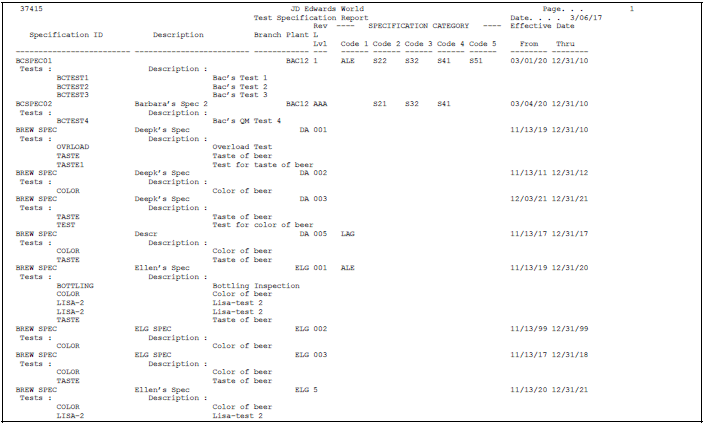
5 Set Up Specifications
This chapter contains these topics:
5.1 Setting Up Specifications
You should group tests that will always be performed at the same time into a specification. Specifications can be unique to a branch/plant or common across all branch/plants.
An example of a specification is a blending specification for a soft drink, which contains tests for caffeine, color shade and syrup concentration.
For each specification, you can define:
-
Name and description
-
Revision levels
-
Effectivity dates
-
Which tests to include in the specification
5.2 Defining Specifications
From Quality Management (G37), enter 29
From Quality Management Setup (G3741), choose Specification Revisions
As you define a specification, you determine which tests and specifications to perform at the same time.
Defining specifications consists of the following tasks:
-
Entering specifications
-
Locating revision levels
-
Entering text
-
Locating specifications
Figure 5-1 Specification Revisions screen
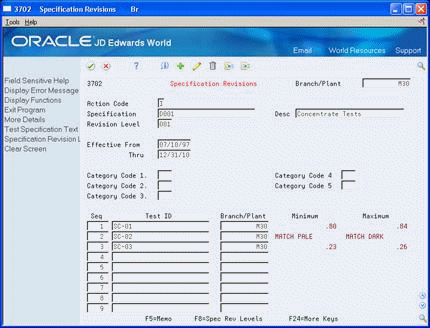
Description of "Figure 5-1 Specification Revisions screen"
-
To identify the specification, complete the following fields:
-
Branch Plant
-
Specification
-
Description
-
Revision Level
-
-
To define the specification's range of effectivity, complete the following fields:
-
Effective From
-
Effective Thru
-
-
To categorize specifications into groups, complete the following fields:
-
Category Codes 1-5
-
-
To group the tests and other specifications, complete the following fields:
-
Test
-
Branch Plant
After you enter a specification, you can review revision levels for that specification.
-
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Revision Level | The revision level of the specification. |
| Effective From | A date that indicates one of the following:
The default is the current system date. You can enter future effective dates so that the system plans for upcoming changes. Items that are no longer effective in the future can still be recorded and recognized in Product Costing, Shop Floor Control, and Capacity Requirements Planning. The Material Requirements Planning system determines valid components by effectivity dates, not by the bill of material revision level. Some forms display data based on the effectivity dates you enter. |
| Effective Thru | A date that indicates one of the following:
The default is December 31 of the default year defined in the Data Dictionary for Century Change Year. You can enter future effective dates so that the system plans for upcoming changes. Items that are no longer effective in the future can still be recorded and recognized in Product Costing, Shop Floor Control, and Capacity Requirements Planning. The Material Requirements Planning system determines valid components by effectivity dates, not by the bill of material revision level. Some forms display data based on the effectivity dates you enter. |
| Category Code 1 | One of five reporting codes that can be assigned to each specification defined. Use these codes to categorize specifications into different groups. Category codes are user defined (System 37, types S1 through S5).
Examples: Category code S1 - Specification Group Category code S2 - FDA Code |
A revision level is an alphanumeric character that represents the number of times a specification has changed. To avoid overlapping revisions, the system verifies that the start dates of revisions are not greater than the end date for other revisions.
-
Choose the Specification Revision Levels function.
Figure 5-2 Specification Selection screen
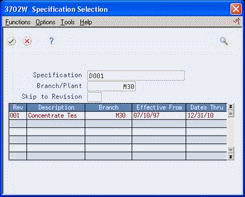
Description of "Figure 5-2 Specification Selection screen"
-
On Specification Selection, review the following fields:
-
Revision Level
-
Effective From
-
Effective Thru
-
Branch Plant
-
-
To work with a revision level, choose the Select option.
After you locate revision levels, you can enter text for the specification.
On Specifications Revisions
-
Figure 5-3 Test Specification Text screen
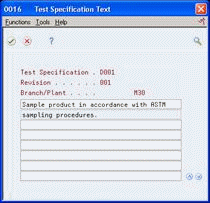
Description of "Figure 5-3 Test Specification Text screen"
-
On Test Specification Text, type instructions.
The message See Memo appears on Specification Revisions for specifications with text. After you enter text, you can locate all specifications for a branch/plant.
On Specification Revisions
-
Place the cursor on the following field:
-
Specification
-
-
Figure 5-4 Test/Specification Search screen
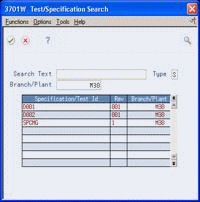
Description of "Figure 5-4 Test/Specification Search screen"
-
On Test/Specification Search, review the following fields:
-
Specification/Test ID
-
Revision
-
Branch/Plant
-
-
To work with a specification, choose the Select option.
5.2.1 What You Should Know About
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Import Test Specifications (Release A9.3 Update) | You can use the Test Specification - Z File (P3702Z) program to create, update, or delete test specification definitions. P3702Z launches the Specification Revisions (P3702) as a batch program and processes the data from the Specifications Definition Header Z (F3702HZ) and Specifications Definition Detail Z (F3702DZ) files into P3702.
See Appendix B, "Import Mass Data into Quality Management"for more information about Z File processes. |
5.3 Reviewing Specifications
From Quality Management (G37), enter 29
From Quality Management Setup (G3741), choose Test/Specification Where Used
Use the Test/Specification Where Used program to review where specifications are used within your branch/plants.
On Test/Specification Where Used
Figure 5-5 Test/Specification Where Used screen
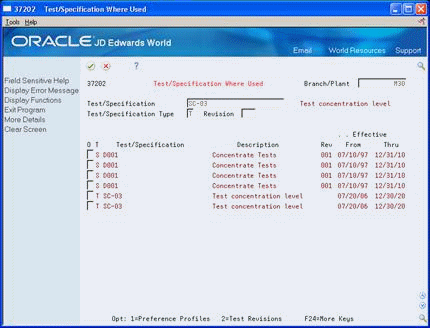
Description of "Figure 5-5 Test/Specification Where Used screen"
-
To locate a specification, complete the following fields:
-
Branch/Plant
-
Test/Specification
-
Revision
-
-
Enter S in the following field:
-
Test/Specification Type
-
-
Access the detail area (F4).
Figure 5-6 Test/Specification Where Used (Detail) screen
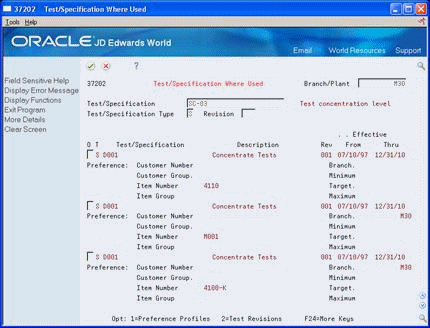
Description of "Figure 5-6 Test/Specification Where Used (Detail) screen"
-
Review the following fields:
-
Test/Specification Flag
-
Description
-
Revision Level
-
Effective From
-
Effective Thru
-
Customer Number
-
Customer Group
-
Item Number
-
Item Group
-
Branch
-
Minimum
-
Maximum
-
Target
-
5.4 Printing Specifications
From Quality Management (G37), enter 29
From Quality Management Setup (G3741), choose Specifications Report
Use the Specifications Report program to create a report that includes all the test specifications for the branch/plant you select. Use this information to review and maintain specifications within your business.