Release 2 (8.1.6)
A76989-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle8i SQL Reference Release 2 (8.1.6) A76989-01 |
|
SQL Statements (continued), 6 of 8
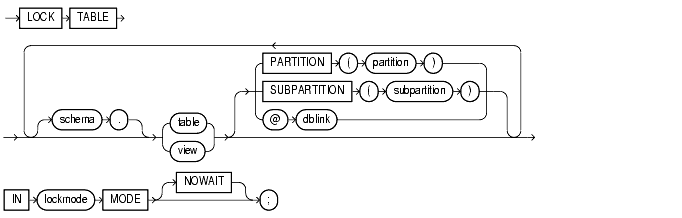
To lock one or more tables (or table partitions or subpartitions) in a specified mode. This lock manually overrides automatic locking and permits or denies access to a table or view by other users for the duration of your operation.
Some forms of locks can be placed on the same table at the same time. Other locks allow only one lock per table. For a complete description of the interaction of lock modes, see Oracle8i Concepts.
A locked table remains locked until you either commit your transaction or roll it back, either entirely or to a savepoint before you locked the table.
A lock never prevents other users from querying the table. A query never places a lock on a table. Readers never block writers and writers never block readers.
The table or view must be in your own schema or you must have the LOCK ANY TABLE system privilege, or you must have any object privilege on the table or view.
|
schema |
is the schema containing the table or view. If you omit schema, Oracle assumes the table or view is in your own schema. |
|
table / view |
is the name of the table to be locked. If you specify view, Oracle locks the view's base tables.
If you specify
If you specify |
|
dblink |
is a database link to a remote Oracle database where the table or view is located. For information on specifying database links, see "Referring to Objects in Remote Databases". You can lock tables and views on a remote database only if you are using Oracle's distributed functionality. All tables locked by a |
|
|
If you omit dblink, Oracle assumes the table or view is on the local database. |
|
lockmode |
|
|
|
specifies that Oracle returns control to you immediately if the specified table (or specified partition or subpartition) is already locked by another user. In this case, Oracle returns a message indicating that the table, partition, or subpartition is already locked by another user. |
|
|
If you omit this clause, Oracle waits until the table is available, locks it, and returns control to you. |
The following statement locks the EMP table in exclusive mode, but does not wait if another user already has locked the table:
LOCK TABLE empIN EXCLUSIVE MODE NOWAIT;
The following statement locks the remote ACCOUNTS table that is accessible through the database link BOSTON:
LOCK TABLE accounts@bostonIN SHARE MODE;
|
|
 Copyright © 1999 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|