Release 2 (8.1.6)
A76989-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle8i SQL Reference Release 2 (8.1.6) A76989-01 |
|
Functions, 40 of 121
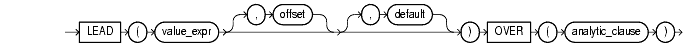
For information on syntax and semantics, see "Analytic Functions".
LEAD is an analytic function. It provides access to more than one row of a table at the same time without a self-join. Given a series of rows returned from a query and a position of the cursor, LEAD provides access to a row at a given physical offset beyond that position.
If you do not specify offset, its default is 1. The optional default value is returned if the offset goes beyond the scope of the table. If you do not specify default, its default value is null.
The following example provides, for each employee in the EMP table, the hiredate of the employee hired just after:
SELECT ename, hiredate, LEAD(hiredate, 1) OVER (ORDER BY hiredate) AS next_hire_date FROM emp; ENAME HIREDATE NEXT_HIRE ---------- --------- --------- SMITH 17-DEC-80 20-FEB-81 ALLEN 20-FEB-81 22-FEB-81 WARD 22-FEB-81 02-APR-81 JONES 02-APR-81 01-MAY-81 BLAKE 01-MAY-81 09-JUN-81 CLARK 09-JUN-81 08-SEP-81 TURNER 08-SEP-81 28-SEP-81 MARTIN 28-SEP-81 17-NOV-81 KING 17-NOV-81 03-DEC-81 JAMES 03-DEC-81 03-DEC-81 FORD 03-DEC-81 23-JAN-82 MILLER 23-JAN-82 19-APR-87 SCOTT 19-APR-87 23-MAY-87 ADAMS 23-MAY-87
|
|
 Copyright © 1999 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|