Release 3 (8.1.7)
Part Number A86030-01
Library |
Solution Area |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle8i Application Developer's Guide - XML Release 3 (8.1.7) Part Number A86030-01 |
|
Using XML Parser for C, 4 of 10
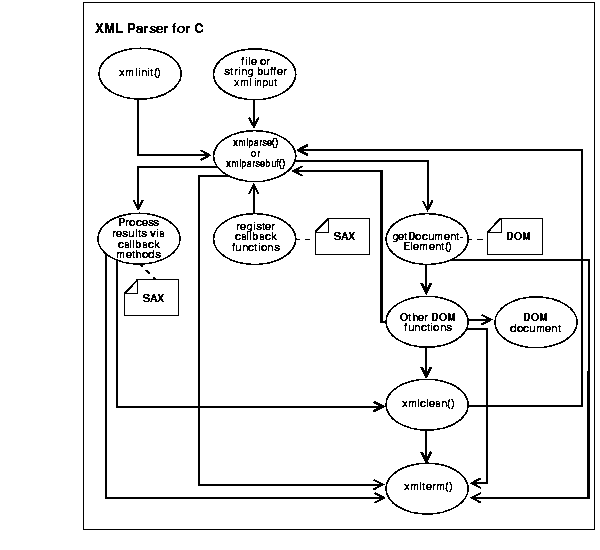
Figure 21-1 illustrates the XML Parser for C functionality as follows:
XMLinit() function initializes the parsing process.
xmlparser() function. If the input is a string buffer, it is parsed using the xmlparserbuf() function.
DOM: If you are using the DOM interface, include the following steps:
xmlparse() or xmlparseBuffer() function calls .getDocumentElement(). If no other DOM functions are being applied, you can invoke xmlterm().
xmlterm()
xmlclean() to clean up any data structures created during the parse process. You would then call xmlterm()
SAX: If you are using the SAX interface, include the following steps:
xmlclean() to clean up the memory and structures used during a parse, and go to Step 5. or return to Step 2.
xmlterm()
The sequence of calls to the parser can be any of the following:
xmlinit() - xmlparse() or
xmlparsebuf() - xmlterm()
xmlinit() - xmlparse() or
xmlparsebuf() - xmlclean() - xmlparse() or
xmlparsebuf() - xmlclean() - ... - xmlterm()
xmlinit() - xmlparse() or
xmlparsebuf() - xmlparse() or
xmlparsebuf() -... - xmlterm()
|
|
 Copyright © 1996-2000, Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|