Release 9.0.2
Part Number A95407-01
Home |
Solution Area |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide Release 9.0.2 Part Number A95407-01 |
|
This chapter describes the component of Oracle Enterprise Manager used to administer Enterprise User Security for the Advanced Security Option. The chapter explains use of Enterprise Manager within a simple scenario in which an Oracle Internet Directory Server is used as the central repository for users in a large organization. It contains the following sections
Oracle Enterprise Security Manager provides an easy-to-use graphical interface to administer enterprise user security and access control for large numbers of databases in your enterprise environment through a LDAP-compliant directory server such as Oracle Internet Directory. You use Oracle Enterprise Security Manager to perform the following tasks:
Upon logging in, Enterprise Security Manager appears as shown in Figure 9-1, "Enterprise Security Manager", given that the Directory contains at least the Oracle 9i Default Oracle Context.
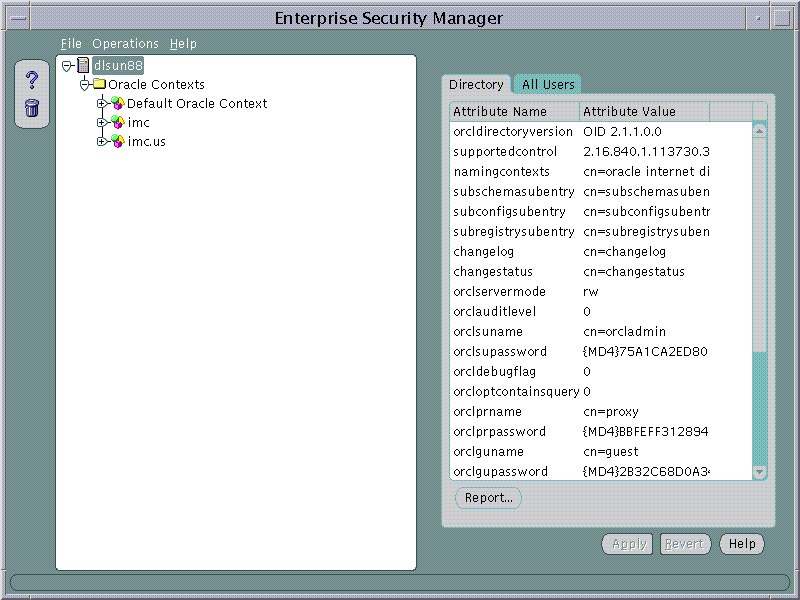
Enterprise Security Manager manages one Directory Server, identified at the top of the main application tree. It has a series of menu operations that apply to this Directory Server.
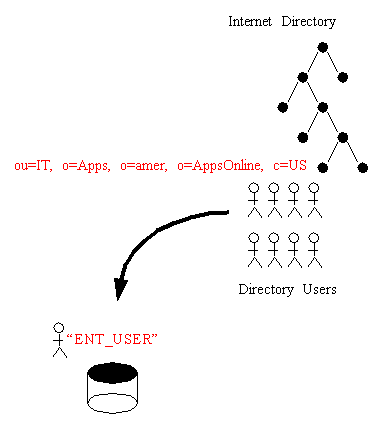
Users are managed in the Directory using Enterprise Security Manager. The application shows the directory to which it is connected and allows you to add, delete and browse Users in that Directory. Enterprise Security Manager may also be used to manage Oracle Contexts in the Directory. An Oracle Context is an area of structured information in the Directory recognizable to Oracle 8i and Oracle 9i products as well as an administrator hierarchy for management of the data in Oracle Contexts for different Oracle product areas.
This chapter is presented in two parts; Administering Users and Administering Oracle Contexts. It will use the example the "AppsOnline" Application Service Provider to illustrate both facets of Enterprise User Security management.
A Directory Server may be used a a general purpose means to centralize definitions of user and server access information over an entire network. As well as just naming information, the Directory may be employed to centralize password definitions, digital certificates and application authorizations for the users that it defines. This is possible, in the particular case of Oracle Internet Directory, as it allows for secured access and modification of sensitive information held in the Directory such as passwords or application authorizations.
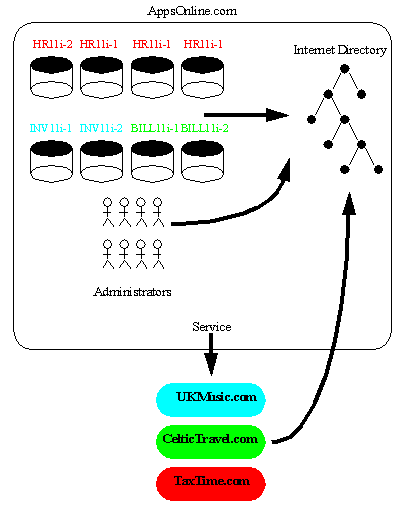
This chapter shall use as its example an Application Service Provider called, "AppsOnline". AppsOnline has a large set of Oracle 9i Databases that it uses to host different types of Application Software for its customers. AppsOnline needs to manage administrative access to these databases for its IT staff.
Text description of the illustration appsonli.gif
AppsOnline maintains Oracle 9i databases upon which are hosted three types of Application for its customers; Human Resources, Inventory and Billing. One customer, "TaxTime.com" subscribes to AppsOnline for its Human Resources Applications. A second customer, "CelticTravel.com" subscribes to the company for its Billing Applications. A third company, "UKMusic.com" subscribes to the company for its Inventory Management Applications.
AppsOnline dedicates some of its databases to each customer and manages these databases on behalf of the customer. The company has used a Oracle Internet Directory to hold information about their own employees, the databases on which they host Applications and the customers for whom they provide a service. In the course of their business they may wish to manage administrative access to their databases by their IT employees and manage access rights to information in these databases based upon each type of customer Application that they support.
This chapter will illustrate how Oracle Enterprise Manager may be used in this example scenario.
Task1: Configure an Oracle Internet Directory.
Task2: Install Oracle Enterprise manager
Task3: Configure Oracle Enterprise Manager for Enterprise User Security
Task4: Start Oracle Enterprise Security Manager
Task5: Log On To the Directory
Oracle 9i Enterprise User Security is based wholly around an Oracle Internet Directory. The Directory Server must be properly installed and configured before Enterprise Manager may be used to manage Enterprise User Security. The following stages of Oracle Internet Directory configuration must be complete before proceeding
Oracle Enterprise Manager is automatically installed with the Oracle 9i Enterprise Edition Server Install and includes all necessary functionality for Enterprise User Security. Oracle Enterprise Manager is also installed by default with the Oracle 9i Infrastructure Install at the same time as Oracle Internet Directory. Oracle Enterprise Manager may also be installed separately in its own ORACLE_HOME using the custom install option.
Oracle Enterprise Manager may be used to manage Enterprise User Security in two modes of operation. The Oracle9i Enterprise Manager Console may be used to connect to the Oracle 9i Management Server (OMS) and discover a Directory Server to manage. Alternatively, a dedicated application called, "Enterprise Security Manager" may be launched from the same ORACLE_HOME as Enterprise Manager and used to connect directly to the Directory Server. In either mode of operation functionality is identical. Only the latter mode, using the Enterprise Security Manager application, will be used in this chapter.
Enterprise Security Manager does not require any special configuration for it to run. However all Oracle Databases in the enterprise that need to avail of Enterprise User Security should be accessible over Oracle Net from the Enterprise Manager ORACLE_HOME.
To launch Enterprise Security Manager from the Enterprise Manager ORACLE_HOME, enter the following at the command line:
oemapp esm
This will cause the Directory Log On box to appear
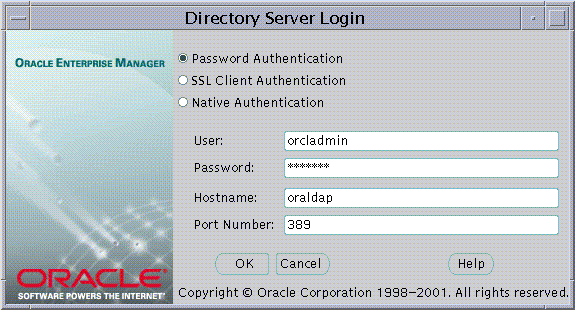
Enterprise Security Manager offers three ways to connect to a Directory Server by selecting the appropriate option in the Log On Box. These options are listed in the table below
For example, Password Authentication may be selected when using the orcladmin Oracle Internet Directory super user name and password to log on.
Enterprise Security Manager may be used to Create Users in the Directory. This is done by selecting "Create Enterprise User..." from the Operations Menu.
The Create User Window will appear in which to enter the name and location of the new User in the Directory.
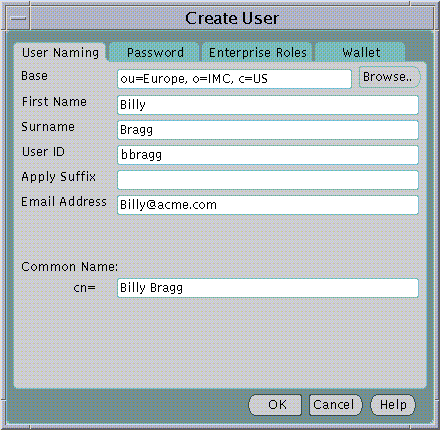
The following fields are mandatory for creation of a new User in the Directory:
The following additional fields are not mandatory for creation of a new User in the Directory but may be recorded for the new User if desired.
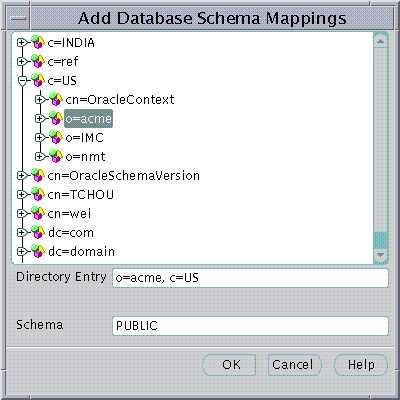
All Users in the Directory must exist at a particular "Base" within the Directory. The Base can be any existing Directory Entry such as Country Entry (e.g "c=US") or an Organization Entry (e.g "o=Acme, c=US". Many Users would typically share the same Base. This Base identifies all the Users contained under it as belonging to the same high level organization.
The Base at which to create a new User can be entered in the Base field in the Create User screen. However, you may explore the entire Directory to choose a suitable Base by clicking on the Browse... button. The Browse Directory dialog will appear.
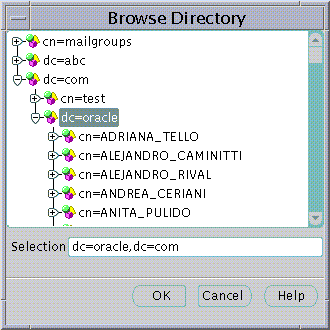
The Browse Directory screen lets you navigate the directory by drilling down into each entry from the top of the Directory Tree. When a Directory Entry is selected its Distinguished Name is placed in the Selection field. To accept the selected Distinguished Name choose the OK button. This value will then be returned as the selected Base for a new Directory User.
|
Note: This value will be preserved for all subsequent operations that create or search for Users in the Directory. However you may change it as many times as you like. |
The second Tab Panel of the New User screen allows you to set an initial password for the new User in the Directory. This will be the new User's initial password for:
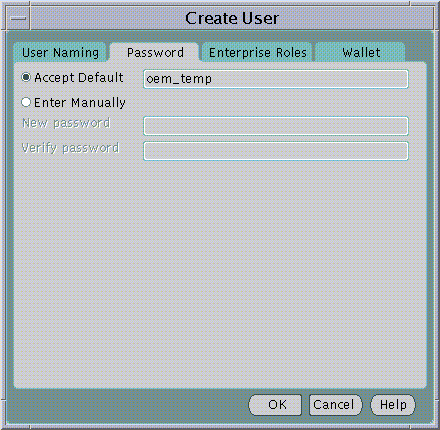
When Entering a password you may choose to accept a default first time password for the new User or manually enter the first time password for the new User. In either case, the new User must change their own password immediately after its first use.
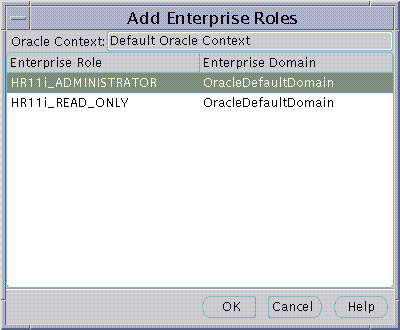
Enterprise Roles are discussed later in this Chapter. At the time of User creation you may select any previously configured Enterprise Roles and grant them to the new User.
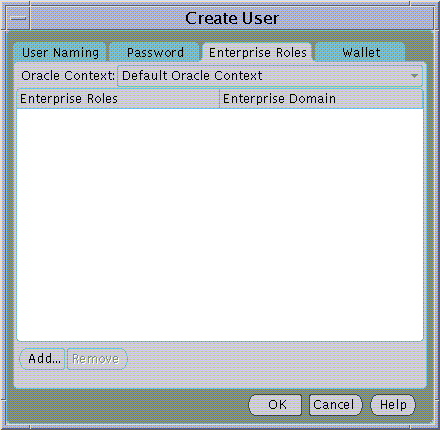
To select one or more Enterprise Roles to grant to the new User at this time choose Add... in the Enterprise Roles page of the Create User screen. The Add Enterprise Roles Page will appear from which you can choose any Enterprise Roles in your Oracle Context to assign to the new User.
An Oracle Wallet containing a new Digital Certificate, Private Key and Certificate Trustpoints may be generated for the new User in an encrypted binary format. The Oracle Wallet will be stored with the new User in the Directory Server as part of the Directory Entry for the User.
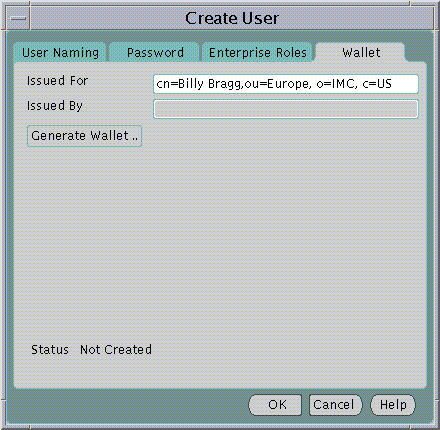
The Distinguished Name under which the new User will be created is used by default as the Distinguished Name for the Digital Certificate to be contained in the new User's Oracle Wallet. It is always good practice to let the Distinguished Names of User Certificates correspond to their Distinguished Names in the Directory. However, you may edit the Distinguished Name to be used for the Certificate before generating the Wallet by editing the contents of the Issued For: field.
An Oracle Wallet will be created when you click on the Generate Wallet... button.
Enterprise Security Manager allows you to browse all Users that are currently stored in the Directory. This is done by selecting the All Users page from the Directory at the top of the main application tree
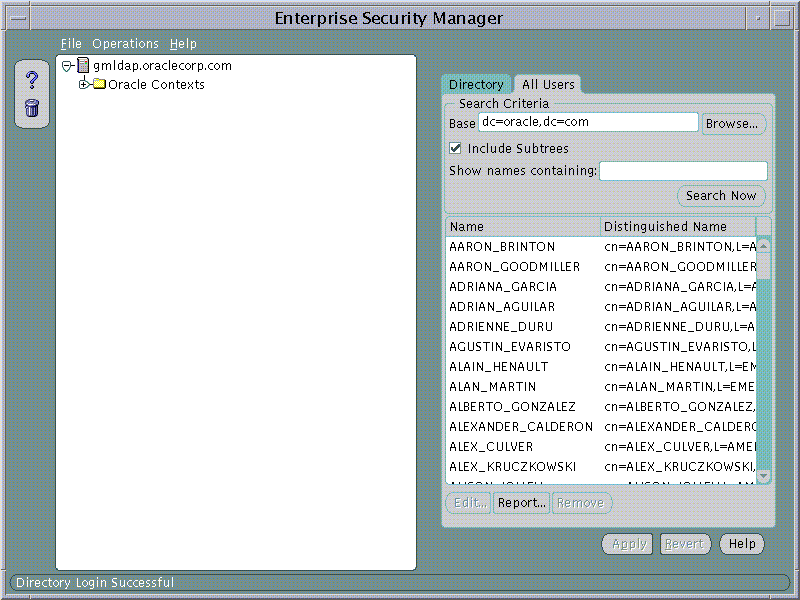
To Search for one or more users the directory, the Search Criteria must be set and the Search Now button used to perform a new search for Users based upon the given Search Criteria. The All Users page will refresh to show the results of this search. There are three factors to User Search Criteria:
For example, the Search Criteria may be set to search this Directory for a User given only that the Base is dc=oracle, dc=com and the first name is "Larry"
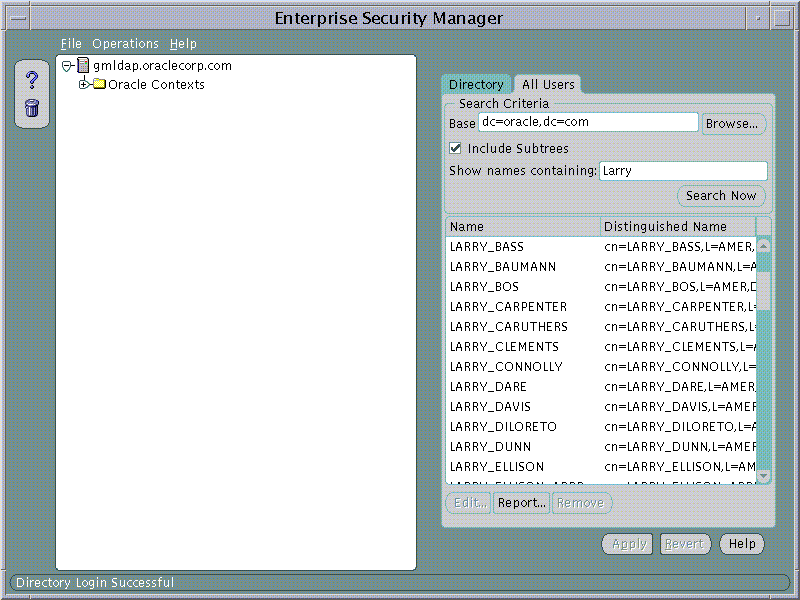
After searching for Users in the Directory, any one user can be chosen from the list and edited. This is achieved either by selecting the User from the list in the All Users page and choosing the Edit... button or by double clicking on that User in the list.
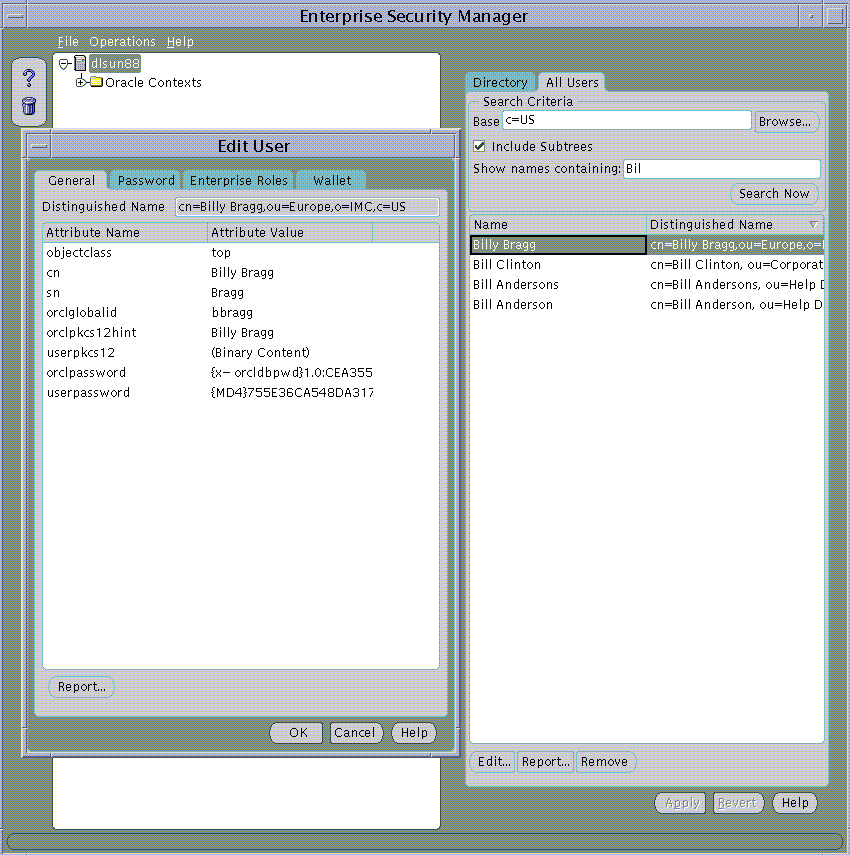
When a User in the Directory is selected for Edit, its password, Enterprise Role assignments and Oracle Wallet can be modified in the same way as discussed during creation of a new User in the Directory.
An Oracle Context is a top level Entry in the Directory underneath which is contained the data used by any Directory aware Oracle product. Enterprise Security Manager allows you to manage database and security related information in the Directory under an Oracle Context.
An Oracle Context in the Directory may either be a version 8i or version 9i Oracle Context. For Enterprise User Security there is some functionality that can only be managed using a 9i Oracle Context, for example, "Password Authenticated Global Users". Enterprise Manager for Oracle 9i may be used to manage version 9i Oracle Contexts as well version 8i Oracle Contexts in the Directory.
Oracle Enterprise Security Manager displays in its main application tree all the Oracle Contexts that exist in the Directory Server. It will display both version 9i and version 8i Oracle Contexts, should they exist. In the example below Enterprise Security Manager is connected to an Oracle Internet Directory that has been configured to support the Oracle 9i Directory Schema and an Oracle 9i Default Oracle Context.
An Oracle Context has a number of general properties that can be viewed and managed in the General page when an Oracle Context is selected on the tree:
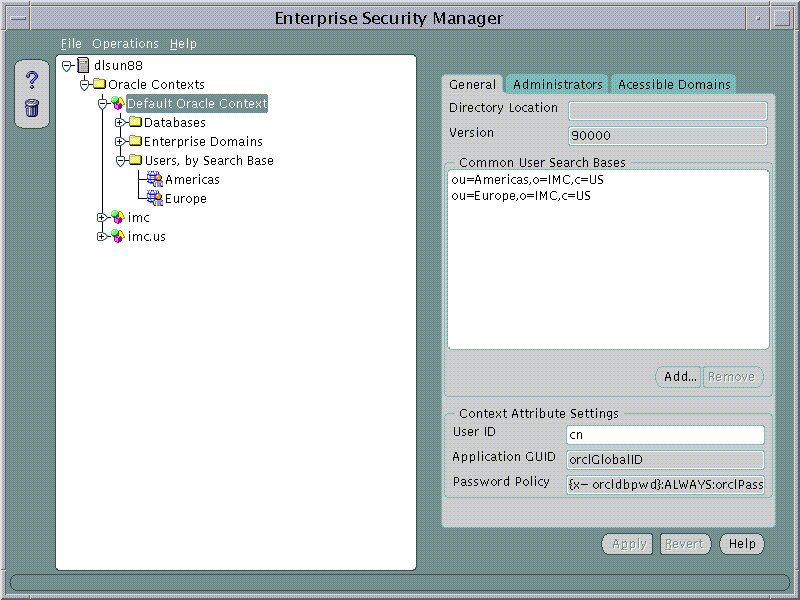
User Search Bases can be added to or removed from a version 9i Oracle Context using the Oracle Context General page.
To remove a User Search Base from the Oracle Context:
To add a new User Search Base to an Oracle Context:

An Oracle Context may define sets of Directory Users that are enabled as different categories of Administrator. Each category has varying levels of privilege for operations within an Oracle Context. Some administrator categories are only available to version 9i Oracle Contexts and some are available to both version 8i and version 9i Oracle Contexts. The Administrator Categories for an Oracle Context are as follows:
Oracle Context Administrators are managed using the Administrators Page of an Oracle Context selected on the main application tree.
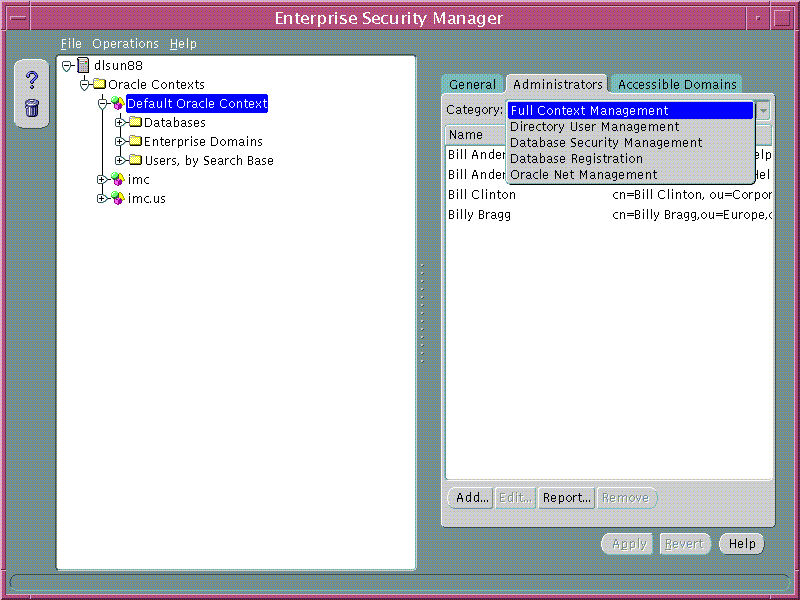
To remove a User from a list of Oracle Context Administrators:
To add a new User a list of Oracle Context Administrators:
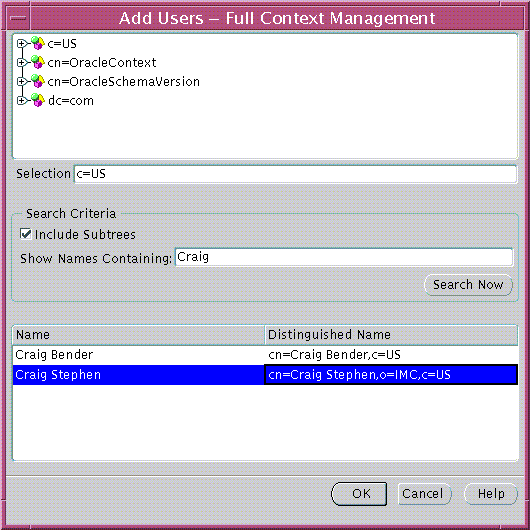
|
Note: This screen is used at all points in Enterprise Security Manager where it is necessary to choose one or more Users from the Directory. |
When an Oracle Context is selected in the main application tree you may manage the list of Enterprise Domains within that Oracle Context whose databases may accept password authenticated connections from users that have their "Database Access Restriction" enabled. To add an Enterprise Domain to the list choose "Add.." and select one of the current Enterprise Domains from the resulting dialog. To remove an Enterprise Domain from the list, select it in the Accessible Domains page and choose "Remove..."
A "Database Access Restriction" may be applied to whole subtree of Users in the Directory when it is selected under the "Users, by Search Base" tree under an Oracle Context. With this option is set, all users under that subtree may only use their passwords to access databases that exist in Enterprise Domains that have been included in the list of Accessible Domains for the Oracle Context.
The default condition for any Enterprise Domain is not to be a member of the Accessible Domains for its Oracle Context. By identifying any Enterprise Domain to be one of the Accessible Domains and also by electing certain Users to have a Database Access Restriction, you are enforcing that it is only certain known databases that may access those Users' database logon settings in the Directory.
The Directory may be used as a central repository that controls authentication and authorization on multiple databases for Users. Enterprise Security Manager allows you to manage an Oracle Context in the Directory for the purpose of database security.
Oracle 8i or 9i Databases are published to the Directory within an Oracle Context using the Oracle Database Configuration Assistant. For more information see the Oracle DBCA Guide. Once databases have been published to the Directory, Enterprise Security Manager may be used to mange User access to those databases. This is achieved using the following Objects in the Oracle Context:
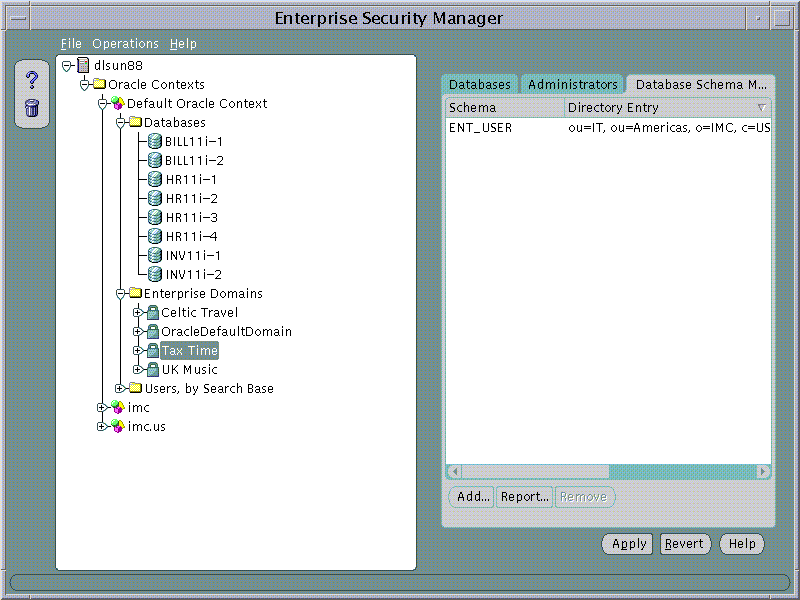
Enterprise Security Manager displays Databases and Enterprise Domains in its main application tree. Using our example of the AppsOnline Application Service provider, each of the company's databases have been published into the 9i Default Oracle Context in the Directory.
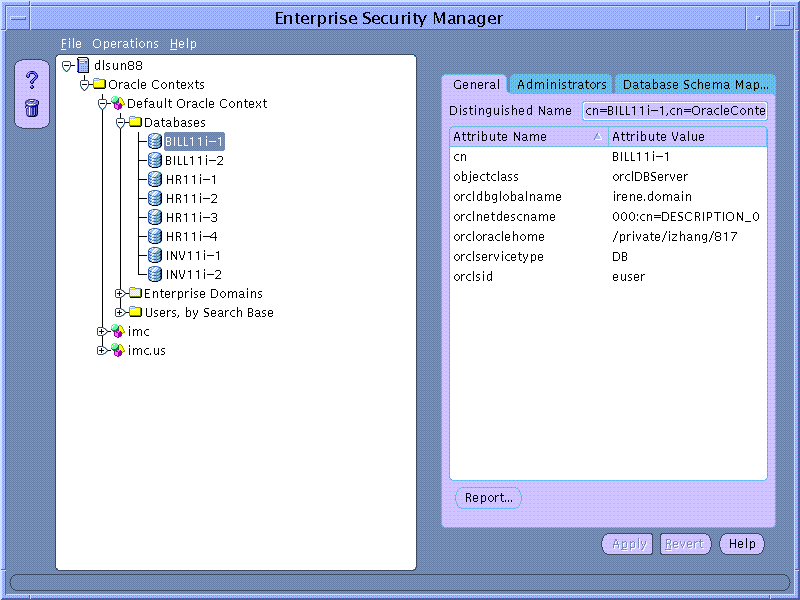
In this example AppsOnline manages Oracle 9i databases that host Applications for three customers; "UKMusic.com", "CelticTravel.com" and "TaxTime.com". Applications for UKMusic are hosted using databases INV11i-1 and INV11i-2. Applications for CelticTravel are hosted using databases BILL11i-1 and BILL11i-2. Applications for TaxTime are hosted using databases HR11i-1, HR11i-2, HR11i-3 and HR11i-4.
Given that the types of application hosted for each customer are different, only those databases that are used to support a common application type implement the same security model for their User Access. AppsOnline has decided to define three Enterprise Domains, one for each customer that it services.
After a database has been published to an Oracle Context in the Directory, Enterprise Security Manager may be used to view and modify security characteristic of that database.
An Database Administrator is a Directory User that only has privileges to modify that Database in the Oracle Context. Database Administrators may be managed using the Administrators Page when a Database is selected under an Oracle Context in the main application tree.
To remove a User from the list of Database Administrators:
To add a new User to the list of Enterprise Domain Administrators:
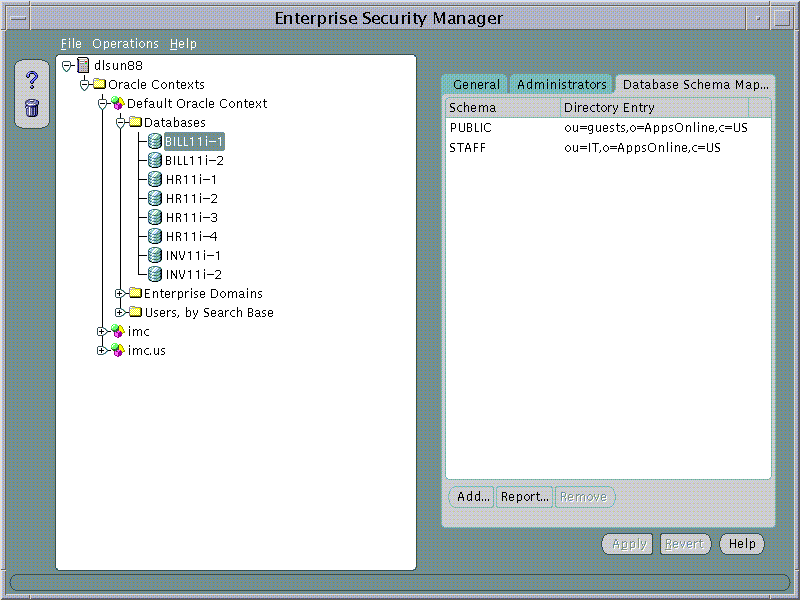
Database Schema Mappings allow databases that are registered in the Directory to accept connections from users without having any dedicated database schemas for them. For example, when user SCOTT connects to a database there must actually exist a database schema called "SCOTT" for that log on to be successful. This becomes difficult to maintain if there are thousands of Users and perhaps hundreds of databases in a very large enterprise.
Users that exist in the Directory do not need to have dedicated schemas on every Oracle 8i or 9i database to which they might connect.
A database may use a "Schema Mapping" to share one database schema between any number of Users that exist in the Directory. The Schema Mapping is a pair of values; the Base in the Directory at which Users exist and the name of the database schema that they will use.
Database Schema Mappings may be managed using the Database Schema Mappings Page when a database is selected under an Oracle Context in the main application tree. This page contains a list of database schema name and Directory Base pairs.
To remove a Mapping from the list of Database Schema Mappings n the Enterprise Domain:
To add a new Mapping to the list of Database Schema Mappings in the Enterprise Domain:
An Oracle Context will always contain at least one Enterprise Domain called, "OracleDefaultDomain". The OracleDefaultDomain is part of the Oracle Context when it is first created in the Directory. When a new database is registered into an Oracle Context it automatically becomes a member of the OracleDefaultDomain in that Oracle Context. You may create and remove your own Enterprise Domains but you cannot remove the OracleDefaultDomain from an Oracle Context.
To create a new Enterprise Domain:
An Enterprise Domain can be created in an Oracle Context either from the Operations Menu or by using a Right Mouse Button click on an Oracle Context selected in the main application tree:
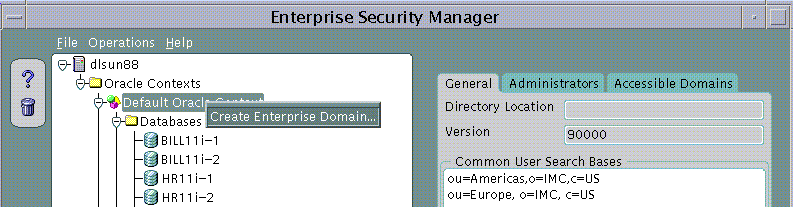
The Create Enterprise Domain screen will appear.
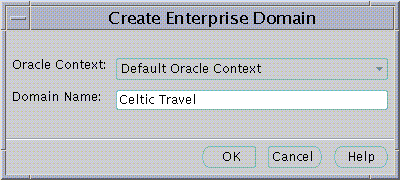
To remove an Enterprise Domain:
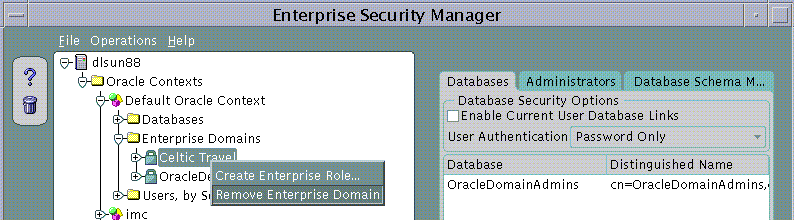
|
Note: You cannot remove an Enterprise Domain from an Oracle Context if that Enterprise Domain still contains any Enterprise Roles. |
Database membership of an Enterprise Domain in the Oracle Context may be managed using the Databases Page when an Enterprise Domain is selected on the main application tree:
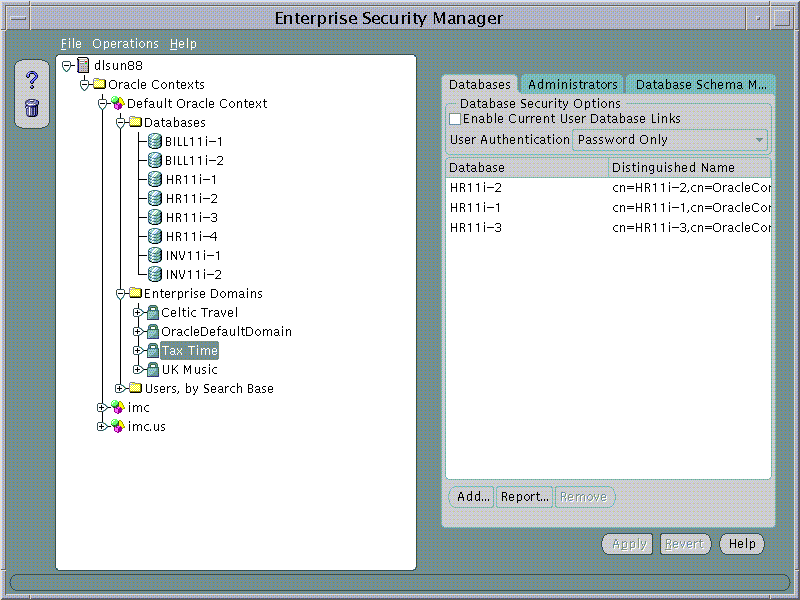
To remove a database from an Enterprise Domain:
To add a database to an Enterprise Domain:
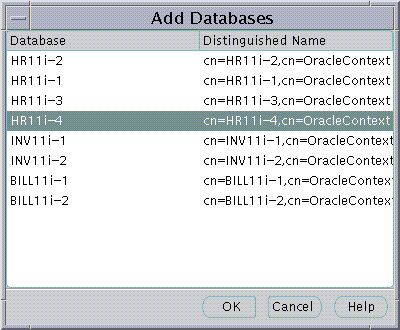
The Databases Page may be used to manage database security options that will apply to all the databases that are members of the Enterprise Domain. These options are as follows:
An Enterprise Domain Administrator is a Directory User that only has privileges to modify the content of that Enterprise Domain. Enterprise Domain Administrators may be managed using the Administrators Page when an Enterprise Domain is selected under an Oracle Context in the main application tree.
To remove a User from the list of Enterprise Domain Administrators:
To add a new User to the list of Enterprise Domain Administrators:
Database Schema Mappings may be managed for each database in an Oracle Context as discussed earlier. Schema Mappings may also be performed for each Enterprise Domain in an Oracle Context using the Database Schema Mappings Page with an Enterprise Domain selected in the main application tree. These Mappings apply to all databases that are members of the Enterprise Domain. Therefore, each database in the Enterprise Domain must have a schema of the same name used in the Mapping.
To remove a Mapping from the list of Database Schema Mappings in the Enterprise Domain:
To add a new Mapping to the list of Database Schema Mappings in the Enterprise Domain:
An Enterprise Domain within an Oracle Context may contain one or more Enterprise Roles.
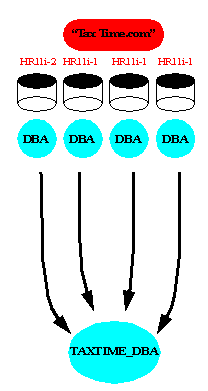
In the example discussed earlier, AppsOnline has created three Enterprise Domains that group the databases it uses to serve each of its customers. This permits the company to define Enterprise Roles for each Enterprise Domain. An Enterprise Role is a set of Oracle Role based authorizations across on or more databases in an Enterprise Domain.
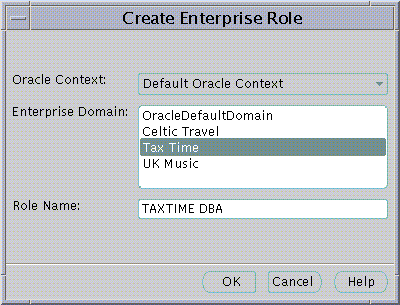
A simple Enterprise Role is defined by AppsOnline for DBA privileges on its databases in the "Tax Time" Enterprise Domain:
An Enterprise Role can be created in an Enterprise Domain either from the Operations Menu or by using a Right Mouse Button click on an Enterprise Domain selected in the main application tree:
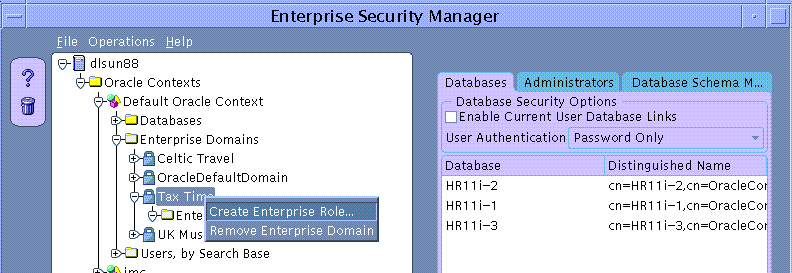
The Create Enterprise Role dialog appears.
Database Role membership of an Enterprise Role in an Enterprise Domain may be managed using the Database Global Roles Page when an Enterprise Role is selected on the main application tree. This page lists the names of each Global Role that belongs to the Enterprise Role along with the name of the database on which that Global Role exists.
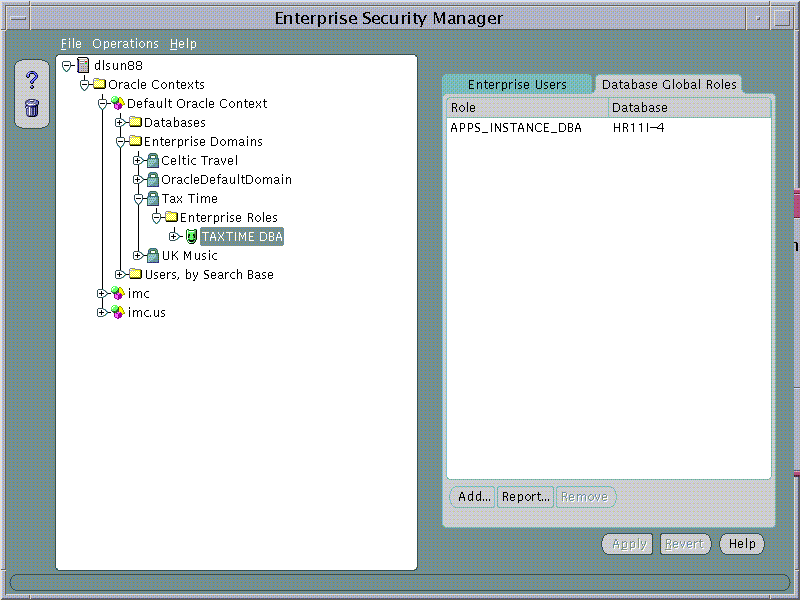
When populating an Enterprise Role with different database roles it is only possible to reference roles on databases that are configured to be "Global Roles" on those databases. A Global Role on a database is identical to a normal Role, except that the administrator of the database has elected it only to be authorized via the Directory. A database administrator cannot locally grant and revoke Global Roles to users of the database.
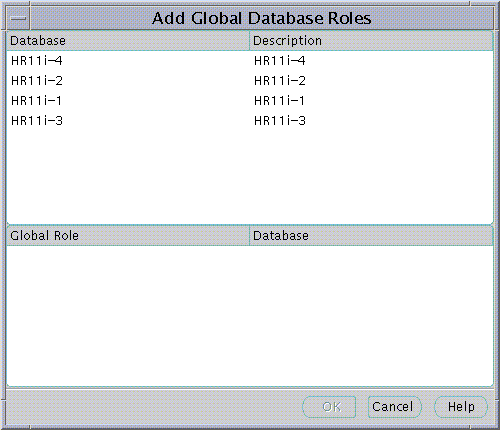
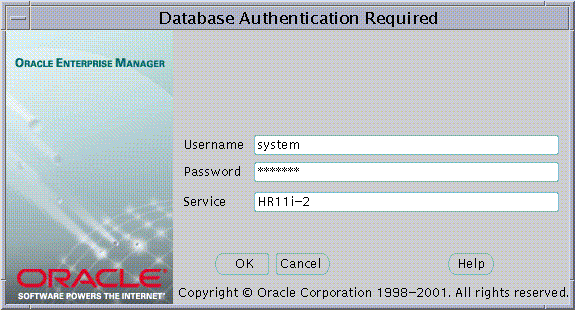
The name of the database appears in the Service field by default.You may use this name to connect to the database if your ORACLE_HOME has LDAP enabled as it Oracle Net Naming method or if this name appears as a TNS alias in your local Oracle Net configuration. Otherwise you may overwrite the content of the Service field with any other TNS alias configured for that database or by a connect string in the format:
<host>:<port>:<oracle sid>
For example, "cartman:1521:broncos"
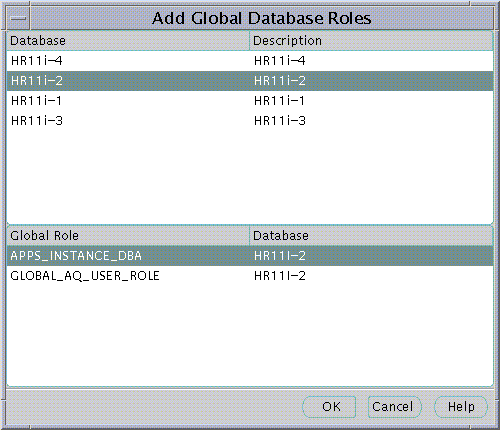
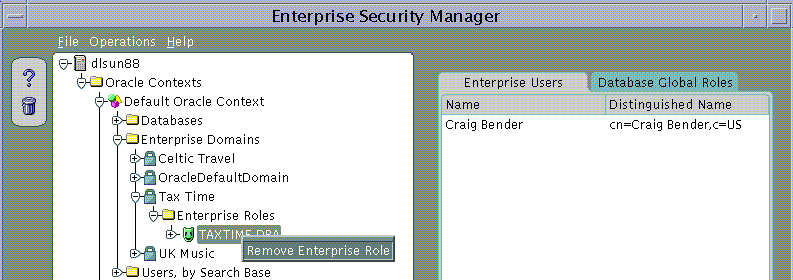
An Enterprise Role Grantee is a Directory User to whom has been granted an Enterprise Role and therefore all database Global Roles contained within that Enterprise Role. Enterprise Role Grantees may be managed using the Enterprise Users Page when an Enterprise Role is selected under an Enterprise Domain in the main application tree.
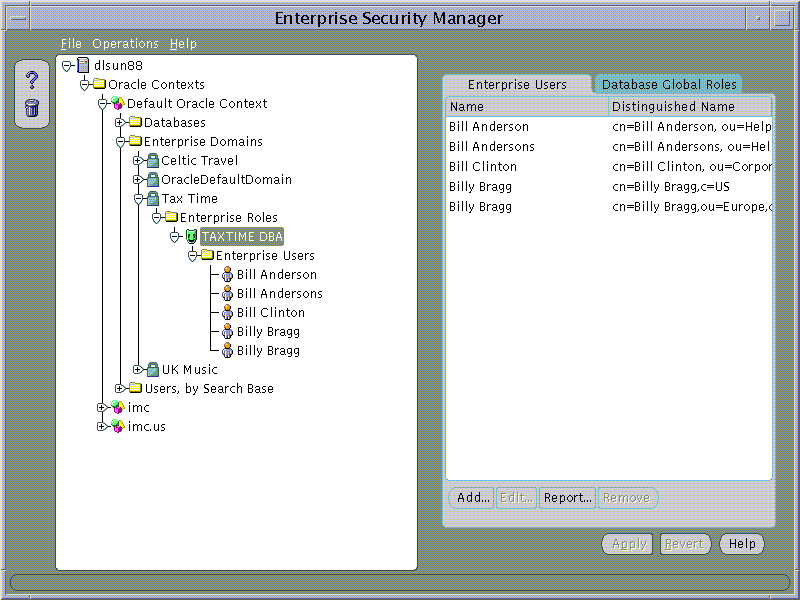
Enterprise Role Grantees will also appear in the Enterprise Users tree under a selected Enterprise Role. A User selected on this tree can be edited as discussed in Part 1.
|
|
 Copyright © 2002 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|