27 Monitoring Instance Message Data With Oracle BAM
This chapter provides end-to-end instructions for setting up Oracle B2B instance message monitoring with Oracle BAM.
The Oracle B2B-BAM integration does not work with Oracle XE database. It will work with Oracle 10g EE and Oracle 11g EE versions.
This chapter includes the following sections:
27.1 Introduction to Monitoring Oracle B2B with Oracle BAM
Oracle BAM provides a framework for creating dashboards that display real-time data inflow and creating rules to send alerts under specified conditions.
Oracle BAM can be configured to monitor an Oracle B2B instance by following the procedures in the remaining sections of this chapter.
Note:
While it is possible to create an Oracle BAM dashboard on an external data source defined on the instance message table, active data is not supported on external data sources, so the resulting report does not display real-time updates.
27.2 Creating a Data Source in Oracle WebLogic Server
You could use an existing data source if it exists or create a new data source.
Follow the steps below:
-
Open the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console and log in.
http://host_name:port_number/console
The
host_nameis the name of the machine where Oracle BAM is installed, and the defaultport_numberfor Oracle WebLogic Server is 7001. -
Select Data Sources in the JDBC section, and click New.
-
Configure the data source:
-
Enter a Name for the data source (for example,
BAMAQDataSource). -
Enter a JNDI name from the data source (for example,
jdbc/oracle/bamaq). This name is used to configure a foreign JMS server. -
Select Oracle for the Database Type.
-
Select Oracle's Driver (Thin) in the Database Driver field.
-
Click Next.
-
-
Uncheck Support Global Transaction, and click Next.
-
Enter your Database SID into the Database Name field (for example,
ORCL). -
Enter the host name of the machine where the database is installed as the HostName (for example,
localhost). -
Enter the database Port number (for example,
1521). -
Enter the Username and Password, and click Next.
-
Click Test Configuration.
-
after the test is successful, click Next.
-
Select the server where Oracle BAM is deployed, and click Finish.
27.3 Creating a Foreign JMS Server
Create a foreign JMS server to monitor messages sent to and from a BAM server.
To create a foreign JMS server:
-
Add an Oracle WebLogic Server JMS module.
-
In Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console, on the Home page navigate to the JMS Modules page.
-
Click New to create a new Oracle WebLogic Server JMS module.
-
Enter a name for the JMS module (for example,
BAMAQsystemModule), and click Next. -
Assign the target as the server where Oracle BAM is deployed, click Next, and click Finish.
Note:
It is recommended that you create a Subdeployment. Select JMS Module>SubDeployment>New. Use the subdeployment in the subsequent steps where you have the Subdeployment tab.
-
-
Target the Subdeployment to the JMS Server by selecting it from the list.
-
Add an AQ JMS Foreign Server to the JMS module.
-
Select the JMS module that was previously created.
-
Click New, and go to the list of JMS resources.
-
Select the Foreign Server option, and click Next.
-
Enter a Name for the Foreign Server (for example,
BAMAQForeignServer), and click Finish.
-
-
Configure the AQ JMS Foreign Server.
-
Select the AQ JMS Foreign Server that was previously created.
-
Enter
oracle.jms.AQjmsInitialContextFactoryin the JNDI Initial Context Factory field. -
Enter
datasource=data_source_jndi_locationin the JNDI Properties field, wheredata_source_jndi_locationis the JNDI location of your data source (for example,jdbc/oracle/bamaq). Typically, your Data Source should point to the Oracle B2BSOAINFRAschema. -
Check the Default Targeting Enabled check box.
-
-
Add Connection Factories to the AQ JMS Foreign Server.
-
Select the AQ JMS Foreign Server that was previously created.
-
Select the Connection Factories tab.
-
Enter a name for the connection factory. This is a logical name referenced by Oracle WebLogic Server.
-
Enter the local JNDI name that will be used by Oracle BAM Enterprise Message Source to look up this connection factory in the Local JNDI Name field (for example,
jms/BAMAQQueueCF). The JNDI name can be arbitrary as long as it matches the name of the created JMS queue. -
Enter
QueueConnectionFactoryin the Remote JNDI Name field.Note:
The following are the alternative options available. If you use this connection factory in a global transaction, select an XA-based connection factory, otherwise select a non-XA based connection factory.
-
QueueConnectionFactory
-
ConnectionFactory
-
XAQueueConnectionFactory
-
XATopicConnectionFactory
-
XAConnectionFactory
-
-
Click OK.
-
-
Add Destinations to the AQ JMS Foreign Server.
-
Select the AQ JMS Foreign Server that was previously created.
-
Select the Destinations tab
-
Enter a name for the destination. This is a logical name referenced by Oracle WebLogic Server. It is not related to the destination name.
-
Enter the local JNDI name that will be used by Oracle BAM Enterprise Message Source to look up the destination in the Local JNDI Name field (for example,
jms/BAMAQQueue). -
In the Remote JNDI Name field, enter
Queues/queue_nameif the destination is a queue, or enterTopics/topic_nameif the destination is a topic.For example, the default name for an AQ queue created for the Oracle B2B - Oracle BAM integration is
Queues/B2B_BAM_QUEUE. -
Click OK.
-
-
Create an Outbound Connection JNDI for Oracle BAM Enterprise Message Source
-
In the left pane of the Administration Console, click Deployments
-
On the Summary of Deployments page, expand BamServer > BeamAdapter.rar. Click BeamAdapter.rar.
-
On the Settings for BeamAdapter page, click Configuration > Outbound Connection Pools, and then click New.
-
Select oracle.tip.adapter.jms.IJmsConnectionFactory, and then click Next.
-
In the JNDI Name field, enter a name that will be used by Oracle BAM Enterprise Message Source. For example, eis/bam/b2bconnection
Message element name must be always “<row>", Type the parent element that contains column values in either its sub-elements or attributes.
To configure Source Value Formatting, check the DateTime Specification check box and click the hyper link specified below the check box.
-
Click Finish.
-
On the Save Deployment Plan Assistant page, click OK
-
-
Add JNDI name to Oracle BAM Enterprise Message Source.
-
On the Settings for BeamAdapter page, click Configuration > Outbound Connection Pools.
-
Expand oracle.tip.adapter.jms.IJmsConnectionFactory and then select the JNDI name that you created in step 7.
-
In the Outbound Connection Properties table, search for Property Name - FactoryProperties and add "java.naming.factory.initial=weblogic.jndi.WLInitialContextFactory;java.naming.provider.url=t3://<host>:<port>;java.naming.security.principal=<user>;java.naming.security.credentials=<pwd>;" under the Property Value column, and then press Save.
-
-
Restart Oracle WebLogic Server and BAM managed server.
27.4 Create a B2B Data Object using Oracle BAM Composer
The BAM Composer can create configured to create B2B data objects.
To create a B2B data object:
For more information about creating Oracle BAM data objects, see "Creating and Managing Oracle BAM Data Objects" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Monitoring Business Activity with Oracle BAM.
27.5 Define a JMS Message Source Using an Oracle BAM Enterprise Message Source
An Oracle BAM Enterprise Message source can be used to define a JMS message source in Oracle B2B.
To define a JMS message source:
After starting the Enterprise Message Source, any messages that are inserted by the database job into the AQ JMS queue are instantly available in the B2BDO data object.
To view the contents of the B2BDO data object, expand Data Objects from the BAM Composer administrator page, and select the B2BDO object. Click Data tab to view the contents.
New rows are inserted into B2BDO as the database job reads incoming messages from the B2B instance table and inserts them onto the AQ JMS queue.
For more information on creating Oracle BAM Enterprise Message Sources, see "Creating Oracle BAM Enterprise Message Sources" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Monitoring Business Activity with Oracle BAM.
27.6 Mapping Oracle B2B Instance Messages to Oracle BAM Data Objects
Oracle B2B instance message fields can be used to design data objects and Enterprise Message Sources in Oracle BAM to monitor Oracle B2B performance in real time.
Table 27-3 lists the Oracle B2B instance message fields.
Note that the payloads (APP_PAYLOAD, PAYLOAD, WIREPAYLOAD) are not included in the list below. They are not transferred for performance reasons.
Table 27-3 Oracle B2B Instance Message Fields
| Field | Type |
|---|---|
|
ID |
NOT NULL VARCHAR2(256) |
|
REFERTOID |
VARCHAR2(256) |
|
B2BMESSAGEID |
NOT NULL VARCHAR2(256) |
|
ACKNOWLEDGEMODE |
VARCHAR2(256) |
|
MESSAGEDATETIME |
DATETIME |
|
MESSAGETYPE |
VARCHAR2(256) |
|
STATE |
VARCHAR2(256) |
|
REMAININGRETRY |
INT |
|
DIRECTION |
VARCHAR2(256) |
|
TIMETOACK |
VARCHAR2(256) |
|
TPA_NAME |
VARCHAR2(256) |
|
XPATH_EXPRESSION1 |
VARCHAR2(1024) |
|
XPATH_EXPRESSION2 |
VARCHAR2(1024) |
|
XPATH_EXPRESSION3 |
VARCHAR2(1024) |
|
XPATH_NAME1 |
VARCHAR2(256) |
|
XPATH_NAME2 |
VARCHAR2(256) |
|
XPATH_NAME3 |
VARCHAR2(256) |
|
XPATH_VALUE1 |
VARCHAR2(256) |
|
XPATH_VALUE2 |
VARCHAR2(256) |
|
XPATH_VALUE3 |
VARCHAR2(256) |
|
DOCUMENT_DEFINITION |
VARCHAR2(256) |
|
CREATED |
DATETIME |
|
MODIFIED |
DATETIME |
|
SEND_TIMESTAMP |
DATETIME |
|
RECEIVE_TIMESTAMP |
DATETIME |
|
NATIVE_MSG_SIZE |
INT |
|
TRANSLATED_MSG_SIZE |
INT |
|
BM_RESUBMIT_COUNT |
INT |
|
ERRORCODE |
VARCHAR2(256) |
|
ERRORTEXT |
VARCHAR2(1024) |
|
ERRORDESCRIPTION |
VARCHAR2(2000) |
|
PROCESSING_TIME |
INT |
|
DOCUMENTTYPE |
VARCHAR2(513) |
|
CORRELATIONID |
VARCHAR2(256) |
|
FABRIC_ECID |
VARCHAR2(512) |
|
FABRIC_COMPOSITE_NAME |
VARCHAR2(512) |
|
AM_RESUBMIT_COUNT |
INT |
|
TRANSACTIONCONTROLNUMBER |
VARCHAR2(256) |
|
GROUPCONTROLNUMBER |
VARCHAR2(256) |
|
INTERCHANGECONTROLNUMBER |
VARCHAR2(256) |
|
B2BWIREMESSAGEID |
VARCHAR2(256) |
|
B2BTIMESTAMP |
DATETIME |
|
CONVERSATIONID |
VARCHAR2(1024) |
|
PROTOCOLMESSAGEID |
VARCHAR2(1024) |
|
URL |
VARCHAR2(1024) |
|
TRANSPORTPROTOCOL |
VARCHAR2(513) |
|
TRANSPORTHEADERS |
VARCHAR2(2000) |
|
WM_RESUBMIT_COUNT |
INT |
|
DOCUMENTPROTOCOL |
VARCHAR2(513) |
|
EXCHANGEPROTOCOL |
VARCHAR2(513) |
|
AGREEMENTID |
VARCHAR2(256) |
|
SENDERNAME |
VARCHAR2(256) |
|
SENDERID |
VARCHAR2(513) |
|
RECEIVERNAME |
VARCHAR2(256) |
|
RECEIVERID |
VARCHAR2(513) |
27.7 Creating a Dashboard to Monitor Oracle B2B
Real-time monitoring dashboards are created using Oracle BAM Active Studio.
To create a dashboard to monitor Oracle B2B using the B2BDO data object, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Monitoring Business Activity with Oracle BAM, chapter 8 Creating Dashboards.
27.8 Enabling the Oracle BAM Integration in Oracle B2B
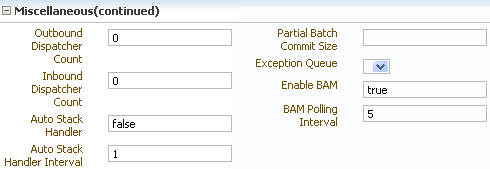
To enable the Oracle BAM integration in Oracle B2B, set properties in the Oracle B2B Administration > Configuration tab.
Enable BAM - Set to true. When b2b.enableBAM is set to true, the Oracle B2B user interface automatically starts the database job in the database to monitor new instances in the b2b_instancemessage view. When b2b.enableBAM is set to false, the user interface automatically removes the database job from the database.
BAM Polling Interval – the interval in minutes when the database job polls the Oracle B2B instance table for any updates and puts them on the AQ JMS queue for uptake by Oracle BAM. Values less than a minute can also be specified, for example, 0.5 minutes.
[also need to update bb_config.fm table with these parameters]