Release 2 (8.1.6)
A76989-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle8i SQL Reference Release 2 (8.1.6) A76989-01 |
|
SQL Statements (continued), 7 of 20
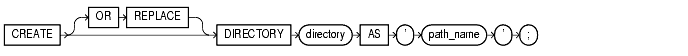
To create a directory object. A directory object specifies an alias for a directory on the server's file system where external binary file LOBs (BFILEs) are located. You can use directory names when referring to BFILEs in your PL/SQL code and OCI calls, rather than hard-coding the operating system pathname, thereby allowing greater file management flexibility.
All directories are created in a single namespace and are not owned by an individual's schema. You can secure access to the BFILEs stored within the directory structure by granting object privileges on the directories to specific users.
When you create a directory, you are automatically granted the READ object privilege and can grant READ privileges to other users and roles. The DBA can also grant this privilege to other users and roles.
|
See Also:
|
You must have CREATE ANY DIRECTORY system privileges to create directories.
You must also create a corresponding operating system directory for file storage. Your system or database administrator must ensure that the operating system directory has the correct read permissions for Oracle processes.
Privileges granted for the directory are created independently of the permissions defined for the operating system directory. Therefore, the two may or may not correspond exactly. For example, an error occurs if user SCOTT is granted READ privilege on the directory schema object, but the corresponding operating system directory does not have READ permission defined for Oracle processes.
|
|
re-creates the directory database object if it already exists. You can use this clause to change the definition of an existing directory without dropping, re-creating, and regranting database object privileges previously granted on the directory. Users who had previously been granted privileges on a redefined directory can still access the directory without being regranted the privileges For information on removing a directory from the database, see "DROP DIRECTORY". |
|
|
directory |
is the name of the directory object to be created. The maximum length of directory is 30 bytes. You cannot qualify a directory object with a schema name. |
|
|
|
Note: Oracle does not verify that the directory you specify actually exists. Therefore, take care that you specify a valid directory in your operating system. In addition, if your operating system uses case-sensitive pathnames, be sure you specify the directory in the correct format. (However, you need not include a trailing slash at the end of the pathname.) |
|
|
'path_name' |
is the full pathname of the operating system directory on the server where the files are located. The single quotes are required, with the result that the path name is case sensitive. |
|
The following statement redefines directory database object BFILE_DIR to enable access to BFILEs stored in the operating system directory /PRIVATE1/LOB/FILES:
CREATE OR REPLACE DIRECTORY bfile_dir AS '/private1/LOB/files';
|
|
 Copyright © 1999 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|