| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
man pages section 1: User Commands Oracle Solaris 11.1 Information Library |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
man pages section 1: User Commands Oracle Solaris 11.1 Information Library |
- typeset mathematics test
eqn [-d xy] [ -f n] [-p n] [ -s n] [file]...
neqn [file]...
checkeq [file]...
eqn and neqn are language processors to assist in describing equations. eqn is a preprocessor for troff(1) and is intended for devices that can print troff's output. neqn is a preprocessor for nroff(1) and is intended for use with terminals. Usage is almost always:
example% eqn file ... | troff example% neqn file ... | nroff
If no files are specified, eqn and neqn read from the standard input. A line beginning with .EQ marks the start of an equation. The end of an equation is marked by a line beginning with .EN. Neither of these lines is altered, so they may be defined in macro packages to get centering, numbering, and so on. It is also possible to set two characters as ``delimiters''; subsequent text between delimiters is also treated as eqn input.
checkeq reports missing or unbalanced delimiters and .EQ/.EN pairs.
The following options are supported:
Sets equation delimiters set to characters x and y with the command-line argument. The more common way to do this is with delim xy between .EQ and .EN. The left and right delimiters may be identical. Delimiters are turned off by delim off appearing in the text. All text that is neither between delimiters nor between .EQ and .EN is passed through untouched.
Changes font to n globally in the document. The font can also be changed globally in the body of the document by using the gfont n directive, where n is the font specification.
Reduces subscripts and superscripts by n point sizes from the previous size. In the absence of the -p option, subscripts and superscripts are reduced by 3 point sizes from the previous size.
Changes point size to n globally in the document. The point size can also be changed globally in the body of the document by using the gsize n directive, where n is the point size.
The following operands are supported:
The nroff or troff file processed by eqn or neqn.
The nroff version of this description depicts the output of neqn to the terminal screen exactly as neqn is able to display it. To see an accurate depiction of the output, view the printed version of this page.
Tokens within eqn are separated by braces, double quotes, tildes, circumflexes, SPACE, TAB, or NEWLINE characters. Braces { } are used for grouping. Generally speaking, anywhere a single character like x could appear, a complicated construction enclosed in braces may be used instead. A tilde (~) represents a full SPACE in the output; a circumflex (^) half as much.
These are produced with the keywords sub and sup.
makes ![]()
produces ![]()
gives ![]()
Fractions are made with over.
yields ![]()
These are made with sqrt
results in 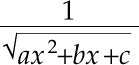
The keywords from and to introduce lower and upper limits on arbitrary things:
makes 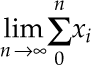
Left and right brackets, braces, and the like, of the right height are made with left and right.
produces ![Equation in the form [ x sup 2 + y sup 2 over alpha ] = 1 image: Equation in the form [ x sup 2 + y sup 2 over alpha ] = 1](figures/eqn_landr.1.png)
The right clause is optional. Legal characters after left and right are braces, brackets, bars, c and f for ceiling and floor, and "" for nothing at all (useful for a right-side-only bracket).
Vertical piles of things are made with pile, lpile, cpile, and rpile.
produces ![]()
There can be an arbitrary number of elements in a pile. lpile left-justifies, pile and cpile center, with different vertical spacing, and rpile right justifies.
Matrices are made with matrix.
produces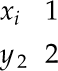
In addition, there is rcol for a right-justified column.
Diacritical marks are made with dot, dotdot, hat, tilde, bar, vec, dyad, and under.
is ![]()
is ![]()
is ![]()
Sizes and font can be changed with size n or size ±n, roman, italic, bold, and font n. Size and fonts can be changed globally in a document by gsize n and gfont n, or by the command-line arguments -sn and -fn.
Successive display arguments can be lined up. Place mark before the desired lineup point in the first equation; place lineup at the place that is to line up vertically in subsequent equations.
Shorthands may be defined or existing keywords redefined with define:
Defines a new token called thing which will be replaced by replacement whenever it appears thereafter. The % may be any character that does not occur in replacement.
Keywords like sum int inf and shorthands like >= → and != are recognized.
Greek letters are spelled out in the desired case, as in alpha or GAMMA.
Mathematical words like sin, cos, and log are made Roman automatically.
troff(1) four-character escapes like \(bu (·) can be used anywhere. Strings enclosed in double quotes ". . ." are passed through untouched; this permits keywords to be entered as text, and can be used to communicate with troff when all else fails.
See attributes(5) for descriptions of the following attributes:
|
nroff(1), tbl(1), troff(1), attributes(5), ms(5)
To embolden characters such as digits and parentheses, it is necessary to quote them, as in `bold "12.3"'.