10g (9.0.4)
Part Number B12118-01
Home |
Solution Area |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle® Internet Directory Administrator's Guide 10g (9.0.4) Part Number B12118-01 |
|
Directory Concepts and Architecture, 15 of 15
To fulfill the requests of users, some Oracle components gather data from various repositories and services. To gather the data, these components require the following information:
This section contains these topics:
Information about the resources that an application uses to service a user request is called resource type information. A resource type can be, for example, an Oracle9i Database Server or a Java Database Connectivity Pluggable Data Source. Resource type information includes such items as the class used to authenticate a user, the user identifier, and the password.
You specify resource type information by using the Oracle Internet Directory Self-Service Console.
Information for connecting and authenticating users to the databases is called resource access information. It is stored in an entry called a resource access descriptor (RAD) from which it can be retrieved and shared by various Oracle components.
For example, to service the request of a user for a sales report, Oracle Application Server Reports Services queries multiple databases. When it does this, it does the following:
Once it has done this, it compiles the report.
You specify resource access information by using the Oracle Internet Directory Self-Service Console. You can specify resource access information for each individual user or commonly for all users. In the latter case, all users connecting to a given application use, by default, the same information to connect to the necessary databases. Oracle Corporation recommends defining default resource access information whenever an application has its own integrated account management--for example, where each user is defined within the application itself by means of a unique single sign-on user name.
Figure 2-10 shows where resource information is located in the DIT.
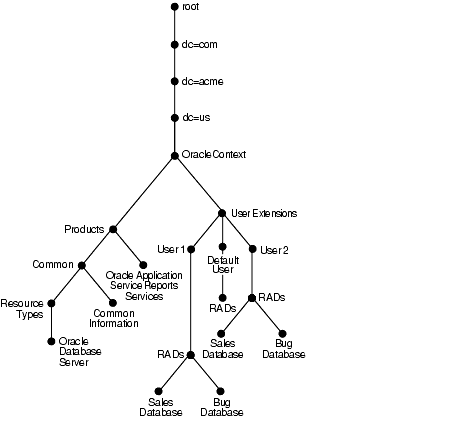
As Figure 2-10 shows, the resource access and resource type information is stored in the Oracle Context.
Resource access information for each user is stored in the cn=User Extensions node in the Oracle Context. In this example, the cn=User Extensions node contains resource access information for both the default user and for specific users. In the latter cases, the resource access information includes that needed for accessing both the Sales and the Bug databases.
Resource access information for each application is stored in the object identified by the application name--in this example, cn=Oracle Application Server Reports Services, cn=Products,cn=Oracle Context,dc=us,dc=acme,dc=com. This is the user information specific to that product.
Resource type information is stored in the container cn=resource types, cn=common,cn=products,cn=Oracle Context.
|
See Also:
|
|
|
 Copyright © 1999, 2003 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|