48 Set Up Fixed Asset Constants
This chapter contains the topic:
You set up fixed asset constants to control how your business environment uses the features in the Fixed Assets system. For example, you can choose whether to access the hard-coded depreciation methods or the user-defined depreciation rules when you determine depreciation for your assets. You can also specify the business unit that appears as a default value for the various asset accounts when you create a master record for a new asset.
48.1 Setting Up Fixed Asset Constants
From Fixed Assets (G12), choose 29
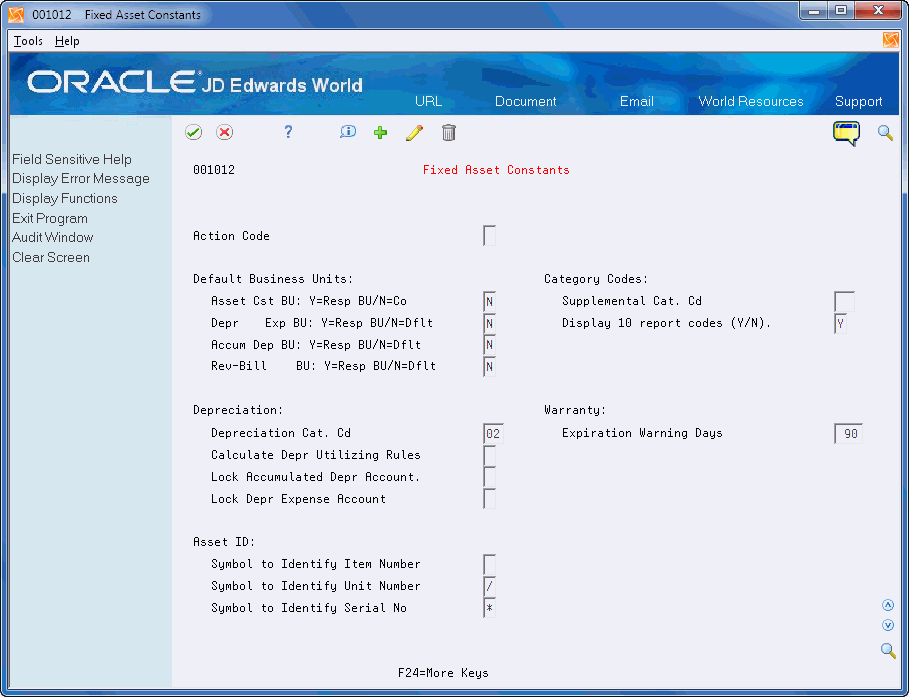
From Fixed Asset System Setup (G1241), choose Fixed Asset Constants
You set up fixed asset constants only one time for the entire Fixed Assets system. Set up constant values for company 00000 so that all the companies in your organization that access the Fixed Assets system use the same constant values. Be aware that the values you set up for the Fixed Assets system on Fixed Asset Constants also affect the Equipment/Plant Management system.
Caution:
To avoid inconsistencies, do not change the constant values that you set up for your system. For example, if you change the default business unit for asset accounts, the change affects only the assets that you add to the system after the change.To set up fixed asset constants
Complete the following fields:
-
Default Asset Cost Business Unit: Y=Resp BU/N=Co
-
Default Depreciation Expense Business Unit: Y=Resp BU/N=Co
-
Default Accumulated Depreciation Business Unit: Y=Resp BU/N=Co
-
Default Revenue-Billing Business Unit: Y=Resp BU/N=Co
-
Depreciation Category Code
-
Calculate Depreciation Utilizing Rules
-
Lock Accumulated Depreciation Account
-
Lock Depreciation Expense Account
-
Symbol to Identify Item Number
-
Symbol to Identify Unit Number
-
Symbol to Identify Serial Number
-
Supplemental Category Code
-
Display 10 report codes (Y/N)
-
Warranty Expiration Warning Days
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Default Asset Cst BU: Y=Resp BU, N=Co No | This code determines where the business unit for the asset cost account comes from when you add a new asset. When you add a new asset, the system uses the business unit that this value represents on Depreciation Information. Valid codes are:
Y – Responsible Business Unit. The system uses the business unit from the responsible business unit on the Master Information screen. N – Company. The system uses the business unit from the company number on the Master Information screen. Note: Typically the business unit and company share the same number. For example, business unit 50 usually contains general accounts for company 50. |
| Default Depr Exp BU: Y=Resp BU, N=Deflt | This code determines where the business unit for the depreciation expense comes from when you add a new asset. When you add an asset, the system uses the business unit that this value represents on Depreciation Information. Valid codes are:
Y – Responsible business unit. The system uses the business unit from the responsible business unit on the Master Information screen. N – Default. The system uses the business unit from the Item Setup Default Coding screen. |
| Default Accum Dep BU: Y=Resp BU, N=Deflt | This code determines where the business unit for accumulated depreciation comes from when you add a new asset. When you add an asset, the system uses the business unit that this value represents on Depreciation Information. Valid codes are:
Y – Responsible business unit. The system uses the business unit from the responsible business unit on the Master Information screen. N – Default. The system uses the business unit from the Item Setup Default Coding screen. |
| Default Rev-Bill BU: Y=Resp BU, N=Deflt | This code determines where the business unit for revenue and billing comes from when you add a new asset. When you add an asset, the system uses the business unit that this value represents on Depreciation Information. Valid codes are:
Y – Responsible business unit. The system uses the business unit from the responsible business unit on the Master Information screen. N – Default. The system uses the business unit from the Item Setup Default Coding screen. |
| Depreciation Calc Use Rules Flag | Controls where the depreciation programs get the depreciation information, including the depreciation accounts to use, the ledgers and subledgers for which depreciation must be calculated, and the depreciation methods to be used. Valid codes are:
blank – The depreciation programs refer to values stored in the Asset Balance table for depreciation information. The system stores information in each asset record. These values are taken as default depreciation values from Company Ledger Depreciation Rules when the asset master is created. 1 – The depreciation programs refer to the Company Ledger Depreciation Rules for the depreciation information. |
| Lock Accumulated Depreciation Account | Controls whether an Accumulated Depreciation Account specified in the Company Depreciation Account Rules is locked to the Asset Cost Account specified on the same screen. Valid codes are:
blank – No lock is present. 1 – Lock is on. In every company depreciation account rule, the accumulated depreciation account specified is locked to the asset cost account. The accumulated depreciation account cannot be changed after the first posting to the account. Prior to the first posting the business unit can be changed. After the first posting, changes must be made through the asset transfer procedure. |
| Lock Depreciation Expense Account | Controls whether the Depreciation Expense Account specified in the Company Depreciation Account Rules is locked to the Asset Cost Account specified on the same screen. Valid codes are:
blank – No lock is present. 1 – Lock is on. In every company depreciation account rule, the depreciation expense account specified is locked to the asset cost account. The depreciation expense account cannot be changed after the first posting to the account. Prior to the first posting the business unit can be changed. After the first posting, changes must be made through the asset transfer procedure. |
| Depreciation Cat. Cd | Use this Fixed Asset category code to group assets into "depreciation" categories. Inquiries, reports, journals, and other processes that depend on the depreciation category will make reference to the value in this category code.
Note: You must set up a default value for this category code. |
| Symbol to Identify Item Number | You can assign one of three different numbers to an asset. These numbers are:
When you enter an asset number, you may use a prefix or symbol to designate the number you enter. If you use this number most often, you should leave the symbol blank so that you just need to enter the number. If it is not the number you use most often, you should define a symbol, such as / or *, that you will type before you enter the number so that the system knows which number you are representing. Note: You can leave only one asset number blank. The other two must have a symbol so that all three numbers are unique. Verify that the symbols you use are not significant for any other purposes of data entry, for example, a period or comma. |
| Symbol to Identify Unit Number | You can assign one of three different numbers to an asset. These numbers are:
When you enter an asset number, you may use a prefix or symbol to designate the number you enter. If you use this number most often, you should leave the symbol blank so that you just need to enter the number. If it is not the number you use most often, you should define a symbol, such as / or *, that you will type before you enter the number so that the system knows which number you are representing. Note: You can leave only one asset number blank. The other two must have a symbol so that all three numbers are unique. Be sure that this symbol is not significant for any other purposes of entry, for example, a period or comma. |
| Symbol to Identify Serial Number | You can assign one of three different numbers to an asset. These numbers are:
When you enter an asset number, you may use a prefix or symbol to designate the number you enter. If you use this number most often, you should leave the symbol blank so that you just need to enter the number. If it is not the number you use most often, you should define a symbol, such as ' or *, that you will type before you enter the number so that the system knows which number you are representing. Note: You can leave only one asset number blank. The other two must have a symbol so that all three numbers are unique. Be sure that this symbol is not significant for any other purposes of entry, for example, a period or comma. |
| Supplemental Cat. Cd | Enter the number of the equipment category code that controls which supplemental data types the system displays on the Equipment Management supplemental data screens.
When you set up supplemental data, you use Data Type Cross Reference to specify which types of data appear on supplemental data screens. For example, on Equipment Constants, you can specify equipment category code 2 (Major Equipment Class) as the supplemental data category code. Then, on Data Type Cross Reference, you can specify which data types are appropriate for each class of equipment you set up under Major Equipment Class, such as specification sheets and transportation notes for heavy equipment. |
| Display all 10 report codes (Y/N) | This code controls the number of category code fields the system displays on various screens. Examples of these fields might include Accounting Class, Equipment Class, and so on. Valid codes are:
Y – Display first 10 category codes N – Display only the first five category codes Set the number of category codes that appear on your screens to accommodate the number of category codes you use in your system. You can change the value in this field at any time. |
| Warranty Expiration Warning Days | It is often necessary to give warnings when an item, object, contract, etc. is due to expire. This is the number of days to use when calculating whether to give an expiration warning or not. If an item is to expire within this many days of today's date (the system date), a warning will be issued. |
48.1.1 What You Should Know About
See Also:
-
Section 24.1, "Setting Up User Defined Depreciation" for more information on depreciation rules.