
Note:
If you select a conditional expression, and click Continue, one of the following actions occurs:
Oracle Identity Manager adds the conditional statement to the adapter directly; or
A secondary window is displayed, containing fields about the conditional expression that you can configure.
To see what happens when you select a particular conditional statement, refer to Table 2-6.
Table 2-6 Actions Resulting from Particular Conditional Statements
Conditional Statement Statement Is Added to the Adapter Directly Secondary Window Appears FOR
X
WHILE
X
IF
X
ELSE
X
ELSE IF
X
BREAK
X
RETURN
X
CONTINUE
X
Table 2-7 explains the various regions of the Add Adapter Factory Logic Task Parameters window:
Table 2-7 Regions of the Add Adapter Factory Logic Task Window
Name Description Operand Type
These combo boxes contain types of operands, such as adapter tasks and adapter variables.
Comparator Combo Box
From this combo box, you can set the relationship between two operands (for example, <, =, >).
Operand Qualifier
These combo boxes contain the qualifiers for the operands.
Literal Text Box
When you select the Literal operand type, enter the specific literal into this field.
Note:
By selecting the FOR conditional statement, an Add Adapter Factory Logic Task Parameters window is displayed. However, it contains different text and combo boxes.
For the FOR conditional expression, use Table 2-8 to understand the various regions of this Add Adapter Factory Logic Task Parameters window.
Table 2-8 Add Adapter Factory Logic Task Parameters for FOR Conditional Statement
Name Description Operand Type
These combo boxes contain types of operands, such as adapter tasks and adapter variables.
Comparator Combo Box
From this combo box, you can set the relationship between two operands (for example, <, =, >).
Operand Qualifier
These combo boxes contain the qualifiers for the operands.
Increment Combo Box
Within this area, you can set whether the initial value will increase or decrease, and by how much.
Note:
If you select the ELSE, BREAK, RETURN, or CONTINUE conditional expressions, proceed to Step 8.
-
Set the parameters for your conditional expression.
This logic task will check to see if the length of the User ID is greater than 10 characters.
-
From the Add Adapter Factory Logic Task Parameters window toolbar, click Save.
The logic task you created is stored in the Oracle Identity Manager database.
-
From this window toolbar, click Close. The Add Adapter Factory Logic Task Parameters window disappears, and the main screen is active once again. The logic task that you created—for example, If (Check ID Length > 10)—appears within the Adapter Factory form.
-
(Optional.) Repeat Steps 3-8 to create additional logic tasks for the adapter.
Caution:
All adapter tasks that can be executed for a condition of a logic task should be nested properly under that logic task.
See Also:
Section 2.10, "Changing the Order and Nesting of Tasks" for more information about nesting tasks
You are now ready to compile the adapter, so it can be used with a process task or form field.
-
To compile the adapter, click Build.
The text in the Compile Status field changes from Recompile to OK. This indicates that Oracle Identity Manager compiled the adapter and did not find any errors. You can now attach the adapter to a process task or form field.
2.9 Modifying Adapter Tasks
The following procedure will show you how to edit an adapter task, in case you must make changes to it. To modify an adapter task
-
Select the adapter that contains the adapter task you wish to edit (for example, the Update Solaris User Group adapter).
-
Click the Adapter Tasks tab.
-
Double-click the adapter task that you want to modify.
The Edit Adapter Factory Task Parameters window is displayed, displaying information that relates to the adapter task you selected. Within this window, make the necessary modifications.
-
On the Edit Adapter Factory Task Parameters window toolbar, click Save.
The information you modified is stored in the Oracle Identity Manager database.
-
On the toolbar, click Close.
The Edit Adapter Factory Task Parameters window disappears. The main screen is active again. The modified task appears within the child table of the Adapter Factory form. You must re-compile the adapter, so it can be used with a process task or form field.
-
To recompile the adapter, click Build.
The text in the Compile Status field changes from Recompile to OK. This indicates that Oracle Identity Manager compiled the adapter and did not find any errors. You can now attach the adapter to a process task or form field.
Caution:
You cannot modify the API call inside a Java, Xellerate API, or Utility task. The adapter task has to be deleted and re-created. In addition, if CODE GEN ERROR appears in the Compile Status field, Oracle Identity Manager encountered errors while compiling the adapter. Rectify the errors, if necessary re-do the adapter task modifications, and compile the adapter again.
2.10 Changing the Order and Nesting of Tasks
If you add multiple tasks to an adapter, you can either change the order in which the tasks are executed, or place one task inside of another task for the adapter to work.
The following procedure will show you how to change the order and nesting of tasks.
Caution:
You should not change the order and nesting of adapter tasks unless you understand the mapping dependencies of the adapter tasks.
To change the order and nesting of tasks:
-
Select the adapter that contains tasks of which you want to change the order and/or nest (for example, the Check the Solaris User ID adapter).
-
Click the Adapter Tasks tab.
The tasks appear, which belong to the current adapter.
In this example, the following changes must occur:
-
The error handler task must be nested inside of the IF (Check ID Length > 10) logic task.
-
The set variable task has to be nested inside of the ELSE logic task.
-
The IF logic task precedes the ELSE logic task.
Therefore, you must first reorganize the logic tasks. Then, you must nest the error handler task and set variable task inside of the IF and ELSE logic tasks, respectively. To reorganize tasks:
-
-
Select the task that must run before another task, and click the Up arrow button. The selected task will switch places with the task that precedes it.
or
Select the task that must be executed after another task, and click the Down arrow button. The highlighted task is displayed below the task that previously followed it.
To nest tasks/remove task nestings:
-
Select the task that must be placed inside of another task, and click the Right arrow button. The selected task will be nested inside of the task that appears above it.
or
Select the task that no longer be nested inside of another task, and click the Left arrow button. The highlighted task will not be nested inside of the task that is displayed above it.
-
On the toolbar, click Save.
The order and nesting of the adapter's tasks is stored in the Oracle Identity Manager database. If the adapter is logically complete and all variables on the adapter tasks are mapped, you can compile it to use with a process task or form field.
-
To compile the adapter, click Build.
The text in the Compile Status field changes from Recompile to OK. This indicates that Oracle Identity Manager compiled the adapter and did not find any errors. You can now attach the adapter to a process task or form field.
Caution:
If you see CODE GEN ERROR in the Compile Status field, Oracle Identity Manager found errors while compiling the adapter. Rectify the errors, if necessary re-do the adapter task modifications, and compile the adapter again.
2.11 Deleting Adapter Tasks
When an adapter task is no longer necessary for the adapter to run, you must remove it from the adapter. To delete an adapter task:
-
Select the adapter that contains the task you wish to remove (for example, the Update Solaris User Group adapter).
-
Click the Adapter Tasks tab.
-
Select the task that you want to remove (for example, the CONTINUE logic task).
-
Click Delete.
The selected task is deleted and disappears from the child table.
-
On the toolbar, click Save.
-
Recompile the adapter.
Caution:
While deleting adapter tasks, ensure that the logic of the adapter is consistent and maintained.
2.12 Working with Responses
Adapters can have different outcomes, called responses. Based on these responses, adapters can trigger other process tasks.
For example, if the adapter returns a True response, the process task's status can be set automatically to Completed. However, if the adapter returns a False response, the process task's status can be set automatically to Rejected, and another process task can be triggered.
These responses can be added, modified, or removed on the Responses tab of the Adapter Factory form.
The following procedures will show you how to create, modify, and delete responses.
Note:
Responses are used only with process task adapters, because these adapters are attached to process tasks. Rule generators, pre-populate adapters, and entity adapters are not connected to processes. In addition, task assignment adapters are not associated with responses. Therefore, if the active adapter is a task assignment adapter, rule generator, pre-populate adapter, or entity adapter, Oracle Identity Manager disables the Responses tab.
2.12.1 To Create a Response
-
Select the adapter to which you want to add responses (for example, the Create Solaris User adapter).
-
Click the Responses tab.
-
Click Add.
An empty row is inserted into the Responses tab.
-
Click the field that appears within the Code Name column.
-
Enter a code, which represents a response type that can be generated (for example, True).
-
Click the field that appears within the Description column.
-
Enter a description for this response (for example, The user was created successfully.).
-
Double-click the field that appears within the Status column.
The Lookup popup window is displayed, containing the different status levels that you can associate with the response.
Note:
For more information about Oracle Identity Manager's status levels, refer to Chapter 4, "About Process Task Adapters" on page 4-1.
-
Click the desired status level (for example, Completed (C)). Then, click OK.
The Lookup window disappears, and the Responses tab is active once again.
-
Create another response, by clicking the Add button, and entering False and The user was not created successfully. into the Code Name and Description fields, respectively. Then, access the Lookup window, and assign the Rejected (R) status level to this response.
-
On the toolbar, click Save.
The responses that you created for this adapter have been stored in the Oracle Identity Manager database. After you attach this adapter to a process task, these responses will appear in the Responses tab of the Editing Task window of the Process Definition form.
2.12.2 To Modify a Response
The following procedure demonstrates how to edit a response.
-
Select the adapter that contains the response you want to edit (for example, the Create Solaris User adapter).
-
Click the Responses tab.
-
Double-click the field of the response, which contains information that you want to modify.
-
If the field is a text field, Oracle Identity Manager enables it. You can now edit the contents within this field.
-
When the field is a lookup field, the Lookup popup window is displayed, containing the different status levels that you can associate with the response. Click the desired status level, click OK.
For example, double-click the Status column of the False response, select the Suspended (S) status level, and click OK.
-
-
On the toolbar, click Save.
The information that you modified for the response is stored in the Oracle Identity Manager database.
2.12.3 To Delete a Response
When a response is no longer necessary, you can delete it from the adapter.
-
Select the adapter, which contains a response that you want to remove.
-
Click the Responses tab.
-
Select the response that you want to delete.
-
Click Delete.
The response disappears. This indicates that Oracle Identity Manager has deleted the response.
2.13 Scheduling Rule Generators and Entity Adapters
Oracle Identity Manager triggers a process task adapter or a task assignment adapter automatically if it is attached to a process task, and the process task's status is Pending. In addition, Oracle Identity Manager always triggers pre-populate adapters on pre-insert. Therefore, you do not schedule when process task adapters, task assignment adapters, or pre-populate adapters will be executed.
On the other hand, a rule generator and an entity adapter are attached to a form field. The only way that Oracle Identity Manager will be able to execute the rule generator or entity adapter is for you to specify when it will be triggered. You do this through the Execution Schedule tab.
Note:
If an entity adapter is attached to a process form or an object form for validation of field values, these adapters will trigger if we edit data in these forms after completing direct or request provisioning.
Using this tab, you can determine that Oracle Identity Manager will trigger the rule generator or entity adapter on preinsert or preupdate. In addition, you can also schedule an entity adapter to be executed on predelete, postinsert, postupdate, and postdelete.
This procedure demonstrates how to configure Oracle Identity Manager to trigger a rule generator or entity adapter.
2.13.1 Scheduling Rule Generators and Entity Adapters
To schedule rule generator and entity adapters:
-
Select the rule generator or entity adapter that you want Oracle Identity Manager to trigger (for example, Solaris User ID Generator).
Note:
When you work with process task adapters or pre-populate adapters, you do not use the Execution Schedule tab. As a result, this tab, as well as its contents, are grayed out.
-
Click the Execution Schedule tab.
The contents of the Execution Schedule tab appear.
The following table will help you understand the various check boxes of the Execution Schedule tab:
Name Description Pre-Insert
By clicking this check box, Oracle Identity Manager can trigger the rule generator or entity adapter before the record is inserted into the database.
Pre-Update
When you click this check box, Oracle Identity Manager can trigger the rule generator or entity adapter before the record is updated in the database.
Pre-Delete
By clicking this check box, Oracle Identity Manager can trigger the entity adapter before the record is deleted from the database.
Post-Insert
When you click this check box, Oracle Identity Manager can trigger the entity adapter after the record is inserted into the database.
Post-Update
By clicking this check box, Oracle Identity Manager can trigger the entity adapter after the record is updated in the database.
Post-Delete
When you click this check box, Oracle Identity Manager can trigger the entity adapter after the record is deleted from the database.
Note:
By clicking the check boxes of the Execution Schedule tab, you are defining the times when Oracle Identity Manager can trigger the rule generator or entity adapter. The Data Object Manager form allows you to specify when Oracle Identity Manager will trigger the rule generator or entity adapter.
For more information about the Data Object Manager form, refer to "Mapping Rule Generator Adapter Variables".
-
Enable the desired check boxes. Then, from the toolbar, click Save.
The criteria you set for Oracle Identity Manager to execute the rule generator or entity adapter is stored in the Oracle Identity Manager database.