Release 1 (9.0.1)
Part Number A90135-01
Home |
Book List |
Contents |
Index | Master Index | Feedback |
| Oracle9i Recovery Manager User's Guide Release 1 (9.0.1) Part Number A90135-01 |
|
This chapter describes the basic concepts involved in using RMAN to restore, recover, and duplicate databases.
This chapter contains these topics:
This section contains these topics:
Use the RMAN RESTORE command to restore datafiles, control files, and archived redo logs from backup sets or image copies on disk. Because a backup set is in an Oracle proprietary format, you cannot simply import it; you must use the RMAN RESTORE command to extract it. In contrast, Oracle can use image copies created by RMAN without additional processing. By using RMAN, you can restore the whole database or individual tablespaces, datafiles, control files (current or copies), or archived redo logs.
|
See Also:
"Restoring and Recovering with RMAN: Overview" to learn how to restore, and Oracle9i Recovery Manager Reference for |
RMAN automates the procedure for restoring files. You do not need to go into the operating system, locate the backup or copy that you want to use, and manually copy files into the appropriate directories. When you issue a RESTORE command, RMAN directs a server session to restore the correct backups and copies to either:
SET NEWNAME command
When RMAN performs a restore, the RESTORE command actually creates the restored files as datafile copies and records them in the repository. If you do not specify a SET NEWNAME command for the restored files, then RMAN restores the backups to the default location and immediately removes the repository records for the datafile copies created during the restore.
For example, if you restore datafile /data/df1.f to its default location, then RMAN restores the file /data/df1.f and overwrites any file that it finds with the same filename. If you run a SET NEWNAME command before you restore a file, then RMAN creates a datafile copy with the name that you specify. For example, assume that you run the following commands:
SET NEWNAME FOR DATAFILE '/data/df1.f' TO '/alt_loc/df1.f'; RESTORE DATAFILE '/data/df1.f';
In this case, RMAN creates a datafile copy of /data/df1.f called /alt_loc/df1.f and records it as such in the repository. To change the name for /data/df1.f to /alt_loc/df1.f in the control file, run a SWITCH command so that RMAN considers the restored file as the current database file. For example:
SWITCH DATAFILE '/data/df1.f' TO DATAFILECOPY '/alt_loc/df1.f';
The SWITCH command is equivalent to the SQL statement ALTER DATABASE RENAME FILE.
|
See Also:
Oracle9i Recovery Manager Reference for |
RMAN uses the recovery catalog--or target database control file if no recovery catalog is available--to select the best available backup sets or image copies for use in the restore operation. It gives preference to image copies rather than backup sets. When multiple choices are available, RMAN uses the most current backup sets or copies, taking into account whether you specified an UNTIL clause in the RESTORE command.
All specifications of the RESTORE command must be satisfied before RMAN restores a backup set or file copy. The RESTORE command searches for backups and copies on all device types of configured channels.
If no available backup or copy in the recovery catalog satisfies all the specified criteria, then RMAN returns an error during the compilation phase of the restore job. If you manually allocate channels, and the file cannot be restored because no backup sets or datafile copies exist on the device types allocated in the job, then create a new job specifying channels for devices containing the existing backup sets or copies. This problem does not occur when you configure automatic channels.
By default, RMAN does not perform a restore if the file to be restored is in the correct place and its header contains the expected information. In releases prior to Oracle9i, RMAN always restored the requested files. In Oracle9i, RMAN only restores a file if the header check does not succeed, although you can use the FORCE option of the RESTORE command to override this behavior and restore the requested files unconditionally.
Restore optimization is particularly useful in cases where a restore only partially completes. For example, assume that a full database restore encounters a power failure after all except one of the datafiles has been restored. If you start the same restore again, then RMAN only restores the single datafile that was not restored during the previous attempt.
The concepts of datafile media recovery is the application of online or archived redo logs or incremental backups to a restored datafile in order to update it to the current time or some other specified time. Use the RMAN RECOVER command to perform media recovery and apply logs or incremental backups automatically.
This section contains these topics:
If possible, make the recovery catalog available to perform the media recovery. If it is not available, then RMAN uses metadata from the target database control file. If both the control file and recovery catalog are lost, then you can still recover the database--assuming that you have backups of the datafiles and at least one autobackup of the control file.
The generic steps for media recovery using RMAN are as follows:
SET UNTIL command to specify the time, SCN, or log sequence number at which recovery terminates. Alternatively, specify the UNTIL clause on the RESTORE and RECOVER commands.
RESTORE command.
RECOVER command.
Figure 6-1 illustrates an example of RMAN media recovery. The DBA runs the following commands:
RESTORE DATABASE; RECOVER DATABASE;
RMAN then queries the repository, which in this example is a recovery catalog. The recovery catalog obtains its metadata from the target database control file. RMAN then decides which backup sets to restore, and which incremental backups and archived logs to use for recovery. A server session on the target database instance performs the actual work of restore and recovery.
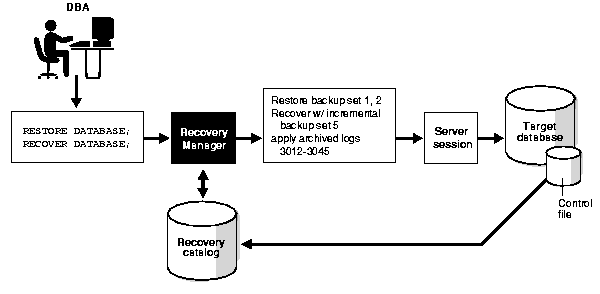
|
See Also:
|
If RMAN has a choice between applying an incremental backup or applying redo to the restored datafiles, then it always chooses to use an incremental backup. If overlapping levels of incremental backup are available, then RMAN automatically chooses the one covering the longest period of time. Note that RMAN does not need to apply incremental backups to a restored level 0 incremental backup: RMAN simply restores the datafiles that it needs from available backups and copies, and then applies incremental backups to the datafiles if it can.
If RMAN cannot find an incremental backup, then it looks in the repository for the names of archived redo logs to use for recovery. Oracle records an archived log in the control file whenever one of the following occurs:
COPY command copies a log
CATALOG command catalogs a user-managed backup of an archived log
RMAN propagates archived log data into the recovery catalog during resynchronization, classifying archived logs as image copies. You can view the log information through:
During recovery, RMAN looks for the needed archived logs using the filenames specified in the V$ARCHIVED_LOG view. If the logs were created in multiple destinations or were generated by the COPY, CATALOG, or RESTORE commands, then multiple, identical copies of each log sequence number exist on disk. RMAN does not have a preference for one copy over another during recovery: all copies of a log sequence number listed as AVAILABLE are viable candidates. In a sense, RMAN is blind to the fact that the logs were generated in different destinations or in different ways.
If the RMAN repository indicates that a log has been deleted or uncataloged, then RMAN ceases to consider it as available for recovery. For example, assume that the database archives log 100 to directories /dest1 and /dest2. The RMAN repository indicates that /dest1/log100.arc and /dest2/log100.arc exist. If you delete /dest1/log100.arc with the DELETE command, then the repository indicates that only /dest2/log100.arc is available for recovery.
If the RMAN repository indicates that no copies of a needed log sequence number exist on disk, then RMAN looks in backups and restores archived redo logs as needed to perform the media recovery. By default, RMAN restores the archived redo logs to the first local archiving destination specified in the initialization parameter file. You can run the SET ARCHIVELOG DESTINATION command to specify a different restore location.
If an archived log is deleted from disk and the repository does not reflect this fact, then RMAN does not perform automatic failover during recovery. For example, if the repository indicates that /dest1/log100.arc is on disk when in fact this log was deleted using an operating system command, and RMAN attempts to apply this log file during recovery, then recovery terminates with an error. RMAN does not automatically attempt to apply other copies of log 100 that are listed as available in the repository.
This situation can sometimes occur when you delete an archived log using an operating system utility and then fail to run a CROSSCHECK to synchronize the repository. If you run a CROSSCHECK so that the repository is synchronized, then recovery can proceed by applying available copies of the log or restoring a backup of the log if no disk copies are available.
RMAN can perform either complete or incomplete recovery. You can specify a time, SCN, or log sequence number as a limit for incomplete recovery with the SET UNTIL command or with an UNTIL clause specified directory on the RESTORE and RECOVER commands. The easiest method is run the SET UNTIL command before issuing the RESTORE and RECOVER commands. After performing incomplete recovery, you must open the database with the RESETLOGS option.
Recovery Manager automated Tablespace Point-in-Time Recovery (TSPITR) enables you to recover one or more tablespaces to a point in time that is different from that of the rest of the database. RMAN TSPITR is most useful in these cases:
Similar to a table export, RMAN TSPITR enables you to recover a consistent data set; however, the data set is the entire tablespace rather than a single object.
|
See Also:
Chapter 11, "Performing RMAN Tablespace Point-in-Time Recovery" to learn how to perform TSPITR using RMAN |
Assume that you lose both the target database and the recovery catalog. All that you have remaining is a tape with RMAN backups of the target database and archived redo logs. Can you still recover the database? Yes, assuming that you enabled the control file autobackup feature when making backups. In a disaster recovery situation, RMAN can determine the name of a control file autobackup even without a repository available. You can then restore this control file, mount the database, and perform media recovery.
This section contains these topics:
Although datafile media recovery is the principal form of recovery, you can also use the RMAN BLOCKRECOVER command to perform block media recovery. Block media recovery recovers an individual corrupt datablock or set of datablocks within a datafile. In cases when a small number of blocks require media recovery, you can selectively restore and recover damaged blocks rather than whole datafiles.
Block media recovery provides the several advantages over datafile media recovery. For example, block media recovery
Note these restrictions of block media recovery:
V$BACKUP_CORRUPTION and V$COPY_CORRUPTION views, which are populated by the RMAN BACKUP, BACKUP ... VALIDATE, and COPY commands, indicate which blocks are corrupt.
"Recovering Datablocks with RMAN" and Oracle9i Recovery Manager Reference for
See Also:
BLOCKRECOVER syntax
Block media recovery is not intended for cases where the extent of data loss or corruption is unknown and the entire datafile requires recovery. In such cases, datafile media recovery is the best solution. Block media recovery is not a replacement for traditional datafile media recovery, but a supplement to it.
In most cases, Oracle marks a block as media corrupt, invalidates the block in the instances (or all enabled instances in an Oracle Real Application Clusters configuration), and then writes it to disk when the corruption is first encountered. No subsequent read of the block will be successful until the block is recovered. You can only perform block recovery on blocks that are marked corrupt. This corrupt status effectively takes the block offline in all database instances and prevents user access during recovery.
Block media recovery is most useful for data losses that affect specific blocks. Block-level data loss usually results from intermittent, random I/O errors that do not cause widespread data loss, as well as memory corruptions that get written to disk. Typically, these types of block corruption are reported in these locations:
alert.log
ANALYZE TABLE and ANALYZE INDEX
For example, you may discover the following messages in a user trace file:
ORA-01578: ORACLE data block corrupted (file # 7, block # 3) ORA-01110: data file 7: '/oracle/dbs/tbs_71.f' ORA-01578: ORACLE data block corrupted (file # 2, block # 235) ORA-01110: data file 2: '/oracle/dbs/tbs_21.f'
You can then specify the corrupt blocks in the BLOCKRECOVER command as follows:
BLOCKRECOVER DATAFILE 7 BLOCK 3 DATAFILE 2 BLOCK 235;
Like datafile media recovery, block media recovery cannot survive a missing or inaccessible archived log. Nevertheless, block media recovery can survive gaps in the redo stream if the missing or corrupt redo records do not affect the blocks being recovered. Whereas datafile recovery requires an unbroken series of redo changes from the beginning of recovery to the end, block media recovery only requires an unbroken set of redo changes for the blocks being recovered.
When RMAN first detects missing or corrupt redo records during block media recovery, it does not immediately signal an error because the block undergoing recovery may become a newed block later in the redo stream. When a block is newed all previous redo for that block becomes irrelevant because the redo applies to an old incarnation of the block. For example, Oracle can new a block when users delete all the rows recorded in the block or drop a table.
Assume that media recovery is performed on block 13 as depicted in Figure 6-2.
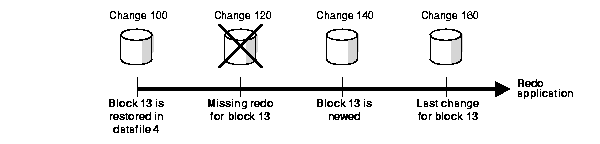
After block recovery begins, RMAN discovers that change 120 is missing. RMAN does not terminate recovery in the hope that block 13 will be newed later in the redo stream. Assume that in change 140 a user drops the table EMPLOYEE stored in block 13. At this point, Oracle formats block 13 as a new block. Because the redo for block 13 in change 120 related to the EMPLOYEE table, and the EMPLOYEE table was dropped in change 140, RMAN can skip this missing change and apply the redo between changes 140 and 160.
Use the RMAN DUPLICATE command to create a test database on which to practice your backup and recovery procedures. The command takes backups and copies of the primary database's files and uses them to create a new database. A test database is especially useful if your production database must maintain high availability.
As part of the duplicating operation, RMAN manages the following:
RESETLOGS option after incomplete recovery to create the online redo logs.
Note also the following features of RMAN duplication. You can:
SKIP READONLY clause. Read-only tablespaces are included by default. If you omit them, then you can add them later.
NOFILENAMECHECK option and reuse the target datafile filenames for the duplicate datafiles.
SET UNTIL option to recover it to a noncurrent time. By default, the DUPLICATE command creates the database using the most recent backups of the target database and then performs recovery to the most recent consistent point contained in the incremental and archived redo log backups.
Figure 6-3 illustrates a case of database duplication. In this example, RMAN creates two duplicate database by using one set of datafile backups: one database on the local host and one database a remote host.
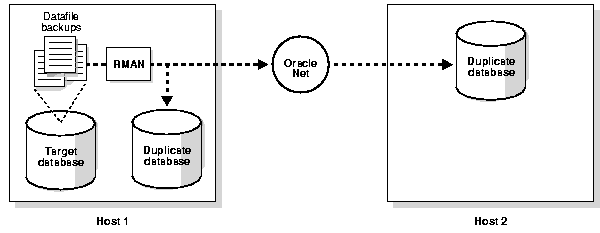
The method you use to duplicate your database depends on whether you are creating your duplicate database on the same or a different host and whether the duplicate directory structure is the same as your target database directory structure. For example, in some cases you can keep the same directory structure and filenames in your duplicate database, while other times you must rename the files.
|
See Also:
Chapter 12, "Duplicating a Database with Recovery Manager" to learn how to make a duplicate database, and Oracle9i Recovery Manager Reference for |
You can use the Recovery Manager DUPLICATE command to create a standby database. RMAN automates the following steps of the creation procedure:
RMAN cannot fully automate creation of the standby database because the user must manually create an initialization parameter file for the standby database, start the standby instance without mounting the control file, and perform any Oracle Net setup required before performing the creation of the standby.
RMAN can back up the standby database and archived redo logs. These standby backups are fully interchangeable with primary backups. In other words, you can restore a backup of a standby datafile to the primary database, and you can restore a backup of a primary datafile to the standby database.
|
See Also:
|
|
|
 Copyright © 1996-2001, Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|