| Previous | Next | Contents | Index | Navigation | Glossary | Library |
Current and Prior Period Addition
Construction-in-Process (CIP) Addition
For manual additions, Oracle Assets gets the clearing account from the category. For mass additions, the clearing account comes from your source system.
Example: The recoverable cost is $4,000 and the method is straight-line 4 years.
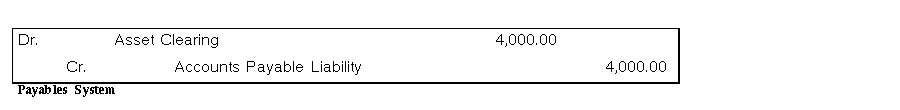

You place an asset in service in Year 1, Quarter 1, but you do not enter it into Oracle Assets until Year 2, Quarter 2. Your payables system creates the same journal entries to asset clearing and accounts payable liability as for a current period addition.

As an audit trail after the merge, the original cost of the invoice line remains on each line. When you create an asset from the merged line, the asset cost is the total merged cost.
Oracle Assets creates journal entries for the asset cost account for the mass addition into which the others were merged. Oracle Assets creates journal entries for each asset clearing account. For example, you merge mass addition #1 into mass addition #2, so Oracle Assets creates the following journal entries:

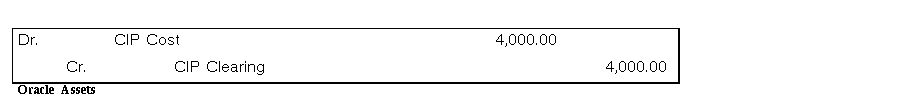
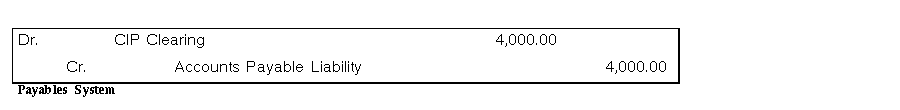

When you capitalize an asset in a period after the period you added it, Oracle Assets creates journal entries that transfer the cost from the CIP cost account to the asset cost account. The clearing account has already been cleared.


Construction-In-Process (CIP) Assets
Cost Adjustment by Adding a Mass Addition to an Existing Asset
Adding an Asset Accepting Defaults (QuickAdditions)
Adding an Asset Specifying Details (Detail Additions)
Adding an Asset Automatically from External Sources (Mass Additions)
Placing Construction-In-Process (CIP) Assets in Service
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index | Navigation | Glossary | Library |