36 Orchestrate ADF Business Components Services
When to implement: This pattern describes how to use a SOA composite application to invoke business methods within an Oracle ADF web application. In this pattern, the Oracle ADF web application business methods make changes to data, whereas the SOA composite does not. For example:
-
A BPEL process service component must retrieve data from a database using an ADF Business Components service. However, the BPEL process service component will not post any changes back to the database.
-
A BPEL process service component must access an exposed service method on an ADF Business Components service, and that method contains only business logic and does not update data.
-
A BPEL process service component must access an exposed service method on an ADF Business Components service. The exposed service method on the business component service does not require a conversational callback style of interaction. Instead, it provides a single invocation, wrapping all of the business logic and view object manipulation. An example of this is a service method that deletes an order and all line items, given an order ID as a parameter.
Related Links
The following document provides additional information related to subjects discussed in this section:
See Manipulating Back-End Data from a SOA Composite for information regarding patterns in which both the Oracle ADF web application and SOA composite must update data without conflicting.
Design Pattern Summary: A BPEL process service component uses an invoke activity to invoke a partner link that accesses a SOAP service created for a business component.
Involved components:
-
SOA composite application that includes a BPEL process service component
-
Oracle ADF web application that includes ADF Business Components
36.1 Introduction to the Recommended Design Pattern
Oracle Fusion applications may require that a BPEL process service component access data values from ADF Business Components in an Oracle ADF web application. Oracle Fusion applications may also require that a BPEL process service component invoke a method contained in ADF Business Components. Instead of directly accessing the ADF Business Components, you can publish the component as a web service. The composite then accesses the published component over SOAP using an invoke activity and partner link in the BPEL process service component. Figure 36-1 shows a high-level overview of this design pattern.
Figure 36-1 SOA Composite Application Accesses ADF Business Components Using SOAP
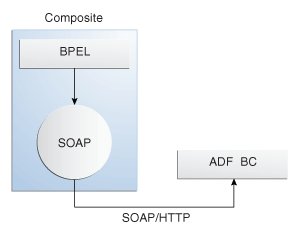
This approach is recommended because SOAP bindings do not require that the Oracle ADF web application and the SOA components be co-located in the same container.
36.2 Other Approaches
There are no other approaches to implementing this use case. The only supported way to invoke ADF Business Components services is to use a web service SOAP binding.
WARNING:
Using the Oracle ADF binding to invoke ADF Business Components services is prohibited due to topology and security requirements. (Oracle ADF services and SOA composites must be collocated; there are no application roles and privileges cannot be escalated.)
36.4 How to Invoke an ADF Business Components Service from a BPEL Process Service Component
To invoke ADF Business Components using a SOAP binding, you first publish the business component as a web service. You then create a BPEL process service component that contains a partner link to the ADF Business Components service. The partner link is accessed from an invoke activity. An assign activity is used to populate data into a variable used to pass data to the ADF Business Components service.
To invoke ADF Business Components from a BPEL process service component:
-
Create ADF Business Components, including an application module.
-
Optionally, create any SDO classes for view objects.
Any top-level view objects referenced in a service interface created from an application module will automatically be service-enabled. However, creating the SDO classes for individual view and entity objects allows you to configure the SDO name or namespace, or selectively service-enable child view objects.
-
Configure the service interface for the application module.
You can elect to include in your service interface custom methods, top-level service view instances, and any find operations based on view criteria.
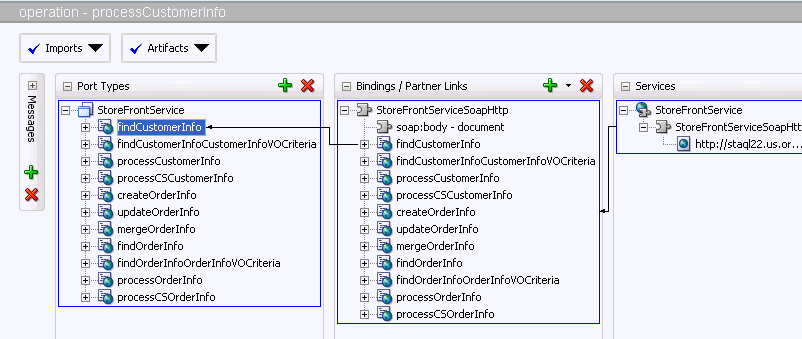
At the end of this step, Oracle JDeveloper creates the WSDL files that will be used by the BPEL process service component to access any required methods or data. Figure 36-2 shows the WSDL created for StoreFrontService in the sample application. This service accesses the customer and order information needed by the SOA composite application.
Figure 36-2 StoreFrontService WSDL File in Oracle JDeveloper
-
Implement the security as described in Securing the Design Pattern.
-
For verification purposes, you can either run the Oracle ADF web application from the Integrated Weblogic Server container included with Oracle JDeveloper, or you can deploy the Oracle ADF web application to a standalone container. To deploy to a standalone container:
-
Create a deployment profile for the web application.
-
Make an Oracle WebLogic Server connection to the container.
-
Deploy the profile to the container.
-
Add a library reference to
oracle.soa.workflow.wc. Add the following entry to the file inMW_HOME/user_projects/domains/<domain name>/config/config.xmldirectory, and add the line shown in Example 36-1 tooracle.adf.domain.loader.Note:
Skip this step if deploying the profile to the WLS container included in the SOA installation.
-
-
Add the WSDL file for the ADF Business Components service to the Resource Palette of Oracle JDeveloper. If you are using the embedded server, you first need to run your application. You then create a new URL connection in the Resource Palette to the embedded server. The URL is:
http://host:7101/ApplicationName-ProjectName-context-root/AppModuleService Name
The URL for the embedded server is generated at the bottom of the WSDL file. Alternatively, you can open the file and copy the
soap:addressURI.If you have deployed the Oracle ADF web application to a standalone server, then create a new Application Server connection in the Resource Palette. For more information about using the Resource Palette, see the Oracle JDeveloper Online Help.
-
Create a SOA composite application that includes a BPEL process service component.
-
In the SOA composite application, create the reference web service binding to the WSDL file for the ADF Business Components service. When creating the binding, be sure to select the WSDL from the Resource Palette.
Note:
The ADF Business Components service must be running in order for it to be discoverable.
Figure 36-3 shows the
composite.xmlfile for the sample application.Figure 36-3 Composite Application
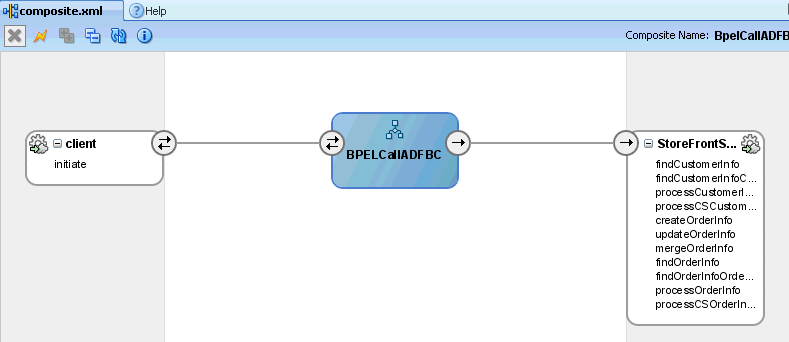
A Partner Link for the ADF Business Components is automatically created when the reference is wired to the BPEL process.
-
Wire the BPEL component to the Oracle ADF web service
Use a web service binding so that the ADF Business Components service can be remotely deployed.
-
Create an Invoke activity that invokes the partner link for the ADF Business Components.
-
Create an Assign activity to assign any values (for example, a static XML fragment) to variables for the BPEL process service component. These can then be passed to the ADF Business Components service.
-
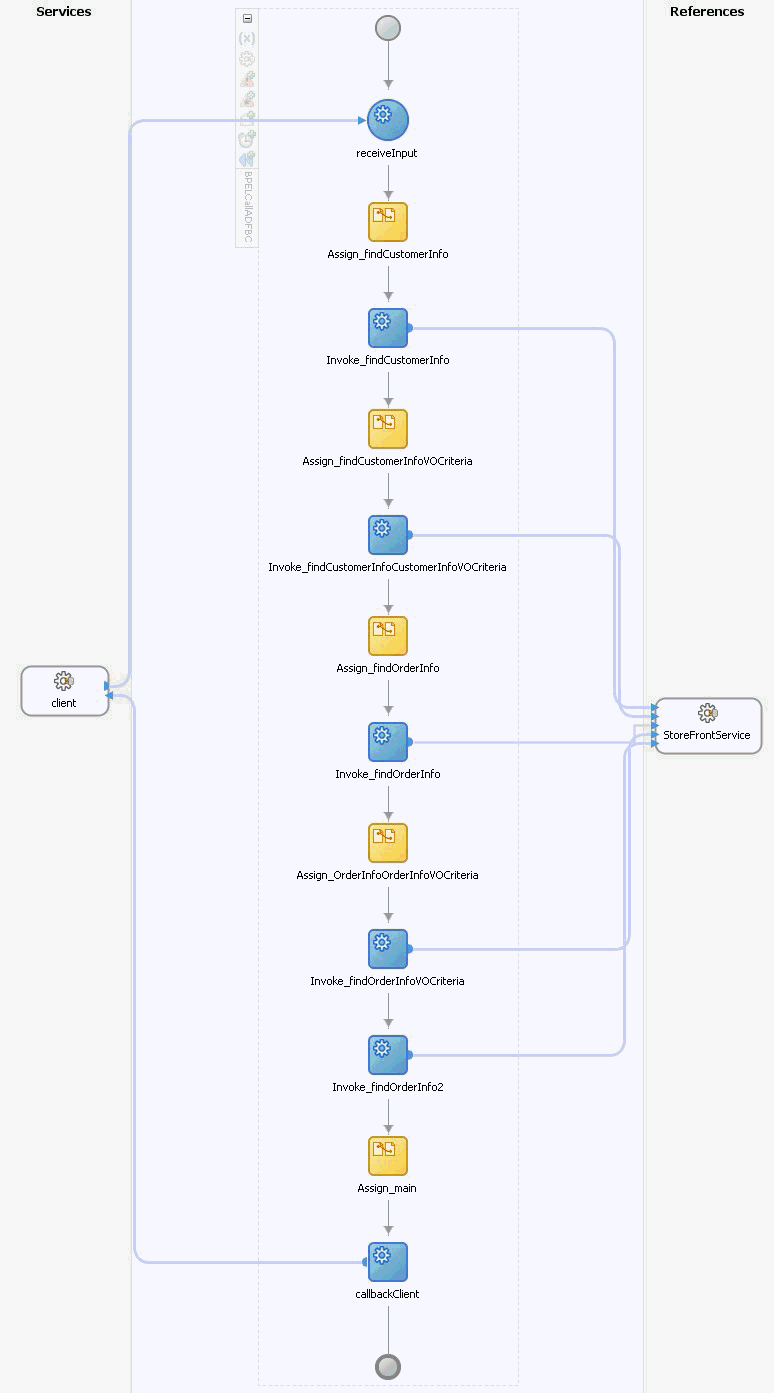
Repeat adding assign and invoke activities as needed. Figure 36-4 shows the BPEL flow for the sample application.
Figure 36-4 BPEL Flow for Invoking an ADF Business Components Service
-
Implement the security as described in Securing the Design Pattern.
Related Links
The following documents provide additional information related to subjects discussed in this section:
-
For more information about creating ADF Business Components, see Part II: Building Your Business Services in the Developing Fusion Web Applications with Oracle Application Development Framework.
-
For more information about configuring a service interface for an application module and creating SDO classes for view objects, see the chapter Integrating Service-Enabled Application Modules in the Developing Fusion Web Applications with Oracle Application Development Framework.
-
For more information about creating a deployment profile for a web application, see the chapter Deploying Fusion Web Applications of the Developing Fusion Web Applications with Oracle Application Development Framework.
-
For more information about creating SOA composite applications, as well as bindings and wiring references, see the chapter Developing SOA Composite Applications with Oracle SOA Suite in the Developing SOA Applications with Oracle SOA Suite.
-
For more information about creating Assign and Invoke activities, see the chapter r Getting Started with Oracle BPEL Process Manager in the Developing SOA Applications with Oracle SOA Suite.
Example 36-1 Shared Library Name
<shared-library name="adf.oracle.domain" version="11.1.1"
library-compatible="true">
...
<import-shared-library name="oracle.soa.workflow.wc"/>
36.5 Securing the Design Pattern
You need to secure the following:
-
Secure the ADF Business Components web service data control and the SOA composite using SAML policies.
-
Secure the ADF Business Components web service and the SOA composite with username token policies.
For information about securing the design pattern, see Securing Web Services Use Cases .
36.6 Verifying the Deployment
To properly verify this design pattern, you should test your ADF Business Components, then deploy and verify the SOA composite application.
To verify this design pattern:
- Test your Oracle ADF web application.
- Deploy the SOA composite application to the standalone WLS where the SOA infrastructure has been installed. Because you created a web service binding from the SOA composite application to the ADF Business Components web service, the ADF Business Components web service need not be deployed to the SOA infrastructure.
- Test the deployed SOA composite service using Fusion Middleware Control Console. Every deployed service has its own test page, so you can quickly test that the service functions as you expect.
Related Links
The following document provides additional information related to subjects discussed in this section:
-
For more information about testing and debugging your Oracle ADF web application, see the chapter Testing and Debugging ADF Componentsof the Developing Fusion Web Applications with Oracle Application Development Framework.
-
For information about testing the ADF Business Components service, see the chapter Integrating Service-Enabled Application Modules chapter of the Developing Fusion Web Applications with Oracle Application Development Framework.
-
For more information about testing a deployed SOA composite service, see Managing SOA Composite Application Instances in the Administering Oracle SOA Suite and Oracle Business Process Management Suite.
36.7 Troubleshooting the Use Case
Following are tips that may help resolve common issues that arise when developing or running this use case.
Use Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control Console to troubleshoot the use case:
http://localhost:8888/em
You can test your SOA composite using Fusion Middleware Control Console.
Related Links
The following document provides additional information related to subjects discussed in this section:
For more information about testing your SOA composite, see the section "Automating Testing for SOA Composite Applications" in the chapter Managing SOA Composite Application Instances in the Administering Oracle SOA Suite and Oracle Business Process Management Suite.
36.8 What You May Need to Know About Orchestrating ADF Business Components Services
Before you implement these design patterns, you should be aware of the following:
Any time you invoke an ADF Business Components service, the database transaction for that operation is committed when it completes.
There is no session propagation between the BPEL process and Oracle ADF. While the identity is passed in when security policies are in place, a new Oracle Fusion Data Security session is created with each invocation of the ADF Business Components service operations.
If you invoke ADF Business Components service operations that use event-raising entities, those events are not raised.