Release 2.1
A76910-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle(R) Enterprise Manager Getting Started with the Oracle(R) Standard Management Pack Release 2.1 A76910-01 |
|
The change management applications provided by the Oracle Standard Management Pack are a group of integrated applications used to track changes to database object definitions. The change management applications are components of Oracle Enterprise Manager.
The change management applications provided by the Oracle Standard Management Pack are:
This chapter provides an overview of important change management concepts and features.
The following section describes new features for this release of the change management applications.
The following list describes the major new features for this version of the change management applications:
Change Manager, a new application, is now the central control panel for the change management applications. In most cases, interaction with the change management applications is directly or indirectly through Change Manager.
The change management applications provide improved multiple user support. Each user has read and write access to the object definitions that he or she owns, and has read-only access to object definitions owned by other users. The Change Manager navigator tree displays baselines and comparisons, organized by owner.
See "Capturing a Baseline from the Oracle Enterprise Manager Console or DBA Studio" and "Performing a Comparison from the Oracle Enterprise Manager Console or DBA Studio" for more information.
You can now view history entries that show the status of the following change management tasks:
By viewing the history entries for tasks, you can determine when each change management task was performed and which user performed it. See "Viewing History Entries for Tasks" for more information on history entries for tasks.
You can launch DBA Studio directly from Change Manager to modify database objects. On the Change Manager Tools menu, click DBA Studio to start DBA Studio.
After you create a named baseline specification that describes the object definitions to include in the baseline, use the specification as often as you like to generate baseline versions that match the baseline specification criteria.
Any differences between versions of a baseline accurately reflect differences in the database contents, not changes to the baseline specification (a baseline specification is a read-only object). Storing these baseline versions is an easy way to record changes in your database at different times in a development cycle.
You can view a particular version of a baseline. See "Working With a Particular Version of a Baseline or Comparison" for more information on viewing baseline versions.
After you create a comparison specification that describes the sets of object definitions to compare, use the specification as often as you like to generate comparison versions that determine the differences between the sets of object definitions.
Any differences between comparison versions accurately reflect differences in the database contents, not changes to the comparison specification (a comparison specification is a read-only object). Storing these comparison versions is an easy way to record the differences between two sets of definitions at different times in a development cycle.
You can view a particular version of a comparison. See "Working With a Particular Version of a Baseline or Comparison" for more information on viewing comparison versions.
The DB Diff application now lets you view the text differences in the SQL for objects such as check constraints, procedures, functions, packages, trigger bodies, and views.
After performing a comparison, select an object pair in the DB Diff tree view and in the detail view to the right of the tree view, select the text attribute of the object, then choose Show Text Difference on the Tools menu. This option only applies to text attributes such as the body of a procedure.
When you capture a baseline using the Advanced mode of DB Capture, the user interface now allows you to specify that you want to exclude the SYS and SYSTEM schemas from the operation.
See the online help for more information.
Use Baseline Viewer, a new application, to view baselines.
The types of database object definitions that the change management applications supports are:
In this release, the change management applications do not support the following features of the database objects in the previous list:
For a more complete list that describes the level of support the change management applications offer for specific database objects and attributes, see the section on currently unsupported database features and attributes in the Oracle Standard Management Pack Readme.
The following types of objects are created only by change management applications and are used to track changes to other object definitions:
A baseline is a group of database object definitions captured by the DB Capture application at a particular point in time. Each baseline has the name of its baseline specification and a version number. A baseline is stored in a format that can be used by multiple change management applications.
A baseline specification is used to generate baselines. A baseline specification includes a baseline name, source database, scope specification, and owner. The baseline name can be changed after the baseline specification is created, but the source database, scope specification, and owner cannot. The scope specification for a baseline is a set of criteria that an object must meet to be included in the baseline generated from the baseline specification. The scope specification describes the types of database object definitions to be included in the baseline, the schemas in which to look for those object definitions, and the names of those object definitions. See "Overview of DB Capture" for more information about baselines.
A comparison identifies the differences found by the DB Diff application in two sets of database object definitions. Each comparison has the name of its comparison specification and a version number.
A comparison specification is used to generate comparisons. A comparison specification is defined by its name, source database, scope specification, and owner. The name can be changed after the comparison specification is created, but the source database, scope specification, and owner cannot. The scope specification for a comparison is a set of criteria that the set of objects to be compared must meet to be included in a comparison generated from the comparison specification. The scope specification describes the types of database object definitions to be included in the comparison, the schemas in which to look for those object definitions, and the names of those object definitions. See "Overview of DB Diff" for more information about comparisons.
With change management applications, you can track changes by:
The applications and their functions are:
The change management applications also include the Change Manager application, which is a general-purpose interface that provides direct or indirect access to all change management features. See "Starting Change Manager" for more information on starting Change Manager.
The following sections provide additional overview information on the change management applications.
The DB Capture application guides you through the process of capturing a database (or a subset of a database) in a form that is readable by other change management applications. DB Capture lets you specify the set of database object definitions to capture, then captures those definitions in their current state at the time of the capture operation.
DB Capture can capture object definitions in both of the following forms:
Figure 5-1 shows the functional capabilities of DB Capture.
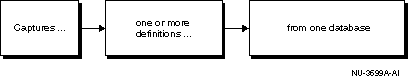
To view a baseline created with DB Capture, use the Baseline Viewer application.
When you have Oracle Standard Management Pack installed, you can perform a capture operation from the Oracle Enterprise Manager console or DBA Studio by following these steps:
DB Capture is started to capture a baseline for the selected database, then after the capture operation is completed, the Baseline Viewer is started to allow you to view the baseline.
The online help contains more information about the specifics of using DB Capture.
The Baseline Viewer application lets you display baselines created earlier using DB Capture.
Figure 5-2 shows the functional capabilities of Baseline Viewer.
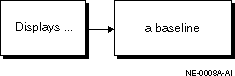
You can also use Baseline Viewer to generate a SQL DDL script for the baseline if you did not generate one when the baseline was captured.
The online help contains more information about the specifics of using Baseline Viewer.
The DB Diff application guides you through the steps of selecting two sets of object definitions and then comparing them. The object definitions can be selected from current database definitions or they can be selected from baselines created earlier with DB Capture. If differences are found when the two sets of object definitions are compared, DB Diff allows you to view the differences between the corresponding object definitions.
The result of comparing two sets of object definitions using DB Diff is called a comparison. You can name a comparison, save it, and view it later.
Figure 5-3 shows the functional capabilities of DB Diff.

You can also generate a report in HTML format about a DB Diff comparison. The report includes:
When you have the Oracle Standard Management Pack installed, you can perform a comparison operation from the Oracle Enterprise Manager console or DBA Studio by following these steps:
DB Diff is started to perform a comparison, then the DB Diff viewer is started to allow you to view the comparison.
The online help contains more information about the specifics of using DB Diff.
The Change Manager application is the change management central interface. In most cases, Change Manager gives you direct or indirect access to change management operations.
Using Change Manager, you can view change management objects (baselines and comparisons), as well as check on the status of current tasks. You can also view history information that tells you which change management operations were performed by what users at what time.
Figure 5-4 shows the functional capabilities of Change Manager.

See Chapter 6, "Using Change Manager" for more information on using Change Manager.
Some of the common usage scenarios for the change management applications are:
Online help is provided for all of the Oracle Change Management Pack applications. Note that the Oracle Standard Management Pack includes only the Change Manager, Baseline Viewer, DB Capture, and DB Diff applications, and provides read-only access to database object definitions. Also, you cannot create change plans with Oracle Standard Management Pack. You can display either the Contents page of the Oracle Change Management Pack help system, or you can display a help topic for your current context in an application.
Depending on the application that you are using, you can display the Contents page for the Oracle Change Management Pack online help by using one of the following methods:
Use the help system's Contents page, Index page, or Help Search page to locate help topics of interest. To access the Help Search page, on the Help Navigator window's Tools menu, choose Search.
You can display context-sensitive help in several ways, depending on your context in an application.
In addition to providing context-sensitive help, the Oracle Change Management Pack help system contains conceptual topics, task topics, and a glossary. To locate each type of topic: