Oracle® Enterprise Manager Ops Center
Enabling and Testing Auto Service Request
12c Release 2 (12.2.2.0.0)
E57472-01
December 2014
This guide provides an end-to-end example for how to use Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center.
Introduction to Auto Service Request
This guide explains how to enable and test the Auto Service Request (ASR) feature.
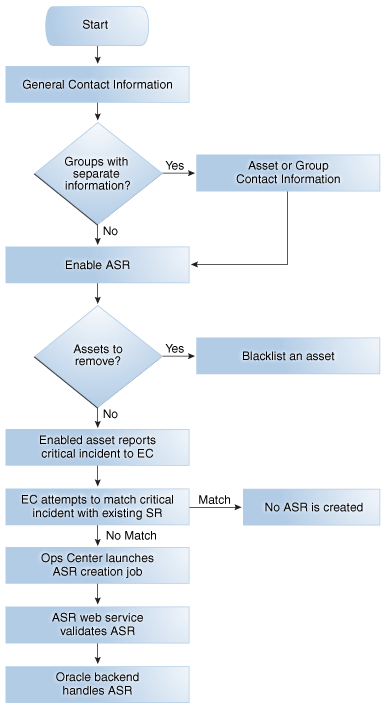
The Auto Service Request (ASR) feature files service requests automatically based on qualified incidents in Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center. You can provide contact information for your environment and enable ASR, then use a test fault to verify that ASR is working correctly.
The Overview of ASR section explains how ASR works and explains the processes involved in creating and enabling ASR.
As part of enabling and testing Auto Service Request, you will complete the following tasks:
-
Providing Contact Information: Providing contact information gives Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center the necessary information to create new Auto Service Requests.
-
Enabling ASR: Enabling ASR activates qualified assets for ASR and enables the creation of Auto Service Requests.
-
Testing ASR: Testing ASR using a test fault lets you verify that ASR is working correctly.
See Related Articles and Resources for links to related information and articles about ASR and service requests.
What You Will Need
You will need the following:
-
A configured Enterprise Controller in Connected Mode
-
Access to the Enterprise Controller system
-
A user with the Ops Center Admin role
-
A valid My Oracle Support (MOS) account, associated with a Customer Service Identifier (CSI)
-
A managed ILOM hardware asset
Overview of ASR
Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center can use ASR to generate service requests based on known issues. The data from an incident in Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center and the asset's contact information are used to create the service request.
Prerequisites
You must provide contact information for your assets and enable this feature before service requests can be generated using ASR.
An ASR can only be generated for an asset if a set of valid My Oracle Support (MOS) credentials have been provided. The asset must be present in MOS, and the credentials must be associated with a Customer Service Identifier (CSI) with rights over the asset. The CSI must be a direct CSI. Service Request Creation rights are required to create new service requests, and Admin rights are required if the contact information for the asset must be updated.
Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center's ability to create an ASR is also limited by the available credentials. Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center can only monitor an asset for ASR telemetry using the management credentials for the asset. To ensure full coverage for your hardware, provide management credentials for all applicable protocols for each OS and hardware asset. See the Asset Management chapter of the Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center Feature Reference Guide for more information about adding credentials, and see http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E37710_01/nav/faultcoverage.htm for more information about the telemetry used by ASR.
How ASR Activation Works
After ASR creation is enabled, Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center launches a daily job to activate assets for ASR, and attempts to activate all assets when they are discovered. The asset activation job is also run whenever the Enterprise Controller is restarted. You can view the details of this job to see what assets have been activated. You can also view an asset's ASR status. If you do not want an asset to be enabled for ASR creation, you can add the serial number of that asset to a blacklist.
Note:
Blade chassis can be enabled for ASR, but individual blades cannot be enabled for ASR.When an asset is activated for ASR, Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center monitors the asset for faults, using either an Agent Controller if one is installed or the asset's Proxy Controller if no Agent Controller is installed. This monitoring is performed automatically, and does not create a job.
To detect faults, Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center uses the ILOM and FMA telemetry sources as well as HALRT faults from Exadata systems. It collects SNMP traps from hardware assets and uses SNMP to monitor switch and PDU assets. It can process SNMP V1 and V2 fault alerts, but it can only process SNMP V1 sensor alerts, and it does not check the SNMP community string. It also gathers faults from ILOM using IPMI and SSH to detect faults that occurred before the asset was activated.
Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center sends a daily heartbeat event to Oracle for each asset that is enabled for ASR. If this heartbeat is not received, this is reflected for the asset in MOS. The status of this asset is changed to "Active — No Heartbeat" with a date when a heartbeat was last received listed in MOS. The next time a heartbeat is received, the asset's status is changed to the standard ASR status of "Active".
Note:
Some assets, such as Solaris 11 and Sun ZFS Storage Appliances, include embedded ASR support. You can choose to enable these assets for ASR directly, or to enable ASR through Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center. See the Storage Libraries chapter of the Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center Feature Reference Guide for more information.How ASR Creation Works
When a fault occurs on an activated asset, Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center first checks to see if the fault matches an existing incident. If not, a new incident is created, a job is run to create a new ASR, and an annotation is added to the incident indicating the ASR creation attempt. The creation job sends the ASR to the ASR web service for validation. When the ASR is validated, it is sent to Oracle.
When the ASR creation is successful, another annotation is added, indicating that the ASR was successfully created and providing a URL for the ASR. Once it is created, an ASR is identical to other service requests and can be viewed and managed using the same processes and tools.
Note:
If you create a manual service request for an incident that has already generated an ASR, the duplicate service request is not automatically removed.For more information about the assets that can be activated for ASR and the incidents that can create an ASR, see the ASR documentation at http://www.oracle.com/asr.
Providing Contact Information
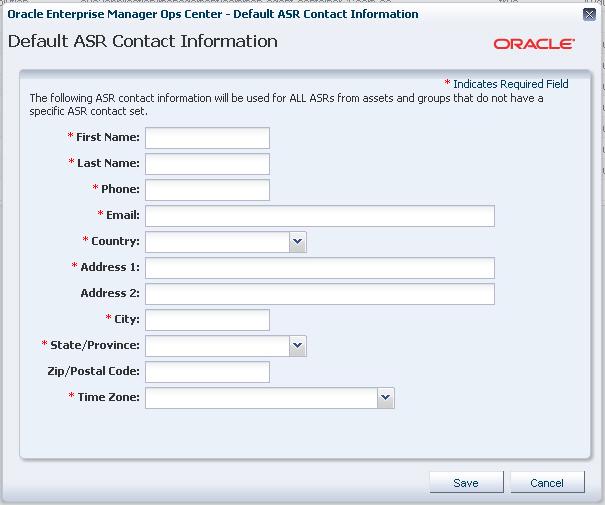
Default contact information is used for assets without asset-specific contact information. This contact information is used to create the ASR with the location of the asset. It must be provided before ASR can be enabled.
If an asset has one set of contact information in the My Oracle Support interface and a separate set in Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center, the MOS set is used in the ASR. If MOS has no contact information for the asset, the contact information provided in Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center is used.
-
Click the Enterprise Controller in the Administration section of the Navigation pane.
-
Click Edit ASR Default Contact in the Actions pane.
The Default ASR Contact Information page is displayed.
-
Enter the contact information:
-
First name
-
Last name
-
Phone
-
Email
-
Country
-
Address: Two address fields are provided, but only the first is required.
-
City
-
State or Province
-
(Optional) Zip or Postal Code
-
Time Zone
-
-
Click Save.
Enabling ASR
When ASR is enabled, service requests are automatically generated for your assets when a qualified incident occurs.
-
Click the Enterprise Controller in the Administration section of the Navigation pane.
-
Click Enable ASR.
A confirmation window is displayed.
-
Click OK.
Auto Service Requests are enabled.
Testing ASR
You can create a test fault on a managed asset to verify that ASR is working correctly.
-
Log in to a managed ILOM asset using the web console.
-
Navigate to Notification in the Administration section of the UI.
-
Add or edit a test rule to include an SNMP test trap, then test this new rule.
-
Log in to the Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center UI.
-
Click the Incidents section and verify that an incident for the test trap is displayed.
-
Click the Jobs section and verify that an ASR creation job has been created.
Related Articles and Resources
See the Auto Service Requests chapter in the Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center Administration Guide for more information about enabling and using ASR.
See the Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center Feature Reference Guide for information about viewing service requests.
See the Using Service Requests Guide for more information about using service requests.
These documents are available in the Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center Documentation Library at http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E40871_01/index.htm.
Documentation Accessibility
For information about Oracle's commitment to accessibility, visit the Oracle Accessibility Program website at http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=docacc.
Oracle customers that have purchased support have access to electronic support through My Oracle Support. For information, visit http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=info or visit http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=trs if you are hearing impaired.
Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center Enabling and Testing Auto Service Request, 12c Release 2 (12.2.2.0.0)
E57472-01
Copyright © 2007, 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
This software and related documentation are provided under a license agreement containing restrictions on use and disclosure and are protected by intellectual property laws. Except as expressly permitted in your license agreement or allowed by law, you may not use, copy, reproduce, translate, broadcast, modify, license, transmit, distribute, exhibit, perform, publish, or display any part, in any form, or by any means. Reverse engineering, disassembly, or decompilation of this software, unless required by law for interoperability, is prohibited.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice and is not warranted to be error-free. If you find any errors, please report them to us in writing.
If this is software or related documentation that is delivered to the U.S. Government or anyone licensing it on behalf of the U.S. Government, then the following notice is applicable:
U.S. GOVERNMENT END USERS: Oracle programs, including any operating system, integrated software, any programs installed on the hardware, and/or documentation, delivered to U.S. Government end users are "commercial computer software" pursuant to the applicable Federal Acquisition Regulation and agency-specific supplemental regulations. As such, use, duplication, disclosure, modification, and adaptation of the programs, including any operating system, integrated software, any programs installed on the hardware, and/or documentation, shall be subject to license terms and license restrictions applicable to the programs. No other rights are granted to the U.S. Government.
This software or hardware is developed for general use in a variety of information management applications. It is not developed or intended for use in any inherently dangerous applications, including applications that may create a risk of personal injury. If you use this software or hardware in dangerous applications, then you shall be responsible to take all appropriate fail-safe, backup, redundancy, and other measures to ensure its safe use. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates disclaim any liability for any damages caused by use of this software or hardware in dangerous applications.
Oracle and Java are registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Intel and Intel Xeon are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation. All SPARC trademarks are used under license and are trademarks or registered trademarks of SPARC International, Inc. AMD, Opteron, the AMD logo, and the AMD Opteron logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices. UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
This software or hardware and documentation may provide access to or information about content, products, and services from third parties. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates are not responsible for and expressly disclaim all warranties of any kind with respect to third-party content, products, and services unless otherwise set forth in an applicable agreement between you and Oracle. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates will not be responsible for any loss, costs, or damages incurred due to your access to or use of third-party content, products, or services, except as set forth in an applicable agreement between you and Oracle.