23 Monitoring Human Workflow Service Components and Engines
This chapter includes the following topics:
For more information, see the following sections
23.1 Monitoring Human Workflow Service Engine Active Requests and Operation Performance Statistics
You can view details about active requests in the human workflow service engine and operational statistics. such as service used, operations performed, and active and completed requests.
To monitor human workflow service engine active requests and operation statistics:
-
Access this page through one of the following options:
From the SOA Infrastructure Menu... From the SOA Folder in the Navigator... -
Select Service Engines > Human Workflow.
-
Right-click soa-infra.
-
Select Service Engines > Human Workflow.
-
-
Click Statistics.
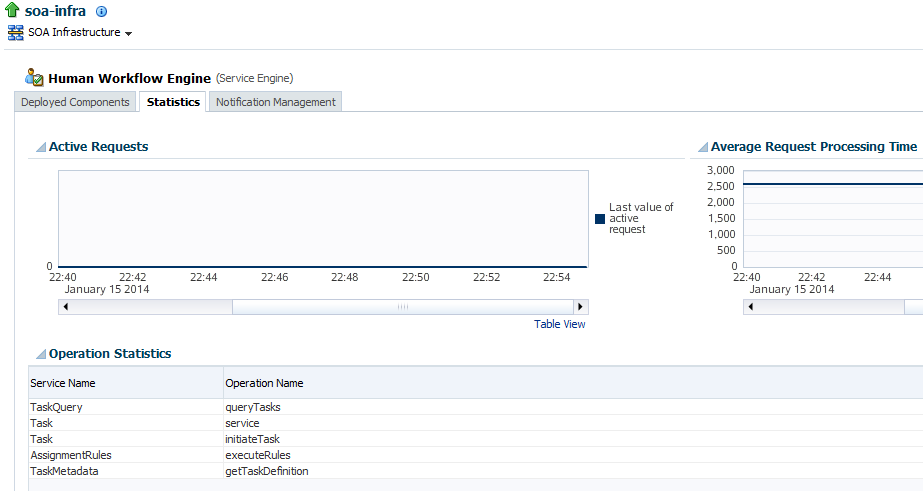
The Statistics page displays the following details.
-
Active requests in the service engine. Use this graph to get an idea of the current service engine load. Only under extreme load conditions is there data shown in the graph. This is because most requests are processed instantaneously by the service engine. The data is collected by a Dynamic Monitoring Service (DMS) state sensor. After the requests are processed by the service engine, the count goes to zero. This action enables you to know the current load on the service engine (for example, if it is too high).
-
Average request message processing time in the service engine since the last startup of the SOA Infrastructure. Use this graph to check service engine performance. While the processing time is calculated based on the last startup of the SOA Infrastructure, the data that is displayed in the graph is gathered only from the time at which you first accessed this page. The graph does not continue calculating and displaying data if you have not accessed this page. The DMS phase event sensor calculates the average request processing time and provides the processing time data.
-
Operation statistics about human workflow services used in the service engine, including the human workflow service used, the operation performed by the service, the number of active and completed requests, the count, and the average processing time.
-
Users with the highest backlog provides a snapshot of the workload assigned to various users, groups, or roles. Using this table you can identify assignees with a large number of pending human workflow service tasks as well as the average time it takes for each assignee to complete their tasks.
For more information, see the following documentation:
-
Developing SOA Applications with Oracle SOA Suite for details about human workflow services and operations
-
Tuning Performance for more details about human workflow tuning and performance properties
-
23.2 Monitoring Deployed Human Workflows in the Service Engine
You can monitor all deployed SOA composite applications with human workflow service components running in the service engine.
To monitor deployed human workflows in service engines:
-
Access this page through one of the following options:
From the SOA Infrastructure Menu... From the SOA Folder in the Navigator... -
Select Service Engines > Human Workflow.
-
Right-click soa-infra.
-
Select Service Engines > Human Workflow.
-
-
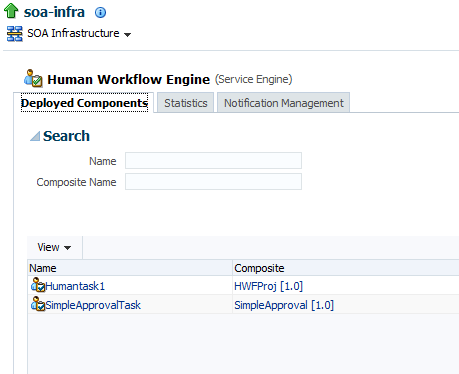
The Deployed Components tab is displayed.
The Deployed Components page displays the following details:
-
A utility for searching for a specific deployed SOA composite application by specifying the full name and clicking Search.
-
Details about deployed human workflow service components running in this service engine, including the service component name, the SOA composite application, the current status, and the number of total, faulted, and running instances.
-
-
In the Name column, click a specific service component to access its home page.
-
In the Composite column, click a specific SOA composite application to access its home page.