12 Creating and Maintaining the Presentation Layer
This chapter contains the following topics:
About the Presentation Layer
You can provide customized, secure, role-based views of a business model to users in the Presentation layer.
Role-based views provide object security and also provide a way to hide some of the complexity of the business model.
In the Presentation layer, you can set an implicit fact column. The primary function of the Presentation layer is to provide custom names, dictionary entries, organization, and security for different groups of users.
Presentation layer views are called subject areas. In previous versions, subject areas were called presentation catalogs. You can create a subject area that is identical to your business model, or you can create role-based subject areas that show a single subject or that supports a specific business role. Subject areas are not abstract views. You should create subject areas that organize your content in a way that benefits your users.
Subject areas in the Presentation layer appear as catalogs to client tools that use the Oracle BI Server as an ODBC data source. Subject areas contain presentation tables, columns, hierarchies, and levels.
Even though the Logical SQL requests from Answers and other clients query the presentation tables and columns, the logic for entities, relationships, and joins is in the Business Model and Mapping layer.
Creating and Customizing the Presentation Layer
After you have created the Business Model and Mapping layer, you can drag and drop entire business models to the Presentation layer in the Administration Tool to create subject areas.
You can create subject areas and other Presentation layer objects manually.
This section contains the following topics:
About Creating Subject Areas
There are several ways to create subject areas in the Presentation layer.
The recommended method is to drag and drop a business model from the Business Model and Mapping layer to the Presentation layer, and then modify the Presentation layer based on what you want users to see. You can move columns between presentation tables, remove columns that do not need to be seen by the users, or even present all of the data in a single presentation table. You can create presentation tables to organize and categorize measures in a way that makes sense to your users.
You can also duplicate an existing subject area and its corresponding business model. See Duplicating a Business Model and Subject Area.
Although each subject area must be populated with contents from a single business model, you can create multiple subject areas for one business model. For very large business models, you may want to do this to help users work with the content. Users in Oracle BI Server can create queries that span multiple subject areas, as long as the subject areas correspond to the same business model.
There are many ways to create multiple subject areas from a single business model. One method is to drag a particular business model to the Presentation layer multiple times, then edit the properties or objects of the resulting subject areas as needed.
For example, if you have a business model called ABC that contains the Geography and Products dimensions, you can drag it to the Presentation layer twice. Two subject areas are created, with the default names ABC and ABC#1. You can then edit the subject areas as follows:
-
Rename the
ABCsubject area toDEF, then delete theGeographypresentation hierarchy -
Rename the
ABC#1subject area toXYZ, then delete theProductspresentation hierarchy
Users in Oracle BI Server can run queries that span the DEF subject area containing the Products hierarchy, and the XYZ subject area containing the Geography hierarchy.
Note:
When you query a single subject area, all the columns exposed in that subject area are compatible with all the dimensions exposed in the same subject area. However, when you combine columns and dimensions from multiple subject areas, you must ensure that you do not include combinations of columns and dimensions that are incompatible with one another.
For example, a column in one subject area might not be dimensioned by Project. If columns from the Project dimension from another subject area are added to the request along with columns that are not dimensioned by Project, then the query might fail to return results, or cause the Oracle BI Server error, "No fact table exists at the requested level of detail: XXXX."
Automatically Creating Subject Areas Based on Logical Stars and Snowflakes
You can automatically create one subject area for each logical star or logical snowflake in your business model.
Logical stars and logical snowflakes are both composed of a centralized fact table connected to multiple dimension tables. This feature provides another way to create multiple subject areas from a single business model.
To create a subject area for each fact table that is part of a logical star or snowflake, right-click the business model and select Create Subject Areas for Logical Stars and Snowflakes. The new subject areas are automatically created, each containing a fact table and only the dimension tables with which it is associated. This option is available for any business model that contains logical stars or logical snowflakes.
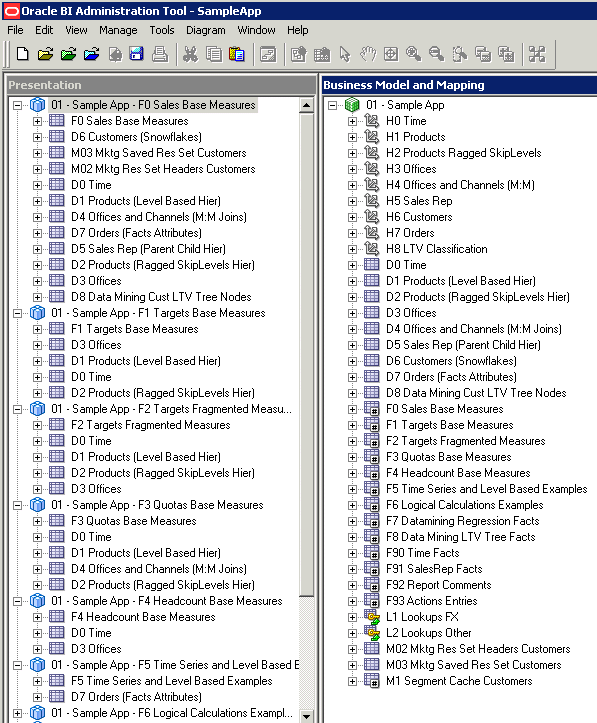
For example, if you choose this option for the SampleApp business model with nine fact tables, nine corresponding subject areas are created, each with one fact table and its associated dimension tables. Subject areas are also created for lookup tables. The image shows exactly how the logical fact tables and dimension tables are modeled in the Presentation layer.
About Removing Columns
One important reason to use a custom Presentation layer is to make the schema as easy to use and understand as possible.
Customize the presentation layer prevent users from seeing columns that provide no meaningful content.
The following columns are examples of columns that you might want to remove from the Presentation layer:
-
Key columns that have no business meaning.
-
Columns that users do not need to view, for example, codes, when text descriptions exist.
-
Columns that users are not authorized to read.
Renaming Presentation Columns to User-Friendly Names
You should try to keep presentation column names and their source logical column names synchronized to reduce maintenance.
By default, presentation columns have the same name as the corresponding logical column in the Business Model and Mapping layer.
To synchronize presentation column names and their source logical column names, select Use Logical Column Name in the Presentation Column dialog.
In some cases, however, you may want a different presentation column name to be shown to users. To do this, change the name of the presentation column in the Presentation Column dialog.
When you change the name of a presentation column, an alias is automatically created for the old name, so compatibility to the old name remains. See Creating Aliases (Synonyms) for Presentation Layer Objects.
Note:
You cannot rename a Presentation layer object to a name that is already in use as an alias for an object of the same type.
Exporting Logical Keys in the Subject Area
For each subject area in the Presentation layer, you can decide whether to export any logical keys as key columns to tools that access it.
Exporting logical keys is irrelevant to users of Oracle BI Presentation Services, but it may be advantageous for some query and reporting tools.
If you decide to export logical keys, make sure that the logical key columns exist in the table folders. In this situation, your business model should use logical key/foreign key joins.
When you select the option Export logical keys in the Subject Area dialog, any columns in the Presentation layer that are key columns in the Business Model and Mapping layer are listed as key columns to any ODBC client. This is the default selection. In most situations, this option should be selected.
Note:
If you are using a tool that issues parameterized SQL queries, such as Microsoft Access, do not select the option Export logical keys. This stops the tool from issuing parameterized queries.
Setting an Implicit Fact Column in the Subject Area
For each subject area in the Presentation layer, you can set an implicit fact column.
The implicit fact column is added to a query when it contains columns from two or more dimension tables and no measures.
The column is not visible in the results. It is used to specify a default join path between dimension tables when there are several possible alternatives or contexts.
If an implicit fact is not configured, Oracle BI Server uses any fact Logical Table Source (LTS) to answer dimension-only subrequest that contains multiple dimensional references but no fact reference.
The Oracle BI Server can also use any fact LTS, if the configured implicit fact column is not relevant to the dimensions that are joined. This could happen, for example, when implicit fact column is a level based measure at a level higher than the dimensional only subrequest.
Maintaining the Presentation Layer
There is no automatic way to synchronize all changes between the Business Model and Mapping layer and the Presentation layer.
For example, if you add logical columns to an existing logical table, or edit existing columns, you must manually update the corresponding Presentation layer objects.
However, the Administration Tool can automatically synchronize the name of presentation columns with their corresponding logical column names. To take advantage of this feature, ensure that Use Logical Column Name is selected in the Presentation Column dialog.
In some cases, if there are many changes to a logical table or even to an entire business model, it is easiest to delete the corresponding presentation table or subject area, and then and drag and drop the updated logical objects to the Presentation layer. For this reason, it is best to wait until the Business Model and Mapping layer is relatively stable before adding customizations in the Presentation layer.
Working with Subject Areas
In the Presentation layer, subject areas enable you to show different views of a business model to different sets of users.
Populate subject areas using the contents from a single business model. Subject areas cannot span business models.
Subject areas are created automatically by dragging and dropping business models from the logical layer.
See Setting Permissions for Presentation Layer Objects.
See Localizing Oracle Business Intelligence in System Administrator's Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition.
See Controlling Presentation Object Visibility and Creating Aliases (Synonyms) for Presentation Layer Objects.
Working with Presentation Tables and Columns
Learn how to customize presentation tables and columns in these topics.
Presentation tables and presentation columns appear as folders and columns in Oracle BI Answers. You can customize presentation tables and presentation columns to help users craft queries based on their business needs.
This section contains the following topics:
Creating and Managing Presentation Tables
You can use presentation tables to organize columns into categories that make sense to the user community.
A presentation table can contain columns from one or more logical tables. The names and object properties of the presentation tables are independent of the logical table properties. Presentation tables are created automatically by dragging and dropping logical tables from the logical layer. A presentation table cannot have the same name as its parent subject area. For example, you cannot have a subject area called Customer that has a Customer table within it.
Aliases are created automatically whenever presentation objects are renamed, so that any queries using the original name do not break. Use the Aliases tab to specify or delete aliases for this presentation table. See Creating Aliases (Synonyms) for Presentation Layer Objects.
For localization when creating presentation tables:
-
Use the Custom display name to dynamically display a name based on a session variable.
-
Use Custom description to dynamically display a custom description based on a session variable.
-
Use the Translation Key along with the custom display name to localize the user interface.
When you externalize strings in the Presentation layer and run the Externalize Strings utility, the results contain the session variable information and the translation key. See Localizing Business Intelligence in System Administrator's Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition .
Use the Child Presentation Tables tab to specify presentation tables that you want to show as nested folders in Oracle BI Answers and BI Composer. See Nesting Folders in and BI Composer and Controlling Presentation Object Visibility.
- In the Presentation layer, from a subject area, double-click a presentation table to open the Properties dialog.
- (Optional) In the Properties dialog for the presentation table, in the General tab, change the name for the presentation table.
- Leave the Hide object if field blank.
- (Optional) In the Columns tab, add, remove, edit, or reorder the presentation columns for the selected presentation table.
- In the Hierarchies tab, add, remove, edit, or reorder the presentation hierarchies for the selected presentation table.
- When you have completed your changes, click OK.
Reordering Presentation Layer Tables
Use this task to reorder a table or sort all tables in a subject area.
About Presentation Columns
Presentation columns provide business intelligence data for display in web clients.
You can create presentation columns by dragging and dropping logical columns from the Oracle BI Administration Tool Business Model and Mapping (logical) layer to the Presentation layer. New columns added to presentation tables cannot use the same name or alias same name of an existing column.
You can drag and drop a column from a single logical table in the Business Model and Mapping layer onto multiple presentation tables. For example, you can create several presentation tables that contain different classes of measures such as one containing volume measures, one containing share measures, and one containing measures from a year ago.
You must enable the Edit presentation names in the Administration Tool option before you can edit the presentation column's name. See Setting Administration Tool Options and Setting Permissions for Presentation Layer Objects.
You can use the Custom display name, Custom description, and Translation Key fields for localization purposes. When you externalize strings in the Presentation layer and run the Externalize Strings utility, the results contain the session variable information and the translation key. See Localizing Business Intelligence in System Administrator's Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition.
You can use the Custom display name and Custom description fields to propagate UI hints (labels and tooltips) from an ADF data source to display in Oracle BI Answers. See Propagating Labels and Tooltips from ADF Data Sources.
Aliases are created automatically whenever presentation objects are renamed, so that any queries using the original name do not break.
Changing the Presentation Column Name
The presentation column names, by default, are identical to the logical column names in the Business Model and Mapping layer. You can change the presentation column name.
- Open the Oracle BI Administration Tool.
- In the Presentation layer, double-click a presentation column to change.
- In the Presentation Column dialog, remove the check from the Use Logical Column Name field.
- Click Edit next to the Logical Column Name field.
- In the Logical Column dialog, in the Name field, type a new name to use for the Presentation Column.
- In the Logical Column dialog, implement other changes, and click OK.
- In the Presentation Column dialog, click Custom display name, and then click OK.
Reordering Presentation Columns
You can change the order of the columns in your presentation.
- Open the Oracle BI Administration Tool
- In the Presentation layer, right-click a presentation table and select Properties.
- Click the Columns tab.
- Select the column you want to reorder.
- Use drag-and-drop to reposition the column, or click the Up and Down buttons.
- Click OK.
Nesting Folders in Answers and BI Composer
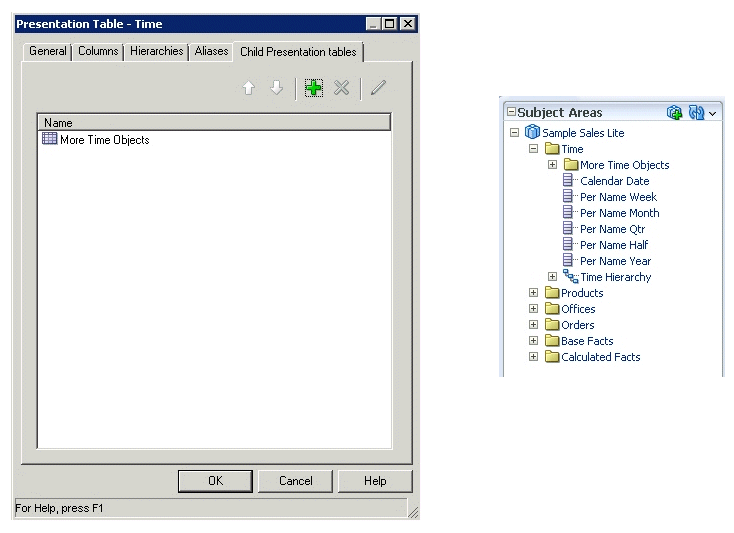
You can designate child presentation tables using the Child Presentation Tables tab in the Presentation Table dialog.
Designate child presentation tables to give the appearance of nested folders in Answers and BI Composer. You can add multiple layers of nesting using this method.
The image shows how a designated child presentation table appears nested in Answers.
The folders only appear nested, but they are not actually nested in drill-down, and the qualified names of the objects remain the same. The Presentation layer in the Administration Tool does not display the nesting; the nesting only appears in Answers and BI Composer. This feature only works for presentation tables, and not for other Presentation layer objects.
When you run a consistency check, the Consistency Check Manager detects any circularity in parent-child presentation table assignment. It also detects and reports project definitions that include child presentation tables without parent presentation tables.
If you previously used hyphens at the beginning of presentation table names or arrows at the beginning of presentation table descriptions to achieve nesting, you should run the Convert Presentation Folders utility to convert your metadata to the new structure. See Using the Convert Presentation Folders Utility.
Working with Presentation Hierarchies and Levels
Presentation hierarchies and presentation levels provide an explicit way to expose the multidimensional model in Oracle BI Answers.
When presentation hierarchies and levels are defined in the Presentation layer, roll-up information is displayed in the Oracle BI Answers navigation pane, providing users with important contextual information.
Members in a presentation hierarchy are not visible in the Presentation layer. You can see hierarchy members in Oracle BI Answers.
Users can create hierarchy-based queries using objects in presentation hierarchies and levels. Presentation hierarchies expose analytic functionality such as member selection, custom member groups, and asymmetric queries.
You can also provide localization information and apply fine-grained access control to presentation hierarchies and levels.
If you have a repository from a previous release, the presentation hierarchies do not appear in the Presentation layer automatically as part of the Oracle BI repository upgrade process. You must manually create the presentation hierarchies and levels objects by dragging logical dimensions from the Business Model and Mapping layer to the appropriate presentation tables.
This section contains the following topics:
Creating and Managing Presentation Hierarchies
To create a presentation hierarchy, you can drag a logical dimension hierarchy from the Business Model and Mapping layer to a table in the Presentation layer.
The presentation hierarchy object must be located within a presentation table, unlike in the Business Model and Mapping layer, where logical dimensions are peer objects of tables. Presentation hierarchies are also displayed within their associated tables in Oracle BI Answers, providing a conceptually simpler model.
If a logical dimension spans multiple logical tables in the Business Model and Mapping layer, it is a best practice to model the separate logical tables as a single presentation table in the Presentation layer.
There are several ways to create presentation hierarchies:
-
When you drag an entire business model to the Presentation layer, the presentation hierarchies and constituent levels appear automatically, along with other presentation objects.
-
When you drag a logical dimension table to the Presentation layer, presentation hierarchies and levels based on those dimensions are created automatically.
-
You can also drag individual logical dimensions to the appropriate presentation tables to create corresponding presentation hierarchies within those tables.
-
As with most other objects in the repository, you can right-click a presentation table, select New Object, and then select Presentation Hierarchy to manually define the object.
You can also drag an individual logical level from the Business Model and Mapping layer to a presentation table to create a presentation hierarchy that is a subset of the logical dimension hierarchy.
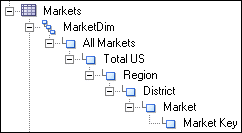
For example, suppose a logical dimension has the levels All Markets, Total US, Region, District, Market, and Market Key. Dragging and dropping the entire logical dimension to the corresponding presentation table appears as follows:
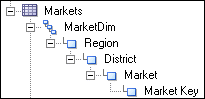
However, dragging and dropping the Region level to the same presentation table appears as follows:
Modeling Dimensions with Multiple Hierarchies in the Presentation Layer
For logical dimensions that contain multiple logical hierarchies, multiple separate presentation hierarchies are created.
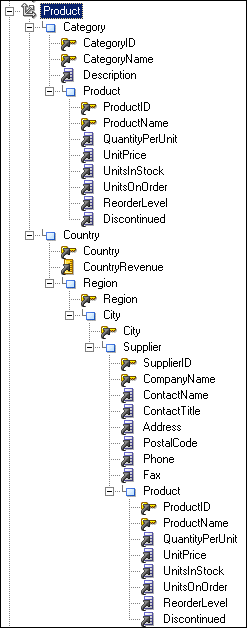
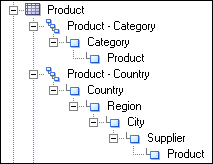
For example, the following logical dimension called Product contains the two hierarchies Category and Country:
In the Business Model and Mapping layer, this logical dimension is modeled as a single dimension object that contains multiple hierarchies. In contrast, the Presentation layer models this dimension as two separate objects: one that displays the drill path through the Category level, and another that shows the drill path through the Country level, as follows:
Editing Presentation Hierarchy Objects
Learn how to edit presentation hierarchy properties.
You can edit presentation hierarchy properties, including setting permissions to apply role-based access control, setting a custom display name for localization purposes, and changing the levels in a hierarchy.
The Display Columns tab is only available for parent-child hierarchies. Because parent-child hierarchies do not contain levels, display columns are defined for the presentation hierarchy object as a whole. Use the Display Columns tab to define which columns should be used for display for this parent-child hierarchy.
You can add, delete, or reorder display columns. You can also click the Edit button to edit properties for a particular column.
The Levels tab lists the levels within the hierarchy and their order. This tab is not available for parent-child hierarchies. You can add, delete, or reorder levels. You can also click the Edit button to edit properties for a particular level. See Creating and Managing Presentation Levels.
See Setting Permissions for Presentation Layer Objects.
Use the Aliases tab to specify or delete aliases for this presentation hierarchy. See Creating Aliases (Synonyms) for Presentation Layer Objects.
See Controlling Presentation Object Visibility and Localizing Oracle Business Intelligence in System Administrator's Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition .
Creating and Managing Presentation Levels
Presentation levels are typically created automatically when presentation hierarchies are created.
Presentation levels are displayed within hierarchical columns in Oracle BI Answers.
See the following:
-
Localizing Business Intelligence in System Administrator's Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition.
You must enable the Edit presentation names Administration Tool option before you can edit a presentation level's name.
Aliases are created automatically whenever presentation objects are renamed, so that any queries using the original name do not break.
The Logical Level field displays the name of the logical level for this presentation level.
The Custom display name and the Custom description options are used typically for localization purposes. When you externalize strings in the Presentation layer and run the Externalize Strings utility, the results contain the session variable information and translation key.
Specifying an expression in the Hide object if field has no effect on the visibility of presentation levels in the Subject Area Tree in Oracle BI Answers and BI Composer.
The Drill To Levels and Drill From Levels tabs, and the Generate Drill Graph are not currently used.
Use the Display Columns tab to define columns used for display for that level on drill-down. For example, if two columns called Name and ID at the same level, you can choose to display Name because it is the more user-friendly option. The display columns that appear by default when a presentation level is created are based on which key columns for the corresponding logical level have the Use for display option selected.
You can add, delete, or reorder display columns. You can also click the Edit button to edit properties for a particular column.
- In the Presentation layer, double-click a presentation level to display the Presentation level dialog.
- In the General tab, type a Name for the presentation level.
- Click Permissions to specify access to the presentation level by application roles and users.
- (Optional) Select Custom display name to dynamically display a name based on a session variable and to edit the Translation Key field.
- (Optional) Select Custom description to dynamically display a custom description based on a session variable.
- (Optional) Click Browse to select a different Logical Level.
- Drag a presentation column to the presentation level in the Presentation layer to automatically add the column as a display column for the presentation level.
- In the Aliases tab to specify or delete aliases for a presentation level.
Setting Permissions for Presentation Layer Objects
You can apply access control to restrict which individual users or application roles (groups) can access particular presentation layer objects.
For example, you can provide read-only access to a set of presentation tables for a particular application role, read-write access for a second application role, and no access for a third application role. See Granting Permissions To Users Using Groups and Application Roles .
You can also use the Identity Manager to set up privileges and permissions. The Identity Manager is useful for setting permissions for individual application roles to many objects at once, unlike permissions in the Presentation layer, which you can only set for one object at a time. See Setting Up Object Permissions and Applying Data Access Security to Repository Objects.
You can control what level of privilege is granted by default to the AuthenticatedUser application role, which is the default application role associated with new repository objects. To do this, set the DEFAULT_PRIVILEGES parameter in the NQSConfig.INI file.
To set permissions for presentation layer objects:
Generating a Permission Report for Presentation Layer Objects
You can generate a permission report for individual presentation layer objects to see a summary of how permissions have been applied for that object.
The Permission Report displays the name and a description of the presentation object, along with a list of users/application roles and their permissions.
- In the Oracle BI Administration Tool, open a repository in online or offline mode.
- In the Presentation layer, right-click an object and select Permission Report.
Sorting Columns in the Permissions Dialog
There are six ways that you can sort the types and User/Application Role names in the Permissions dialog.
To change the sort, click the heading of the first or second column. The first column has no heading and contains an icon that represents the type of user or application role. The second column contains the name of the User/Application Role object.
Note:
You cannot sort on the columns for individual object permissions such as Read, and Read/Write.
There are three ways to sort by type, and two ways to sort the list of user and application role names. This results in a total of six possible sort results (3 x 2 = 6). The following list shows the sort results available by clicking the type column:
-
AuthenticatedUser, Application Roles, Users, ascending by name of type
-
Users, Application Roles, AuthenticatedUser, descending by name of type
-
Type column is in no particular order. The Type value is ignored, as all names in User/Application Role column are sorted in ascending order by value in User/Application Role column.
The following list shows the sort results available by clicking the User/Application Role column:
-
Ascending within the type
-
Descending within the type
Creating Aliases (Synonyms) for Presentation Layer Objects
Each presentation object can have a list of aliases (synonyms) for its name that you can use in Logical SQL queries.
Use the Alias tab in the Properties dialog for the appropriate presentation object such as subject area, presentation table, presentation hierarchy, presentation level, or presentation column to create the list of aliases.
Because Presentation layer objects are often deleted and then re-created during the repository development process, it is best to wait until your logical business model is relatively stable before creating aliases for presentation objects.
You can use this feature to rename presentation objects without breaking references that any existing requests have to the old names, including requests from Answers, Oracle BI Publisher, or other Logical SQL clients. If you are still developing a new repository, you might want to wait until the repository is stable before renaming objects.
For example, consider a subject area called Sample Sales Reduced that contains a presentation table called Facts Other. If you rename the presentation column called # of Customers to Number of Customers, any requests that use # of Customers fail. However, if you add # of Customers to the list of synonyms in the Alias tab for the Number of Customers column, then queries containing both # of Customers and Number of Customers succeed and return the same results.
-
Aliases for presentation objects do not appear in Answers or other query clients when creating new queries. Only the primary names of subject areas, hierarchies, levels, tables, and columns appear.
-
This feature works in a different way from SQL aliases or the alias feature in the Physical layer. It simply provides synonyms for object names, much like synonyms in SQL.
-
Aliases are created automatically when you rename presentation objects. For example, if you change Catalog to Catalog1, the original name Catalog is added to the Aliases list.
-
You cannot rename a Presentation layer object to a name that is already in use as an alias for an object of the same type.
- In the Oracle BI Administration Tool, in the Presentation layer, double-click a presentation object such as a subject area, table, column, or hierarchy.
- In the Properties dialog for the presentation object, click the Aliases tab.
- Click the New button to create an alias, and then type the text string to use for the alias.
- Click OK.
Controlling Presentation Object Visibility
You can use the Hide object if field to hide selected Presentation layer objects in the Subject Area Tree in Answers and BI Composer. You can hide subject areas, tables, columns, and hierarchies.
Although the Hide object if field is shown for presentation levels, it is a placeholder for a future release and currently has no effect on presentation level objects.
The Hide object if field only controls object visibility and does not affect object access. For example, you can query objects that are hidden using tools likenqcmd.
There are three different types of expressions that you can use in the Hide object if field to determine Presentation layer object visibility:
-
Constant. Use any non-zero constant in the field to hide the object. Use zero (0) or leave the field blank to display the object.
-
Session variable. You can use a session variable in the expression to control whether the object is hidden. If the expression evaluates to a non-zero value, the object is hidden. If the expression evaluates to zero, is empty, or has no value definition, the object is displayed. The session variable must be populated using a session initialization block or a row-wise initialization block. You must properly populate the session variable to control the visibility.
The SQL for the
initblock can useCASEstatements to control whether to return zero or a non-zero number in the session variable, for example:VALUEOF(NQ_SESSION."VISIBLE")Session variable names that include periods must be enclosed in double quotes.
-
Session variable comparison. You can use an equality or inequality comparison to control whether the object is hidden, using the following form:
'session_variable_expression' '=|<>' 'constant'If the expression evaluates to zero, null, or empty, the object is displayed. If the expression evaluates to a non-zero value, the object is hidden, for example:
NQ_SESSION."VISIBLE" = 'ABC' NQ_SESSION."VISIBLE" <> 'ABC'
You must enclose session variable names that include periods in double quotes.
You can use any scalar function supported by Oracle BI EE in the
Hide object ifexpression. Scalar functions include any function that accepts a simple value for each of its arguments and returns a single value. You can use the functions listed, except for functions that return non-deterministic results likeRAND,NOW,CURRENT_DATE,CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, andCURRENT_TIME.-
All String Functions, see String Functions.
-
Math Functions, see Math Functions, except RAND.
-
Calendar Date/Time Functions, except NOW, and CURRENT_DATE.
-
Conversion Functions such as CAST, IFNULL, TO_DATETIME, and VALUEOF.
For example, the following expression checks to see if the NQ_SESSION.VISIBLE session variable begins with the letters ABC:
LEFT(VALUEOF(NQ_SESSION."VISIBLE"), 3) = 'ABC'The following expression checks to see if the given variable begins with ExtnAttribute:
Left(VALUEOF(NQ_SESSION."ADF_LABEL_ORACLE.APPS.CRM.MODEL.ANALYTICS. APPLICATIONMODULE.CRMANALYTICSAM_CRMANALYTICSAMLOCAL_CRMANALYTICSAM. OPPORTUNITYAM.OPPORTUNITY_EXTNATTRIBUTECHAR001"), 13) = 'ExtnAttribute'
-
Run the Consistency Check Manager to detect any inconsistencies in the visibility filter expression.