5 Using Oracle Forms Services with the HTTP Listener and Oracle WebLogic Server
Oracle HTTP Server is the Web server component for Oracle Fusion Middleware. It provides a listener for Oracle WebLogic Server and the framework for hosting static pages, dynamic pages, and applications over the Web.
This chapter contains the following sections:
5.1 About Oracle WebLogic Managed Server and HTTP Server
Managed Servers host business applications, application components, Web services, and their associated resources.
To optimize performance, managed servers maintain a read-only copy of the domain's configuration document. When a managed server starts up, it connects to the domain's administration server to synchronize its configuration document with the document that the administration server maintains. Oracle Fusion Middleware system components (such as SOA, WebCenter, and Identity Management components), as well as customer-deployed applications, are deployed to managed servers in the domain. During configuration, some managed servers are created specifically to host the Oracle Fusion Middleware applications (for example, Forms and Reports JavaEE applications).
Figure 5-1 shows a simple scenario of the Oracle WebLogic Managed Server. In the left side of the image, the Forms servlet renders the start HTML file and provides the information about the Forms Listener servlet to the client. An HTTP request is then received by the Oracle HTTP Server Listener, which passes it off to the Forms Listener servlet running inside Oracle WebLogic Managed Server, in the right side of the image. The Forms Listener servlet establishes a runtime process and is responsible for on-going communication between the client browser and the runtime process. As more users request Oracle Forms sessions, the requests are received by the Oracle HTTP Server Listener. The HTTP Listener again passes them off to the Forms Listener servlet, which establishes more runtime processes. The Forms Listener servlet can handle many Forms runtime sessions simultaneously. While there is, of course, a limit to the number of concurrent users, the architecture presents a number of opportunities for tuning and configuration to achieve better performance (see the next section).
Figure 5-1 Oracle WebLogic Managed Server and Forms Services
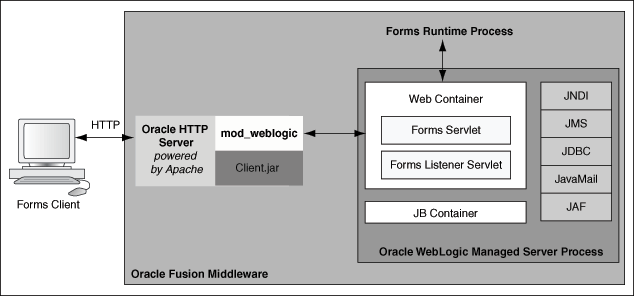
Description of "Figure 5-1 Oracle WebLogic Managed Server and Forms Services"
This illustration shows the HTTP request flow from WebLogic Managed Server to Forms Runtime Process. On the left of the image, resides the Forms client. The Forms servlet renders the start HTML file and provides the information about the Forms Listener servlet to the client. The client passes this HTTP request to the Oracle HTTP Server Listener in the middle. The Oracle HTTP Server Listener, in turn, passes the HTTP request to the Forms Listener servlet running inside WebLogic Managed Server. The WebLogic Managed Server Process includes a Web Container, JB Container, and other services, such as Java Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI), JMS, JavaMail, and so forth. The Forms Listener servlet establishes a Forms Server runtime process and is responsible for on-going communication between the client browser and the runtime process.
5.1.1 Enabling Oracle HTTP Server with Oracle Forms Services
In Oracle Fusion Middleware 12c, enabling Oracle HTTP Server to route requests to the Forms Managed Server manual, post installation steps are required.
-
Use the Forms Configuration Helper Script, as described in Oracle Forms Utilities and Scripts and, pass it the enable_ohs option.
-
Manually edit forms.conf, as described in About Editing forms.conf.
5.1.2 About Editing forms.conf
forms.conf is an Oracle HTTP Server directives file. In Oracle Fusion Middleware, the forms.conf file should be included in the Oracle HTTP Server configuration directory at $DOMAIN_HOME/config/fmwconfig/components/OHS/<OHS INSTANCE NAME>/moduleconf.
If you add any custom Oracle HTTP Server directives to forms.conf, you must restart the Oracle HTTP Server node where it resides.
5.2 Using HTTPS with the Forms Listener Servlet
Using HTTPS with Oracle Forms is no different than using HTTPS with any other Web-based application.
HTTPS requires the use of digital certificates (for example, VeriSign). Because Forms Services servlets are accessed via your Web server, you do not need to purchase special certificates for communications between the Oracle Forms client and the server. You only need to purchase a certificate for your Web server from a recognized certificate authority.
Oracle recommends that for ensuring the highest level of security between your end-user and middle tier, Secure Socket Layer (SSL) should be configured. For details on how to enable SSL in your environment, see Managing Application Security in Administering Oracle HTTP Server and Configuring SSL in Oracle Fusion Middleware in Administering Oracle Fusion Middleware.
5.3 Oracle Forms Services and SSL
You have to perform specific steps to run Oracle Forms Services applications in SSL mode.
Perform the following steps:
-
Create a Wallet to manage certificates.
-
Enable the HTTPS port in Oracle HTTP Server. By default, Oracle HTTP Server has one SSL Port enabled.
-
Optionally, consider enabling HTTPS in WebLogic Server for the Forms managed server (for example, WLS_FORMS).
5.4 Enabling SSL with a Load Balancing Router
Running a Forms application that uses an HTTPS port requires a certificate to be imported. If Oracle Forms is behind a load balancing router, and SSL terminates at it, you need to import the certificate from the load balancing router.
To enable SSL with your Forms applications over a load balancing router:
-
Start a Web browser and enter the Forms application HTTPS URL containing the fully qualified host name (including port number if required) used by your own Oracle installation. For example:
https://example.com:443/forms/frmservletThe Security Alert dialog box is displayed.
-
Click View Certificate.
-
Click the Details tab in the Certificate dialog.
-
Click Copy to File...
-
In the Welcome page of the Certificate Export Wizard, click Next.
-
In the Export File Format page, select Base-64 encoded X.509 (.CER), then click Next.
-
Enter a file name such as
c:\temp\forms, then click Next. -
Click Finish.
A message appears saying that the export was successful.
-
Click OK.
-
Close the Certificate Export Wizard, but keep the Security Alert dialog open.
-
Import the security certificate file that you saved earlier into the certificate store of the JVM you are using.
-
At the Security Alert dialog, click Yes to accept the security certificate and start the Forms application.
To import the certificate into Java Plugin:
- On the client machine, open the Control Panel.
- Open Java.
- Navigate to Securities tab.
- Click Certificate.
- Import the certificate that was exported in the previous section.
- Click Apply.
5.5 Work with Forms Managed Server
By default (out-of-the-box installation), the Forms Services Java EE application (formsapp.ear) is deployed on Forms Managed Server (WLS_FORMS).
You can manage WLS_FORMS and formsapp.ear using Oracle WebLogic Administration Console or Oracle Fusion Middleware Control. Refer the following links:
-
Starting and Stopping Forms Managed Server, as described in Overview of Starting and Stopping Procedures in Administering Oracle Fusion Middleware.
-
Deploying Forms Application to Forms Managed Server, as described in Configuring Forms Using the Configuration Wizard
. -
Custom deployment of Forms Java EE application, as described in Custom Deployment of Forms Java EE Application.
-
Expanding Forms Managed Server Clusters, as described in Expanding Forms Managed Server Clusters.
-
Modifying
weblogic.xml,web.xml,application.xmlandweblogic-application.xmlpost deployment, as described in Modifying of Forms J2EE Application Deployment Descriptors. -
Starting Forms Managed Server as a Windows Service, see Setting Up a WebLogic Server Instance as a Windows Service in Administering Server Startup and Shutdown for Oracle WebLogic Server.
5.5.1 Custom Deployment of Forms Java EE Application
Users can override the default Forms JavaEE application context root (/forms) and the default Forms servlet alias (frmservlet) and customize it.
The default Forms applications access URL: http://host:port/forms/frmservlet can be changed to http://host:port/<user-context>/<user-servlet-alias>.
To create a custom managed server and deploy Forms application on it, perform the following steps:
5.5.1.1 Creating and deploying custom application
To create and deploy custom application perform the following steps:
5.5.1.2 Post-Patching Tasks
After applying Oracle Fusion Middleware 12c Patch Sets, perform the following steps for custom deployments:
- Ensure that the servers in the Domain have been stopped.
- Run the frmconfighelper script using the
update_appoption after applying the patch. - The managed server has to be re-started after running the
update_appoption to take effect.
Note:
For information on the frmconfighelper script, see Oracle Forms Utilities and Scripts.5.5.1.3 Testing the Custom Deployment
Test the deployment using the URL: http://<Host>:<Port Number>/<context root>/<servlet name>.
For the example in this section, the URL would be http://<Host>:<Port Number>/customapp/customservlet. In that case that you are running form with SSO (ssoMode=true or webgate), additional settings with permissions are needed in: DOMAIN_HOME/config/fmwconfig/system-jazn-data.xml file.
5.5.2 Expanding Forms Managed Server Clusters
To improve the scalability and performance of Forms deployments on high-end machines (multiprocessor and high-memory configuration machines), expand the Forms Managed Server cluster (cluster_forms). Perform the following manual steps to expand the Forms Managed Server cluster:
-
Perform the following steps to add a new Managed Server to the default Forms application cluster (
cluster_forms):-
Add additional Managed Server(s) using the config wizard. Make sure that you select the FORMS-MAN-SRV group.
Adding a new manager server.
-
Ensure that it is added to the cluster_forms after creating the Managed Server.
Adding a new managed server.
-
Start the newly created Managed Server.
-
-
Add the new Managed Server's host and port information to the WebLogicCluster entry in
forms.conf:<Location /forms> SetHandler weblogic-handler WebLogicCluster <HostName>:9001, <HostName>:9010 DynamicServerList OFF </Location>
-
Restart OHS.
5.5.3 Creating Multiple Forms System Component Instances on Same Physical Machine
If you setup more than one Forms System Component Instances on the same physical machine, then Forms managed server should be associated with its respective Forms System Component Instance.
This setup can be created by defining forms.instance system property on the Forms managed server and setting it to Forms System Component Instance name.
For example:
Machine 1 forms1 WLS_FORMS
forms2 WLS_FORMS2
Set the forms.instance system property on WLS_FORMS1 to forms1. Similarly, set forms.instance system property on WLS_FORMS2 to forms2. This can be done using the Managed Server setting in the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console.
Figure 5-5 Managed Server setting in the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console
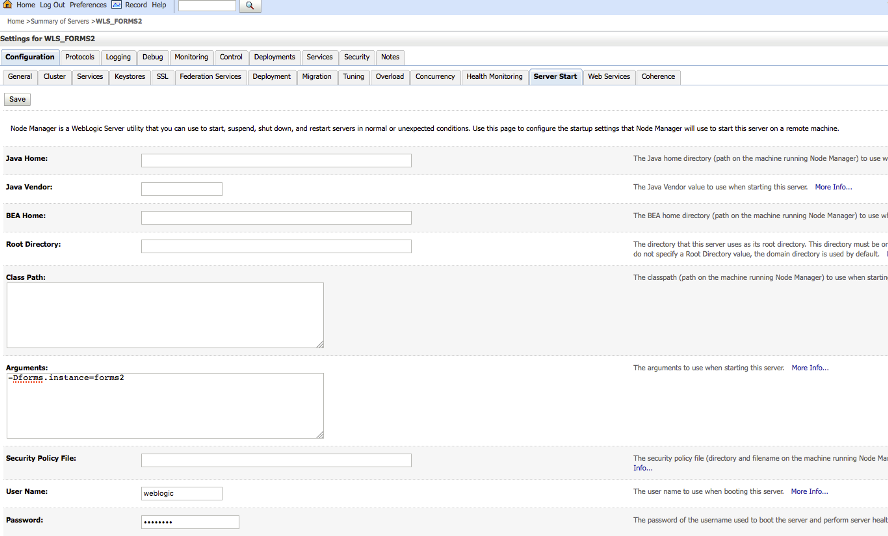
Description of "Figure 5-5 Managed Server setting in the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console"
5.5.4 Modifying of Forms J2EE Application Deployment Descriptors
Post-deployment, Forms J2EE application deployment descriptors (weblogic.xml, web.xml, application.xml and weblogic-application.xml) cannot be modified in Oracle WebLogic Server.
As a workaround, perform the following steps to customize the Forms J2EE application deployment descriptors and redeploy the application:
-
Back up the default formsapp deployment plan,
$DOMAIN_HOME/config/fmwconfig/deployment-plans/formsapp/12.2.1/plan.xml. -
Add the deployment descriptors customizations to the Forms J2EE application's deployment plan.
Note:
See the following example on how to modify a deployment plan.
To update the deployment plan, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Deploying Applications to Oracle WebLogic Server.
-
Using the WebLogic Administration Console, update the forms application (redeploy) and select the option Update this application in place with new deployment plan changes.
-
Restart the Forms J2EE application using the WebLogic Administration Console.
Example: Modifying Deployment Plan:
In this example, the deployment plan is modified to override the Forms Servlet testMode parameter and set it to true. To modify the deployment plan, perform the following steps:
5.6 Performance/Scalability Tuning
The steps for tuning the Forms Listener servlet are similar to steps for tuning any high throughput servlet application.
You have to take into account resource management and user needs for optimal tuning of your particular Forms Services configuration, see Monitoring in Tuning Performance.
5.7 Load Balancing Oracle WebLogic Server
The Forms Listener servlet architecture allows you to load balance the system using any of the standard HTTP load balancing techniques available.
The Oracle HTTP Server Listener provides a load balancing mechanism that allows you to run multiple WebLogic instances on the same host as the HTTP process, on multiple, different hosts, or on any combination of hosts. The HTTP Listener then routes HTTP requests to Oracle WebLogic Managed Server instances.
The following scenarios are just a few of the possible combinations available and are intended to show you some possibilities. The best choice for your site will depend on many factors. For a complete description of this feature, see Monitoring in Tuning Performance.
The following images show four possible deployment scenarios.
Figure 5-6 Multiple Oracle WebLogic Servers on the same host as the Oracle HTTP Listener
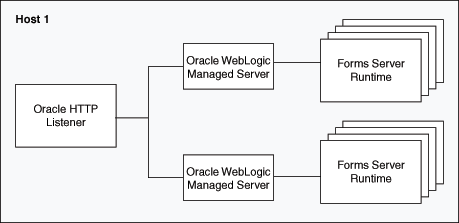
Description of "Figure 5-6 Multiple Oracle WebLogic Servers on the same host as the Oracle HTTP Listener"
Figure 5-7 Multiple Oracle WebLogic Servers on a different host to the Oracle HTTP Listener
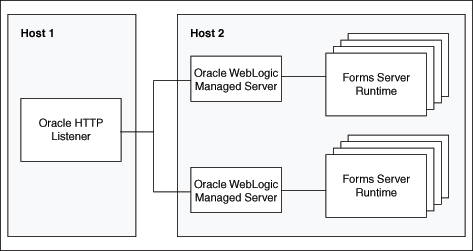
Description of "Figure 5-7 Multiple Oracle WebLogic Servers on a different host to the Oracle HTTP Listener"
Figure 5-8 Multiple Oracle WebLogic Servers and multiple Oracle HTTP Listeners on different hosts
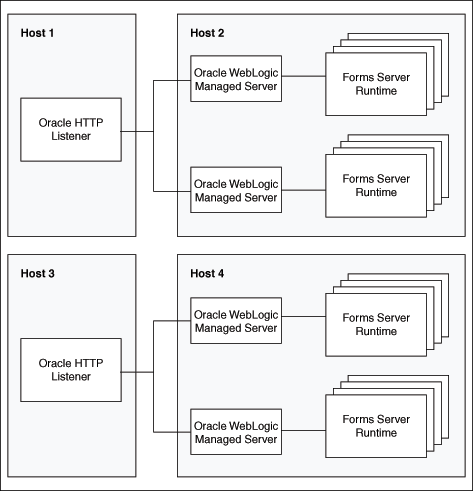
Description of "Figure 5-8 Multiple Oracle WebLogic Servers and multiple Oracle HTTP Listeners on different hosts"
Figure 5-9 Multiple Oracle HTTP Listeners on different hosts with multiple Oracle WebLogic Servers on one host
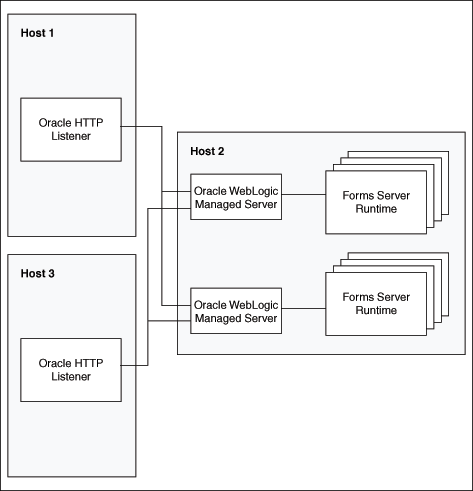
Description of "Figure 5-9 Multiple Oracle HTTP Listeners on different hosts with multiple Oracle WebLogic Servers on one host"
Note:
To tune and optimize Forms Services with the HTTP Listener and Oracle WebLogic Server, see Tuning Oracle HTTP Server in Tuning Performance Guide.
5.8 Using an Authenticating Proxy to Run Oracle Forms Services Applications
The default configuration as set up by the Oracle Fusion Middleware installation process supports authenticating proxies.
An authenticating proxy is one that requires the user to supply a username and password to access the destination server where the application is running. Typically, authenticating proxies set a cookie to detect whether the user has logged on (or been authenticated). The cookie is sent in all subsequent network requests to avoid further logon prompts.
The codebase and server URL values that are set up by the Oracle WebLogic Server installation process include $FMW_HOME/forms/java and /forms/lservlet. As these are under the document base of the page ($FMW_HOME/forms), authenticating proxies will work.