25 Work with High-Volume Consolidations
This chapter contains these topics:
25.1 Working with High-Volume Consolidations
Use high-volume consolidations to combine balances for online review and financial reporting. To accommodate this, you combine balances under a pseudo (fictitious) company that you create solely for this purpose. For example, you can use the pseudo company to consolidate actual balances for each region or division of your company.
High-volume consolidations include two programs:
Both programs are DREAM Writers.
The system consolidates the account balances by one of the following:
-
Business Unit Category Codes (RP01-RP30) in the Business Unit Master table (F0006), for review by organizational structure
-
Account Master Category Codes (R001-R023) in the Account Master table (F0901), for review by an alternate chart of accounts
25.1.1 Example: High-Volume Consolidation
In this example, the following business units are grouped together under the West Region:
-
Business unit 5, associated with company 1
-
Business unit 600, associated with company 100
During high-volume consolidation, these two business units are consolidated into a pseudo business unit named 02W, where:
-
02 represents category code 02
-
W represents the category code value for West Region
The following diagram illustrates a high-volume consolidation that consolidates data by region using business unit category code 2.
Figure 25-1 Consolidation by Region Using Business Unit Category Code 2
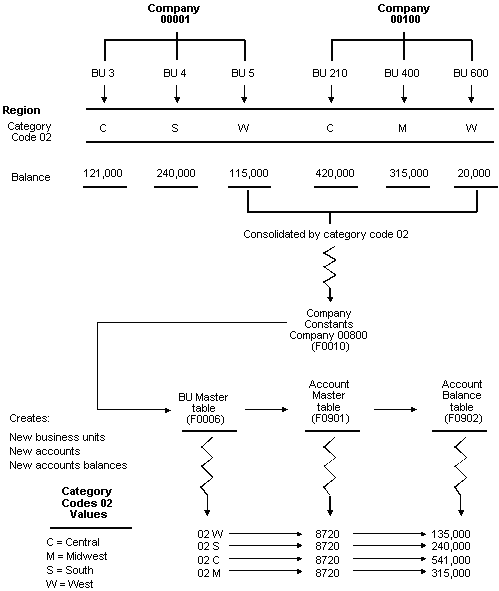
Description of "Figure 25-1 Consolidation by Region Using Business Unit Category Code 2"
25.2 Creating High-Volume Consolidations
From General Accounting (G09), choose Consolidations
From Consolidations (G1011), choose Refresh Consolidation
To create a new consolidation with current balances, you must refresh the consolidation. This creates a second database for pseudo business units, accounts, and account balances within a pseudo company that you have already created specifically for consolidations. The system copies all balances in the accounts to be consolidated into the pseudo company regardless of fiscal year.
The Refresh Consolidation program is a DREAM Writer program.
Note:
The Refresh Consolidation program does not create a pseudo account if the corresponding actual account does not have a balance.High-volume consolidations are based on category codes. You can use either account or business unit category codes. You must set up a separate version for each category code that you use for consolidating. After you refresh consolidations using one category code, you can select another category code and run the program again. This creates additional records for the pseudo company.
You can run more than one consolidation at the same time. To do so, set up a separate pseudo company for each consolidation.
Refreshing consolidations creates records that are based on your setup. These records include:
-
Prior Year-End Net (PYEN), Prior Year-End Cumulative (PYEC), and monthly posting information
-
All accounts with consolidated balances
-
Header and non-posting title accounts for reports, such as Assets
Caution:
You must select a pseudo company for the consolidation. Refreshing consolidations adds records to the Business Unit Master (F0006), Account Master (F0901), and Account Balances (F0902) tables for an entire pseudo company. If you select an actual company for the consolidation, the system creates consolidated records for that company. It is very difficult to separate valid records from those created by the consolidation program.25.2.1 Before You Begin
-
Restrict access to this program
-
Set up a pseudo company for each consolidation that you intend to run
-
Set up a next number for the pseudo company's account ID that does not duplicate account IDs assigned to other accounts
-
Verify the category codes that you want to use for consolidations
-
Delete any prior consolidations
-
Verify that there is enough disk space on your computer for this process to run
25.2.2 What is the Structure of Pseudo Business Units?
A business unit number can contain up to 12 characters. The structure of the pseudo business unit number is AABBB, where:
| Business Unit Code Segment | Explanation |
|---|---|
| AA | Represents the category code number that you designated in data selection, such as 02 |
| BBB | Represents the category code value for the selected category code, such as WES for western region or EAS for eastern region |
For example, if you run the consolidation for business unit category code 5 (RP05), and the values for category code 5 are DEN, ATL, and NYC, the program creates three pseudo business units as follows:
-
05DEN
-
05ATL
-
05NYC
If you run the consolidation for business unit category code 21 (RP21), and the values for category code 21 are CALIFORNIA and COLORADO, the program creates two pseudo business units as follows:
-
21CALIFORNIA
-
21COLORADO
25.2.3 What You Should Know About
25.2.5 Data Selection and Data Sequence for Refresh Consolidations
You can use only one category code for each consolidation. Set up the category code data selection so that it is not equal (NE) to blanks (*BLANKS). In addition to a category code, optional selections can include:
-
Company, to exclude other pseudo companies from the consolidation. Otherwise, the system consolidates previously consolidated information.
-
Ledger Type, to limit the consolidation to specific ledger types or to exclude certain ledger types from the consolidation.
-
Fiscal Year, to limit the consolidation to a fiscal year or to exclude certain fiscal years from the consolidation.
The category code you use must be on the first line of the data sequence. The order of the data sequence for refreshing a consolidation should be:
-
Selected category code
-
Object account
-
Subsidiary
25.3 Reviewing High-Volume Consolidations
From General Accounting (G09), choose Consolidations
From Consolidations (G1011), choose Consolidation Review
After you create high-volume consolidations, you can review them. You can compare the amounts in two types of ledgers for the pseudo company. For example, you compare actual amounts (AA) to budgeted amounts (BA) or to budget-to-actual ratios.
You review account balances by business unit or account number.
25.3.1 Before You Begin
-
If you anticipate reviewing information for more than 100 accounts, set up a maximum count in user defined codes (00/10). The Consolidation Review program notifies you when it reaches the maximum. You can either review the information up to that point or wait until the program consolidates all of the accounts.
To review high-volume consolidations
-
Complete the following field:
-
Account
-
-
To view detail in different formats, choose Toggle Display Formats (F2) to view the following formats:
-
Budget and actual amounts for the period
-
Budget and actual amounts, and the difference between them
-
Budget and actual amounts for the period and year-to-date
-
-
To review additional detail, perform any of the followingchoose:
-
Choose Video Trial Balance (F13/14/15), for single-ledger views of the data.
-
Enter 1 or 2 in the Option field for Account Ledger Inquiry.
-
To view and change enhanced subledgers, choose Additional Selections (F6).
-
Note:
On Trial Balance/Ledger Comparison complete the business unit field and click find. Only journal entries made directly to the pseudo business unit appear because refreshing consolidations creates only balances, not transactions25.4 Deleting Prior High-Volume Consolidations
From General Accounting (G09), choose Consolidations
From Consolidations (G1011), choose Delete Prior Consolidation
You must delete the information in the consolidation database before you run a new consolidation. If you do not, the system adds the new information to the old when you run the new consolidation, and the resulting balances are incorrect.
Run the Delete Prior Consolidation program to delete prior consolidation records for the pseudo company from the following tables:
The Delete Prior Consolidation program is a DREAM Writer program.
Pseudo companies and business units are designed for consolidation purposes. Therefore, this program does not update account balances, nor does it delete:
-
Pseudo business units in the Business Unit Master table (F0006)
-
Pseudo companies in the Company Constants table (F0010)
Caution:
Delete only the pseudo consolidation company. Be very careful not to delete any actual companies.