Understanding Oracle Payments
Overview of Oracle Payments
Oracle Payments is a product in the Oracle E-Business Suite of applications, which serves as a funds capture and funds disbursement engine for other Oracle applications. As the central payment engine, Oracle Payments processes transactions, such as invoice payments from Oracle Payables, bank account transfers from Oracle Cash Management, and settlements against credit cards and bank accounts from Oracle Receivables. Oracle Payments provides the infrastructure needed to connect these applications and others with third party payment systems and financial institutions.
The centralization of payment processing in Oracle Payments offers many benefits to deploying companies. Companies can efficiently centralize the payment process across multiple organizations, currencies, and regions. Better working capital management can be achieved by providing cash managers visibility into cash inflows and outflows. Additionally, a full audit trail and control is supported through a single point of payment administration.
Oracle Payments is integrated with financial institutions and payment systems for receipt and payment processing, known as funds capture and funds disbursement, respectively. Funds capture refers to the electronic retrieval of funds, typically by a payment system on behalf of the deploying company, from payers, such as customers, who owe debts to the deploying company. The payer, in this case, provides Oracle Payments with pertinent payment information, such as a credit card, debit card, or bank account number. Funds disbursement, on the other hand, is the process of paying funds owed to creditors, such as suppliers.
Oracle Payments supports the following types of electronic payments for funds capture payments:
-
credit cards
-
purchase cards
-
PINless debit cards
-
bank account transfers
Oracle Payments supports several payment methods for funds disbursement payments, including:
-
checks
-
wires
-
electronic funds transfers
Understanding Funds Capture
This section presents functionality and terms that are relevant to the funds capture process.
Understanding Payment Methods (Funds Capture)
On the funds capture side of Oracle Payments, a payment method is the medium by which a third party payer chooses to remit payment to the first party payee. For example, a customer remits payment for a product or service to the deploying company. Oracle Payments supports the following types of payment methods for automated funds capture processing:
-
bank account transfers
-
credit cards
-
PINless debit cards
-
bills receivable remittances
Oracle Payments enables flexible setup of funds capture payment methods as follows:
-
You can define unique payment methods for bank account transfers.
-
Oracle Payments seeds a single payment method for credit card and PINless debit cards.
Understanding Offline and Online Payments
This section includes the following topics:
-
Understanding Offline and Online Payments
-
Online Payment Processing
-
Offline Payment Processing
Understanding Offline and Online Payments
Oracle Payments supports two models of payment processing for credit, purchase, and PINless debit cards as follows:
-
Online Payment Processing
-
Offline Payment Processing
Funds capture bank account transfers always occur offline.
The types of operations that you can process online depends on the payment system type you have chosen, gateway or processor model and your operation model, host based or terminal based.
For processor model payment systems, authorization operations must be online and settlement operations are offline and batched. For gateway payment systems, both authorization and settlement operations can be online.
Online Payment Processing
Online payment processing is the model in which a transaction is immediately forwarded to the payment system. The results from the payment system are immediately returned to the source product. Online transactions are supported for credit, purchase, and PINless debit cards. Online validation transactions are supported for Electronic Funds Transfer.
Offline Payment Processing
Offline payment processing is the model in which transactions are not immediately forwarded to payment systems. When a source product submits a transaction in a scheduled mode, if the payment is predated, or if the transaction is a settlement destined for a processor model payment system, the payment information is saved in the Oracle Payments database and is sent to the payment system at a later time.
The offline method uses concurrent programs that submit offline operations at regular intervals. The programs browse the stored transactions, send transactions to the payment systems, and update the source products. The Submit Offline Operations concurrent program is used to submit individual offline transactions to gateway model payment systems and the Create Settlement Batches concurrent program is used to submit batches of transactions to processor model payment systems.
Understanding Credit Card Transactions
Among funds capture payments, Oracle Payments handles credit card, PINless debit card, purchase card, and EFT transactions. This section explains the process flow for a typical credit card transaction.
Traditional Credit Card Transactions
Traditional credit card transaction processing involves a third party payer, a first party payee, an issuing bank, an acquiring bank, a payment processor, and, optionally, a payment gateway. The payment gateway or payment processor that Oracle Payments interacts with directly is called a payment system for simplicity.
A credit card transaction consists of two phases: authorization and settlement. A typical flow might occur as follows:
-
Authorization
The third party payer purchases goods or services and sends credit card information as part of an order or invoice to the first party payee.
The first party payee accepts the order and sends an authorization request to the payment processor through Oracle Payments and, optionally, a payment gateway.
The payment processor matches the information with a database maintained by the issuing bank to determine if the customer has enough available credit to cover the transaction. If so, then the payment processor reserves the funds and sends back an authorization code.
-
Settlement
The first party payee delivers goods to the customer and needs to settle the transaction, that is, capture the funds reserved in the authorization. Settlement may occur at the same time as authorization. Settling transactions may include batch administration.
The first party payee issues capture, void, return, credit, and settlement batch functions to the payment processor through Oracle Payments and optionally, the payment gateway.
The payment processor settles the payment with the issuing bank and causes the funds to transfer to the acquiring bank.
Voice Authorization
Sometimes credit card processing networks decline transactions with a referral message indicating that the merchant must call the cardholder's issuing bank to complete the transaction. The payment information in such cases is submitted over the phone. If the transaction is approved, the merchant is provided with an authorization code for the transaction. To facilitate follow-on transactions through Oracle Payments for this voice authorization (for example, capture or void), Oracle Payments provides voice authorization support for gateway model and processor model payment systems.
The credit card expiration date is always the last day of the month (that is the reason only the month and year values are sufficient to specify the credit card expiration date). So, even though the card expiration date was specified as 7-Jul-2009, it gets rounded to 31-Jul-2009.
Understanding Purchase Cards
A purchase card is a type of credit card that is issued by an organization to its employees. The card is generally used by the employees for purchasing corporate supplies and services. Payments are made by the corporate buyer to the card issuer.
Purchase cards, also known as procurement cards, are a special type of credit card that possess more features, capabilities, and controls than standard consumer credit, or charge, cards. Purchase cards are issued by an organization, known as the buyer, and used by its employees. Payments are made directly by the corporate buyer to the card issuer. With credit cards, payments are made by the individual buyer, who may be an agent of a corporate buyer, to the card issuer.
A merchant receives payment a few days after submitting a transaction and the buyer pays the issuing bank for the aggregate amount of purchases made during the billing period. Purchase cards provide merchants with a mechanism to eliminate the costly paper process of providing and collecting funds for outstanding invoices.
Purchase Card Data Levels
For a purchase card, three levels of data can be captured and sent by a merchant to the buyer organization through the payment system. They are:
Level I:
Level I transaction data consists of only basic data. A standard credit card transaction provides level I data to the payment system. The buyer cannot derive any special benefits from purchase card usage if the merchant passes only level I data.
Level II:
Level II transaction data consists of data such as tax amount and order number in addition to level I data.
Level III:
Level III line item detail provides specific purchase information such as item description, quantity, unit of measure and price. This information is very useful to the buyer to help streamline accounting and business practices and to merge payment data with electronic procurement systems. Data in the table below is only indicative. The actual fields are payment system-dependent.
Note: Oracle Payments supports Level III data for both payment processors and gateway model payment systems.
This table lists information on data that is passed by Oracle Payments in each level.
| Data | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Card Number | X | X | X |
| Card Holder Name | X | X | X |
| Card Expiration Date | X | X | X |
| Card Holder Billing Address | X | X | X |
| Currency Code | X | X | X |
| Tax Amount | X | X | |
| Transaction/Order Number | X | X | |
| Ship from Postal Code | X | X | |
| Destination Postal Code | X | X | |
| Discount Amount | X | ||
| Freight Amount | X | ||
| Duty Amount | X | ||
| Line Item Information | X |
Processing Purchase Card Transactions
The transaction phases in a purchase card transaction are the same as in a credit card transaction. The phases are authorization and settlement. See Understanding Credit Card Transactions for more information about transaction phases.
Oracle Payments automatically recognizes purchase cards based on a set of seeded card number ranges. Oracle Payments passes additional information to the payment system during the settlement or settlement batch operation and through Gateway online requests. Authorization and other settlement operations carry the same information for purchase cards as they do for credit cards.
The business flow differs on the buyer's side and for the payment system, but not for the merchant except for the additional information that is passed.
Understanding Funds Capture Bank Account Transfers
Oracle Payments supports funds capture bank account transfers for both business-to-consumer and business-to-business models. The funds capture bank transfer functionality facilitates electronic transfer of payment amounts from a customer's bank account to the payee's bank account. Online validations are online and real-time, while actual funds transfer transactions are offline. In addition to standard direct debits, Oracle Payments supports remittance of bills receivable instruments. Source products use Oracle Payments as their interface to payment systems that provide connectivity to appropriate clearing house networks.
Note: Oracle Payments has standard integration with Oracle Receivables for direct-debit and bills receivable remittance.
Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) Online Validations
EFT online validations are a real time service provided by some payment systems to validate the third party payer bank account to be used in an EFT transaction. EFT online validations service ensures that the third party payer's bank account instrument exists and that there is no fraud alert against that bank account. Electronic funds transfer transactions are not real time. It is generally not possible, therefore, to ensure that the bank account is still open and has sufficient funds. EFT online validation assists with validity checking as follows:
-
The validation step is an optional step for EFT transactions. It can be performed any number of times.
-
The validation is performed in real time.
-
The EFT online validation response message shares the same message standard with the credit card authorization response message for processor model type payment systems.
Note: EFT online validation is only offered for United States ACH and not for all payment systems. EFT online validation does not reserve funds or check if the account has sufficient funds.
Understanding PINless Debit Card Transactions
PINless debit card transactions are a type of payment method offered by some payment systems to first party payees in selected industries that are traditionally viewed as recurring billers. PINless debit card transactions, like bank account transfers, facilitate electronic transfer of payment amounts from a customer's bank account to the payee's bank account. In the case of PINless debit cards, however, the payer uses a card, as in a credit card transaction. The payer initiates the debit card payment process without providing a PIN. The first party payee authenticates the payers and assumes 100% liability for the transaction and any subsequent adjustments.
The transaction is sent to the debit networks for processing. Currently, three debit networks support PINless debit card payments: Star, NYCE, and Pulse.
Authorization and capture of PINless debit card transactions are handled in a single step by all payment systems. After authorizing the PINless debit card transaction, no modification to the transaction can be made. After the payment request is approved, the payer's account is debited in real time. Any dispute, error, or modification associated with the transaction can be handled offline between the payer and the first party payee.
The settlement step for PINless debit card transactions is flexible. While some payment systems, such as Paymentech, require this step to complete the transaction, other payment systems do not support this step. PINless debit card transactions, however, share the same batch with credit card and purchase card transactions. The payment system differentiates and settles transactions accordingly.
Process Flow for Gateway-Model Payment System
Most gateway model payment systems handle PINless debit card transactions in a single step. After receiving the authorization request, the payment system will send the transaction to the debit network. The payer's account is debited after the authorization request is approved. The first party payee's account is credited sometime later. PINless debit card transactions are different from the process flow of credit card transactions where the authorization and fund capture are separated into two steps.
Process Flow for Processor-Model Payment System
For most processor model payment systems, the flow for PINless debit cards is identical as that for payment gateways. However, some processor model payment systems, such as Paymentech, require an additional settlement step to complete the transaction. The first party payer's account will be credited after settlement and the fund transfer is said to be completed.
Understanding Funds Disbursement
This section includes information on the following topics:
-
Understanding Payment Methods (Funds Disbursement)
-
Understanding Payment Process Profiles
-
Understanding Documents Payable
-
Understanding Payments
-
Understanding Payment Instructions
-
Understanding Payment Process Requests
Understanding Payment Methods (Funds Disbursement)
On the funds disbursement side of Oracle Payments, a payment method is a payment attribute on a document payable. The payment method indicates the medium by which a first party payer makes a payment to a third party payee. Payment methods also include other information used during the early stages of payment processing, such as validations and rules that determine how payment methods can be assigned to documents payable. Examples of funds disbursement payment methods include the following:
-
checks printed in-house by the payer
-
checks outsourced to the bank for printing
-
electronic funds transfers, through ACH in the United States or BACS in the United Kingdom
-
wires
Oracle Payments seeds some payment methods, but also enables you to define your own as well.
A source product user, such as an Oracle Payables clerk, must select a payment method when entering a document payable, such as an invoice. The source product uses Oracle Payments setup to default payment methods onto each document payable and to restrict the user's choice of payment methods to encourage efficient payment processing.
Understanding Payment Process Profiles
A payment process profile is a payment attribute assigned to documents payable, which specifies handling of the documents payable, payments, and payment instructions by Oracle Payments. Payment process profiles include several types of information, including specifications for payment instruction formatting and transmission.
Payment process profiles can be assigned to documents payable either by the source product user or by the Oracle Payments payment administrator. The selection of valid payment process profiles is determined by the payment process profile's usage rules, which are created in Oracle Payments setup. Usage rules for payment process profiles can be based on payment method, payment currency, first party organization, or internal bank account.
Payments are built from documents payable that have the same payment process profile, among other attributes. Payment instructions are built from payments that have the same payment process profile, among other attributes. Therefore, the payment process profile is available to specify Oracle Payments behavior at every step of the payment process.
Understanding Documents Payable
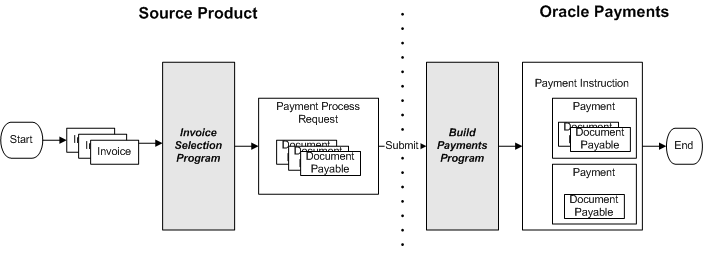
A document payable is a transaction in a source product that is sent to Oracle Payments for payment. An example of a document payable in Oracle Payables is an invoice. During the payment process, documents payable are grouped together into actual payments.
Understanding Payments
A payment is a single transfer of funds from one person or organization to another via printed payment document or electronic transmission. The diagram below shows how payments are processed by the Create Payment Instructions program, which places payments with the same payment process profile in the same payment instruction.
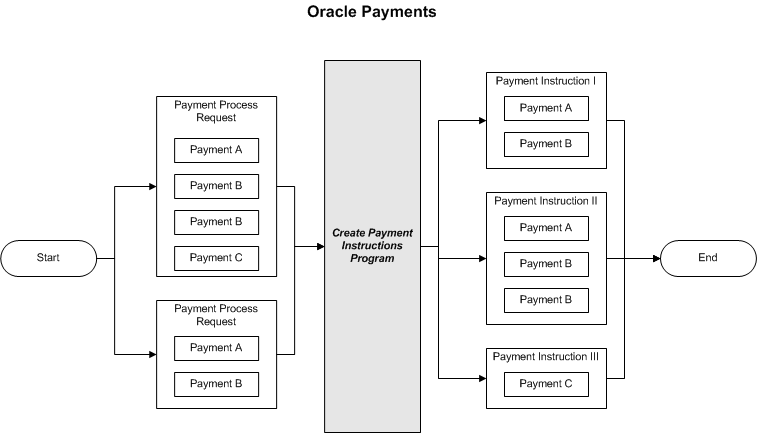
Understanding Payment Instructions
A payment instruction contains one or more payments, along with aggregate payment information, and is created by running the Create Payment Instructions program. Depending on your setup, a payment instruction can be converted into a payment file to be printed onto payment documents, such as checks, or into a payment file that is transmitted to a payment system or financial institution for further processing and disbursement. To see the relationship between payment instructions and payments, see the figure entitled Processing Payments.
Each payment instruction that is electronically transmitted to a payment system or financial institution is associated with a payment file. This payment file contains data that instructs the payment system or financial institution how to make the payment. The following information is typically included in electronically transmitted payment files:
-
number of payments to be made
-
amount of each payment
-
first party payer and third party payee bank account information
-
name of payees
When the Payment Instruction amount exceeds the maximum amount mentioned in the Payment Process Profile setup, multiple payment instructions are created and the payments does not stop.
The payment instructions are generated based on payment instruction creation rules. Different payment instructions are created when payments have different values for a grouping parameter.
The logical reference ID should be unique and it should not repeat in same payment instruction nor in another payment instruction, even with a different payment reference number and amount.
Understanding Payment Process Requests
A payment process request is a request created by a source product for Oracle Payments payment services. The payment process request, which originates in the source product during the documents payable selection process, contains one or more documents payable to be paid, along with information that allows Oracle Payments and the source product to identify the request and optional payment processing instructions. The source product may submit payment process requests to Oracle Payments via user action or concurrent program.
Once the payment process request is submitted to Oracle Payments, the Build Payments program validates the documents payable, groups the documents payable into payments according to document attributes and payment process profile grouping rules, and then validates the payments. Only documents payable that have the same payment process profile, payment method, and payment format can be grouped into the same payment.
Understanding the Payment Process
The Payment Process starts when a source product, such as Payables, needs to pay documents payable, such as invoices. The source product user groups the documents payable into a payment process request and submits the request to Oracle Payments. Within Oracle Payments, the Build Payments program takes the submitted documents payable, validates them, groups them into payments, and then validates the payments. Each payment consists of one or more documents payable. Next, the Create Payment Instructions program groups the payments into payment instructions, and then validates the payment instructions. Each payment represents a check that will be printed or a single electronic funds transfer transaction, depending on the type of processing selected. Each payment instruction results in one payment file that contains pertinent information on one or more payments, such as payment amount and an account to be credited or debited. In the case of electronic payments, the payment file includes the payment instructions in a format required by the financial institution. To actually make payments, you print checks or electronically transmit the payment instruction to an external payment system or to a financial institution.
The figure below depicts the high-level Payment Process.