| Previous | Next | Contents | Index | Navigation | Glossary | Library |
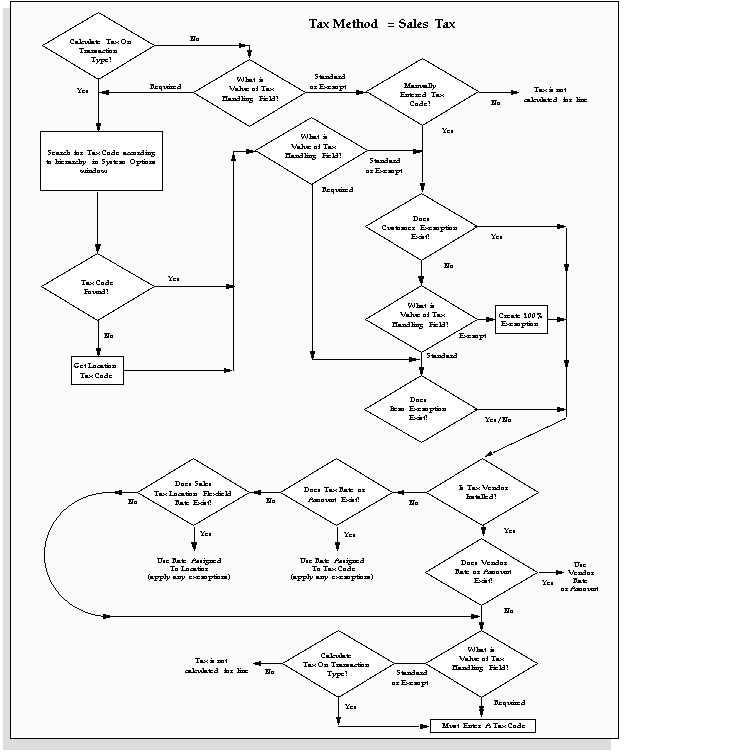
When using either the Sales Tax or Value Added Tax (VAT) method, Receivables uses the Ship-To address on your invoice to determine whether it has rates available for the components of the Sales Tax Location flexfield. If a Ship-To address does not exist for a transaction, Receivables derives tax from the Bill-To information. For example, if a transaction has a Ship-To customer, but no Ship-To address, Receivables uses the Bill-To information along with the appropriate hierarchy to determine the tax.
Attention: You will notice that there is a table associated with each tax hierarchy. They show which system options you can set to let you skip certain levels of the hierarchy when determining your tax. For more information, see: Setting Up Tax: An Overview.
| System Options for Sales Tax | Hierarchy |
|---|---|
| Tax Defaulting System Options | |
| Customer Site | 1 |
| Customer | 2 |
| Product | 3 |
| Exception Rates System Options | Value |
| Use Customer Exemptions | Yes |
| Use Item Exemptions | Yes |
| Use Item Tax Rate Exceptions | Yes |
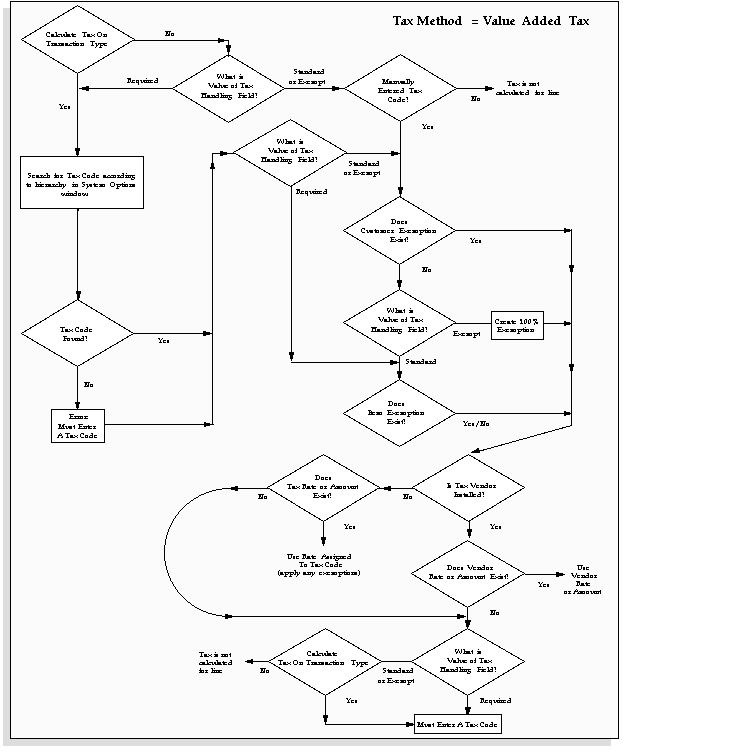
| System Options for VAT | Hierarchy |
|---|---|
| Tax Defaulting System Options | |
| Customer Site | 1 |
| Customer | 2 |
| Product | 3 |
| Exception Rates System Options | Value |
| Use Customer Exemptions | Yes |
| Use Exemptions | Yes |
Defining a Sales Tax Location Flexfield Structure
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index | Navigation | Glossary | Library |