A.3 Configuring High Availability for Oracle Enterprise Scheduler
In order to enable a highly available environment, it is recommended to run Oracle Enterprise Scheduler in a cluster of at least two nodes.
This section includes the following topics:
A.3.1 Oracle Enterprise Scheduler Configuration and Deployment Artifacts
Configuration files are as follows:
ess.xml: This file is part of the Oracle Enterprise Scheduler EAR file deployed to the Oracle Enterprise Scheduler cluster.
MDS repository: The Oracle Metadata repository stores Oracle Enterprise Scheduler job metadata. Oracle Enterprise Scheduler supports both database and file-based MDS repositories.
Deployment artifacts are as follows:
J2EE application for core run-time and hosting applications.
Job metadata within Oracle MDS for core runtime and jobs loaded at startup.
The Oracle WebLogic Server deployment is non-staged.
A.3.2 Oracle Enterprise Scheduler Logging
Use standard Oracle WebLogic Server logging for an Oracle Enterprise Scheduler cluster. Use logs in Oracle WebCenter Content to examine Oracle Enterprise Scheduler behavior. Oracle Enterprise Scheduler logging is configured by default in Oracle WebLogic Server.
The default location for log files for Oracle Enterprise Scheduler process jobs on UNIX servers is /tmp/ess/requestFileDirectory. Oracle Enterprise Scheduler operational log files can be found under <DOMAIN_HOME>/servers/<SERVER_HOME>/logs/<server name>-diagnostic.log, and <MW_HOME>\user_projects\domains\<DOMAIN_HOME>\servers\<SERVER_HOME>\logs\<server name>-diagnostic.log on Windows.
A.3.3 Oracle Enterprise Scheduler Cluster Architecture
Figure A-5 is an architectural diagram of a two node Oracle Enterprise Scheduler cluster.
Figure A-5 Oracle Enterprise Scheduler Two Node Cluster
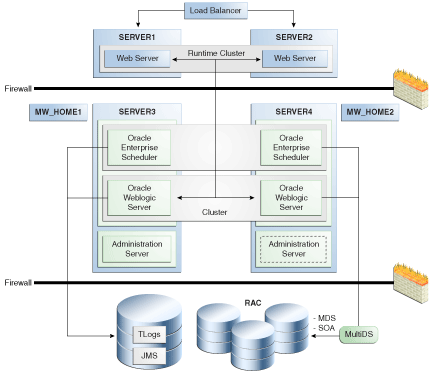
Description of "Figure A-5 Oracle Enterprise Scheduler Two Node Cluster"
This configuration includes the following components:
Hardware load balancer.
A cluster of Oracle WebLogic Servers running on two servers.
Two Oracle Fusion Middleware homes running on two servers.
A two node cluster of Oracle Enterprise Scheduler instances, each running on a different instance of Oracle Fusion Middleware.
A cluster of Oracle RAC databases with multi-DS configuration is required for availability of run-time and MDS schemas. Multi-DS and Oracle RAC provide for database failure.
Shared persistence storage
An HTTP load balancer is required for web service interactions. The HTTP load balancer must be appropriately configured to balance requests to Oracle Enterprise Scheduler web services. Oracle Enterprise Scheduler includes the following web services at the specified URLs:
ESSWebService
http://essHost:essPort/ess/esswebserviceESSAsyncCallback webservice
http://essHost:essPort/ess-async/essasynccallbackWebServiceJobCallback
http://essHost:essPort/ess-wsjob/async/callback
For more information regarding high availability architectures, see “Configuring High Availability for Oracle Fusion Middleware SOA Suite" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware High Availability Guide.
A.3.4 Configuring the Oracle Enterprise Scheduler Front End Host and Port
For enterprise deployment, Oracle Fusion Applications have removed frontend host.port settings and added a checklist to all middleware components so that they do not rely on using the frontend host.port. To enable this EDG requirement, ESSAPP supports explicit configuration for the frontend host and port for its web services.
A.3.4.1 Configuring the ESSAPP Frontend Host and Port
ESSAPP support the following two new configuration properties:
ServerURLThe value of this property value is a string with the following format:
http://host:portIt is used at runtime to determine the
ESSWebServiceend point address and is published as part of theESSWebServiceconcrete WSDL.CallbackServerURLThe value of this property is a string with the following format:
http://host:portIt is used at runtime to determine the end point address of Oracle Enterprise Scheduler callback web services (including
EssAsyncCallbackService, andEssWsJobAsyncCallbackService). These end point addresses are published as part of the respective WSDLs.
If these ESSAPP properties are not configured, then ESSAPP looks up the frontend host and port configuration at runtime by querying the Oracle WebLogic Server cluster. If this cluster's frontend host and port is also not configured, it uses the local ess_server host name and port.
ESSAPP advertises the WSDL URLs for its web services (computed using the above preference order) under its home page at: http://essHost:essPort/ess.
It is recommended that Oracle Enterprise Scheduler HA/Cluster administrators configure the ServerURL and CallbackServerURL properties in ESSAPP as explained in this section. The configuration of the cluster frontend host and port described in Death Detection and Restart can be done as a second preference with lower priority.
It is recommended that end users of Oracle Enterprise Scheduler web services look up the advertised WSDL URLs for individual Oracle Enterprise Scheduler web services and use them to access Oracle Enterprise Scheduler web services.
A.3.4.2 Configuring the WebLogic Server Cluster Frontend Host and Port
For an Oracle Enterprise Scheduler cluster setup involving two or more Oracle Enterprise Scheduler instances, you must configure the cluster front end host and port in the WebLogic Server Administration Console, as follows:
- Log in to the WebLogic Server Administration Console, click on the Clusters link and select the Oracle Enterprise Scheduler cluster (for example, ess_cluster) on the Summary of Clusters page.
- On the Settings for ess_cluster page, click on the Configuration tab. On the General sub-tab, fill in the Configure Cluster Address field with the host and port addresses of the Oracle Enterprise Scheduler instances (for example,
ess_server1_host:port,ess_server2_host:port, and so on). - Click on the HTTP sub-tab and configure the Frontend Host, Frontend HTTP Port and Frontend HTTPS Port with the Oracle HTTP Server details.
- Click on the Servers sub-tab and verify that the Server Name Prefix and Oracle Enterprise Scheduler instances are configured.
A.3.5 Failover Requirements
An HTTP load balancer provides load balancing so as to re-route requests in the event of node failure. There are no time out requirements for the load balancer or firewalls, as long as components use persistent connections. Likewise, session state replication and failover are not required.
Load balancing is used for actions such as submitting a job and querying its status using the Oracle Enterprise Scheduler web service interface. This load balancing occurs independently of where the job is scheduled to execute.
As Oracle Enterprise Scheduler does not use JMS, no JMS failover is required. For a remote EJB invocation to an ESS cluster, server affinity must be enabled. The property weblogic.jndi.enableServerAffinity must be set to true in the context. If oracle.as.scheduler.request.RemoteConnector is used, server affinity is set automatically.
This section contains the following topics:
A.3.5.1 Request Processor Failover
Oracle Enterprise Scheduler includes a request processor component, which represents a single Managed Server in the Oracle Enterprise Scheduler cluster. Request processors process job requests, such that job execution is connected to one or more request processors.
If all jobs are targeted at a number of request processors, jobs are not dependent on a particular request processor. If a job is targeted at a particular request processor, any jobs tied to that request processor execute only when the Managed Server is available and an active workshift exists for the job.
A.3.5.2 External Component Failover
Oracle Enterprise Scheduler interacts with Oracle Fusion Middleware and other components such as Oracle SOA Suite, Oracle ADF Business Components, and so on. If one of these external components fail, it is possible that any running jobs may fail.
You can prevent external component failure from affecting jobs using proper configuration. Table A-1 lists the external components that may fail, along with the steps to take to prevent failed Oracle Enterprise Scheduler jobs.
Table A-1 Oracle Enterprise Scheduler External Component Failover
| External Component | Steps to Prevent Failure |
|---|---|
Oracle WebCenter Portal |
Integrate with a cluster of Oracle WebCenter Portal service through a load balancer. |
Oracle RAC Database |
Use multi-DS for Oracle RAC database integration. |
Oracle SOA Suite, Oracle ADF, and so on |
Configure retries for jobs that depend on these components. |
A.3.6 Scalability
Horizontal scalability—adding Managed Servers on different machines—tends to enable better performance than vertical scalability—(adding Managed Servers on the same machine.
Use standard Oracle WebLogic Server cluster scaling methodologies for horizontal scaling. For more information about Oracle WebLogic Server clustering, see the “High Availability for WebLogic Server" chapter in the Oracle Fusion Middleware High Availability Guide. You can increase the concurrent processing of jobs within a work assignment by increasing the thread allocation of the request processor (by editing the workshift for the request processor) or by binding the work assignment to more than one request processor. For more information, see Creating or Editing a Workshift and Creating or Editing a Work Assignment.
A.3.7 Backup and Recovery
Following are the backup and recovery guidelines for various components:
Components stored on the file system: Product binaries, deployed application EAR files and standard Oracle WebLogic Server files in the domain root.
Changes to the file system: The file system artifacts change when new EAR files are deployed or when the product is patched.
Data stored in the database: The database stores all metadata and run-time data.
Changes to database artifacts: Metadata changes when metadata is created and deployed from Oracle JDeveloper or Fusion Middleware Control. Runtime data changes when jobs are submitted, undergo state changes, and so on.
There is no consistency requirement between the artifacts stored on the file system and those in database. The file system stores EAR files and temporarily stores scheduled job output and log files.