Release 2 (8.1.6)
A76989-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle8i SQL Reference Release 2 (8.1.6) A76989-01 |
|
SQL Statements (continued), 3 of 20
|
WARNING: Oracle recommends that you perform a full backup of all files in the database before using this statement. For more information, see Oracle8i Backup and Recovery Guide. |
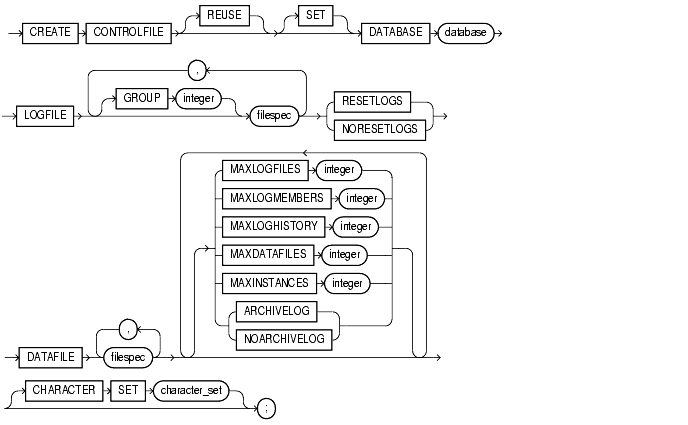
filespec: See "filespec".
To re-create a control file in one of the following cases:
When you issue a CREATE CONTROLFILE statement, Oracle creates a new control file based on the information you specify in the statement. If you omit any clauses, Oracle uses the default values rather than the values for the previous control file. After successfully creating the control file, Oracle mounts the database in the mode specified by the initialization parameter PARALLEL_SERVER. You then must perform media recovery before opening the database. It is recommended that you then shut down the instance and take a full backup of all files in the database.
You must have the OSDBA role enabled. The database must not be mounted by any instance.
If the REMOTE_LOGIN_PASSWORDFILE initialization parameter is set to EXCLUSIVE, Oracle returns an error when you attempt to re-create the control file. To avoid this message, either set the parameter to SHARED, or re-create your password file before re-creating the control file.
|
|
specifies that existing control files identified by the initialization parameter |
|
|
|
specifies the name of the database. The value of this parameter must be the existing database name established by the previous |
|
|
|
changes the name of the database. The name of a database can be as long as eight bytes. |
|
|
|
specifies the redo log files for your database. You must list all members of all redo log file groups. See Also: "filespec" for the syntax of filespec. |
|
|
|
|
specifies logfile group. If you specify |
|
|
ignores the contents of the files listed in the |
|
|
|
specifies that all files in the |
|
|
|
specifies the datafiles of the database. You must list all datafiles. These files must all exist, although they may be restored backups that require media recovery. See the syntax description of filespec in "filespec". |
|
|
|
specifies the maximum number of online redo log file groups that can ever be created for the database. Oracle uses this value to determine how much space in the control file to allocate for the names of redo log files. The default and maximum values depend on your operating system. The value that you specify should not be less than the greatest |
|
|
|
specifies the maximum number of members, or identical copies, for a redo log file group. Oracle uses this value to determine how much space in the control file to allocate for the names of redo log files. The minimum value is 1. The maximum and default values depend on your operating system. |
|
|
|
specifies the maximum number of archived redo log file groups for automatic media recovery of the Oracle Parallel Server. Oracle uses this value to determine how much space in the control file to allocate for the names of archived redo log files. The minimum value is 0. The default value is a multiple of the |
|
|
|
specifies the initial sizing of the datafiles section of the control file at |
|
|
|
The number of datafiles accessible to your instance is also limited by the initialization parameter |
|
|
MAXINSTANCES integer |
specifies the maximum number of instances that can simultaneously have the database mounted and open. This value takes precedence over the value of the initialization parameter |
|
|
|
establishes the mode of archiving the contents of redo log files before reusing them. This clause prepares for the possibility of media recovery as well as instance or crash recovery. |
|
|
|
If you omit both the |
|
|
|
optionally reconstructs character set information in the control file. In case media recovery of the database is required, this information will be available before the database is open, so that tablespace names can be correctly interpreted during recovery. This clause is useful only if you are using a character set other than the default US7ASCII. If you are re-creating your control file and you are using Recovery Manager for tablespace recovery, and if you specify a different character set from the one stored in the data dictionary, then tablespace recovery will not succeed. (However, at database open, the control file character set will be updated with the correct character set from the data dictionary.) See Also: Oracle8i Recovery Manager User's Guide and Reference for more information on tablespace recovery. |
|
|
|
Note: You cannot modify the character set of the database with this clause. |
|
This statement re-creates a control file. In this statement, database ORDERS_2 was created with the F7DEC character set.
CREATE CONTROLFILE REUSE DATABASE orders_2 LOGFILE GROUP 1 ('diskb:log1.log', 'diskc:log1.log') SIZE 50K, GROUP 2 ('diskb:log2.log', 'diskc:log2.log') SIZE 50K NORESETLOGS DATAFILE 'diska:dbone.dat' SIZE 2M MAXLOGFILES 5 MAXLOGHISTORY 100 MAXDATAFILES 10 MAXINSTANCES 2 ARCHIVELOG CHARACTER SET F7DEC;
|
|
 Copyright © 1999 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|