10g (9.0.4)
Part Number B10321-01
Home |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE Servlet Developer's Guide 10g (9.0.4) Part Number B10321-01 |
|
Dynamic Web applications typically access a database to provide content. This chapter, consisting of the following sections, shows how servlets can use JDBC, the Java standard for database connectivity, and Enterprise JavaBeans, used for secure, transactional server-side processing:
A servlet can access a database using a JDBC driver. The recommended way to use JDBC is by using an OC4J data source to get the database connection. See Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE Services Guide for information about OC4J data sources. For more information about JDBC, see the Oracle9i JDBC Developer's Guide and Reference.
Part of the power of servlets comes from their ability to retrieve data from a database. A servlet can generate dynamic HTML by getting information from a database and sending it back to the client. A servlet can also update a database, based on information passed to it in the HTTP request.
The example in this section shows a servlet that gets some information from the user through an HTML form and passes the information to a servlet. The servlet completes and executes a SQL statement, querying the sample Human Resources (HR) schema to get information based on the request data.
A servlet can get information from the client in many ways. This example reads a query string from the HTTP request.
The Web browser accesses a form in a page that is served through the Web listener. Copy the following HTML into a file, EmpInfo.html:
<html> <head> <title>Query the Employees Table</title> </head> <body> <form method=GET ACTION="/servlet/GetEmpInfo"> The query is<br> SELECT LAST_NAME, EMPLOYEE_ID FROM EMPLOYEES WHERE LAST NAME LIKE ?.<p> Enter the WHERE clause ? parameter (use % for wildcards).<br> Example: 'S%':<br> <input type=text name="queryVal"> <p> <input type=submit> </form> </body> </html>
Then save this file in the root directory of the OC4J default Web application (j2ee/home/default-web-app by default).
The servlet that the preceding HTML page calls takes the input from a query string. The input is the completion of the WHERE clause in the SELECT statement. The servlet then appends this input to construct the database query. Much of the code in this servlet consists of the JDBC statements required to connect to the database server and retrieve and process the query rows.
This servlet makes use of the init() method to do a one-time lookup of a data source, using JNDI. The data source lookup assumes a data source such as the following has been defined in the data-sources.xml file in the OC4J configuration files directory, as is the case by default:
<data-source class="com.evermind.sql.DriverManagerDataSource" name="OracleDS" location="jdbc/OracleCoreDS" xa-location="jdbc/xa/OracleXADS" ejb-location="jdbc/OracleDS" connection-driver="oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver" username="hr" password="hr" url="jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl" inactivity-timeout="30" />
It is advisable to use only the ejb-location JNDI name in the JNDI lookup for an emulated data source. See the Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE Services Guide for more information about data sources.
This example also assumes the following data source definition in the web.xml file:
<resource-ref> <res-auth>Container</res-auth> <res-ref-name>jdbc/OracleDS</res-ref-name> <res-type>javax.sql.DataSource</res-type> </resource-ref>
Here is the servlet code:
import javax.servlet.*; import javax.servlet.http.*; import javax.naming.*; // for JNDI import javax.sql.*; // extended JDBC interfaces (such as data sources) import java.sql.*; // standard JDBC interfaces import java.io.*; public class GetEmpInfo extends HttpServlet { DataSource ds = null; Connection conn = null; public void init() throws ServletException { try { InitialContext ic = new InitialContext(); // JNDI initial context ds = (DataSource) ic.lookup("jdbc/OracleDS"); // JNDI lookup conn = ds.getConnection(); // database connection through data source } catch (SQLException se) { throw new ServletException(se); } catch (NamingException ne) { throw new ServletException(ne); } } public void doGet (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { /* Get the user-specified WHERE clause from the HTTP request, then */ /* construct the SQL query. */ String queryVal = req.getParameter("queryVal"); String query = "select last_name, employee_id from employees " + "where last_name like " + queryVal; resp.setContentType("text/html"); PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter(); out.println("<html>"); out.println("<head><title>GetEmpInfo</title></head>"); out.println("<body>"); /* Create a JDBC statement object, execute the query, and set up */ /* HTML table formatting for the output. */ try { Statement stmt = conn.createStatement(); ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(query); out.println("<table border=1 width=50%>"); out.println("<tr><th width=75%>Last Name</th><th width=25%>Employee " + "ID</th></tr>"); /* Loop through the results. Use the ResultSet getString() and */ /* getInt() methods to retrieve the individual data items. */ int count=0; while (rs.next()) { count++; out.println("<tr><td>" + rs.getString(1) + "</td><td>" +rs.getInt(2) + "</td></tr>"); } out.println("</table>"); out.println("<h3>" + count + " rows retrieved</h3>"); rs.close(); stmt.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { se.printStackTrace(out); } out.println("</body></html>"); } public void destroy() { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException se) { se.printStackTrace(); } } }
To deploy this example, save the HTML file in the root directory of the OC4J default Web application (j2ee/home/default-web-app by default) and save the Java servlet in the /WEB-INF/classes directory of the default Web application. The GetEmpInfo.java file is automatically compiled when the servlet is invoked by the form.
To test the example directly through the OC4J listener, such as in OC4J standalone, invoke the EmpInfo.html page from a Web browser as follows:
http://host:8888/EmpInfo.html
This assumes "/" is the context path of the OC4J standalone default Web application.
Complete the form and click Submit Query.
|
Note: For general information about invoking servlets in OC4J, see "Servlet Invocation". |
When you invoke EmpInfo.html, you will see a browser window that looks something like Figure 4-1.
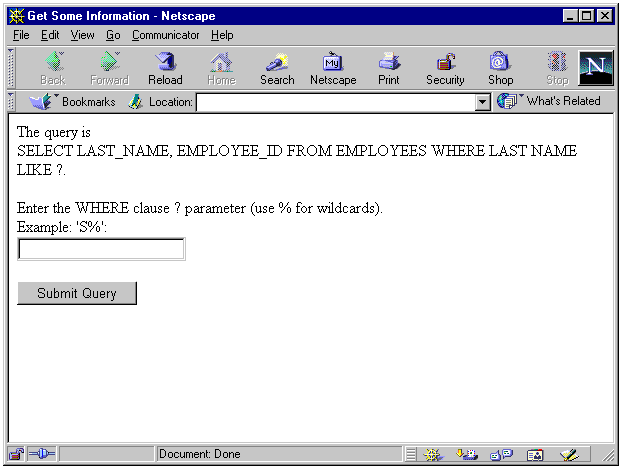
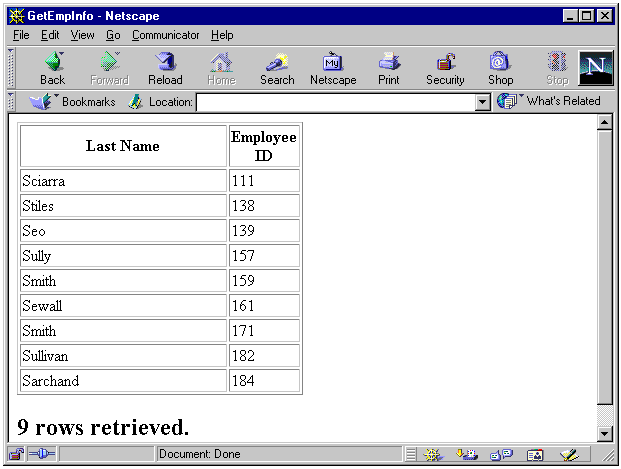
Entering "S%" in the form and clicking Submit Query calls the GetEmpInfo servlet. The results look something like Figure 4-2.
A servlet can call Enterprise JavaBeans to perform additional processing. A typical application design often uses servlets as a front-end to do the initial processing of client requests, with EJBs being called to perform the business logic that accesses or updates a database. Container-managed-persistence (CMP) entity beans, in particular, are well-suited for such tasks.
The following sections discuss and provide examples for typical scenarios for the use of EJBs from servlets:
|
Notes:
|
The following sections provide an overview of considerations for the use of EJBs from servlets:
The servlet-EJB examples in this chapter cover three scenarios:
Servlet-EJB communications use JNDI for lookup and RMI for the EJB calls, over either ORMI (the Oracle implementation of RMI) or IIOP (the standard and interoperable Internet Inter-Orb Protocol). For the JNDI initial context factory, the examples below use the ApplicationInitialContextFactory class, which supports EJB references in web.xml, and the RMIInitialContextFactory class, which does not. Depending on the situation, another possibility is ApplicationClientInitialContextFactory, which supports EJB references in the application-client.xml file. For more information about the use of JNDI and RMI with EJBs, refer to the Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE Enterprise JavaBeans Developer's Guide.
A remote lookup requires a JNDI environment to be set up, including the URL and a user name and password. This setup is typically in the servlet code, as shown in the "EJB Remote Lookup Outside the Application", but for a lookup in the same application it can be in the rmi.xml file instead.
Remote lookup within the same application on different hosts also requires proper setting of the remote flag in the orion-application.xml file for your application on each host, as shown in "Use of the Remote Flag".
As in any application where EJBs are used, there must be an entry for each EJB in the ejb-jar.xml file.
|
Note: The examples here consider only an ORMI scenario. For information about using IIOP, see the Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE Enterprise JavaBeans Developer's Guide. |
In the EJB 1.1 specification, an EJB always had a remote interface extending the javax.ejb.EJBObject interface and a home interface extending the javax.ejb.EJBHome interface. In this model, all EJBs are defined as remote objects, adding unnecessary overhead to EJB calls in situations where the servlet or other calling module is co-located with the EJB.
|
Note:
The OC4J |
The EJB 2.0 specification adds support for local interfaces for co-located lookups. In this case, the EJB has a local interface that extends the javax.ejb.EJBLocalObject interface, in contrast to having a remote interface. And it has a local home interface that extends the javax.ejb.EJBLocalHome interface, in contrast to having a home interface.
Any lookup involving EJB remote interfaces uses RMI and has additional overhead such as for security. RMI and other overhead are eliminated when you use local interfaces.
This section presents an example of a single servlet, HelloServlet, that calls a single co-located EJB, HelloBean, using local interfaces. This is the simplest servlet-EJB scenario.
Here are the key steps of the servlet code:
javax.naming for JNDI and javax.rmi for RMI.
helloWorld() method on the local object, which puts the EJB output message in a Java string.
The following sections cover all aspects of the sample:
For further discussion and another complete example of using local interfaces, see the OC4J How-To document at the following location:
http://otn.oracle.com/tech/java/oc4j/htdocs/how-to-ejb-local-interfaces.html
This section has code for a servlet that calls a co-located EJB, using local interfaces. This includes servlet code, EJB code, and EJB interface code. Note the bold passages in particular.
This section has the servlet code. For a local lookup, the default JNDI context is used.
By default, this servlet uses ApplicationInitialContextFactory for the JNDI initial context factory, and therefore the web.xml file is searched for EJB references. The java:comp syntax for the JNDI lookup indicates there is a reference defined within the application for the EJB, in this case in the web.xml file.
See Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE Enterprise JavaBeans Developer's Guide for information about JNDI initial context factory classes.
package myServlet; // Step 1: Import the EJB package. import myEjb.*; import java.io.*; import javax.servlet.*; import javax.servlet.http.*; import javax.naming.*; // for JNDI import javax.rmi.*; // for RMI, including PortableRemoteObject import javax.ejb.CreateException; public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { response.setContentType("text/html"); PrintWriter out = response.getWriter(); out.println("<html><head><title>Hello from Servlet</title></head>"); // Step 2: Print a message from the servlet. out.println("<body><h1>Hello from hello servlet!</h1></body>"); // Step 3: Create an output string, with an error default. String s = "If you see this message, the ejb was not invoked properly!!"; // Step 4: Use JNDI to look up the EJB local home interface. try { InitialContext ic = new InitialContext(); HelloLocalHome hlh = (HelloLocalHome)ic.lookup ("java:comp/env/ejb/HelloBean"); // Step 5: Create the EJB local interface object. HelloLocal hl = (HelloLocal)hlh.create(); // Step 6: Invoke the helloWorld() method on the local object. s = hl.helloWorld(); } catch (NamingException ne) { System.out.println("Could not locate the bean."); } catch (CreateException ce) { System.out.println("Could not create the bean."); } catch (Exception e) { // Unexpected exception; send back to client for now. throw new ServletException(e); } // Step 7: Print the message from the EJB. out.println("<br>" + s); out.println("</html>"); } }
The EJB, as shown here, implements a single method, helloWorld(), that returns a greeting to the caller. The local home and local EJB interface code is also shown below.
package myEjb; import javax.ejb.*; public class HelloBean implements SessionBean { public String helloWorld () { return "Hello from myEjb.HelloBean"; } public void ejbCreate () throws CreateException {} public void ejbRemove () {} public void setSessionContext (SessionContext ctx) {} public void ejbActivate () {} public void ejbPassivate () {} }
Here is the code for the local home interface:
package myEjb; import javax.ejb.EJBLocalHome; import javax.ejb.CreateException; public interface HelloLocalHome extends EJBLocalHome { public HelloLocal create () throws CreateException; }
Here is the code for the local interface:
package myEjb; import javax.ejb.EJBLocalObject; public interface HelloLocal extends EJBLocalObject { public String helloWorld (); }
This section discusses the deployment steps and configuration for the Servlet-EJB local lookup sample application. In the descriptor files, note the bold passages in particular. To deploy this application, you will need an EAR file that contains the following:
web.xml Web descriptor
ejb-jar.xml EJB descriptor
application.xml application-level descriptor
See Chapter 5, "Deployment and Configuration Overview", for an overview of deployment to OC4J. See the Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE User's Guide for detailed information.
Create a standard web.xml Web descriptor as follows. Note the <ejb-local-ref> element and its <local-home> and <local> subelements for the use of local interfaces.
<?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE WEB-APP PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN" "http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd"> <web-app> <display-name>HelloServlet</display-name> <description> HelloServlet </description> <servlet> <servlet-name>ServletCallingEjb</servlet-name> <servlet-class>myServlet.HelloServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>ServletCallingEjb</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/DoubleHello</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <welcome-file-list> <welcome-file> index.html </welcome-file> </welcome-file-list> <ejb-local-ref> <ejb-ref-name>ejb/HelloBean</ejb-ref-name> <ejb-ref-type>Session</ejb-ref-type> <local-home>myEjb.HelloLocalHome</local-home> <local>myEjb.HelloLocal</local> </ejb-local-ref> </web-app>
Next, create the standard J2EE directory structure for Web application deployment, then move the web.xml Web deployment descriptor and the compiled servlet class file into the structure. Once you create and populate the directory structure, create a WAR file named myapp-web.war (for example) to contain the files. Here are the WAR file contents:
META-INF/ META-INF/MANIFEST.MF WEB-INF/ WEB-INF/classes/ WEB-INF/classes/myServlet/ WEB-INF/classes/myServlet/HelloServlet.class WEB-INF/web.xml
(The MANIFEST.MF file is created automatically by the JAR utility.)
Create a standard ejb-jar.xml EJB descriptor as follows. Note that the <ejb-ref-name> value in the web.xml file above corresponds to the <ejb-name> value here. In this example, they use the same name, which is a good practice but is not required. The Web tier can specify any reference name, which is independent of the JNDI name.
Also note the <local-home> and <local> elements, for the use of local interfaces. These must be the same entries as in the web.xml file.
<?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE ejb-jar PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Enterprise JavaBeans 2.0//EN" "http://java.sun.com/dtd/ejb-jar_2_0.dtd"> <ejb-jar> <enterprise-beans> <session> <description>Hello Bean</description> <ejb-name>ejb/HelloBean</ejb-name> <local-home>myEjb.HelloLocalHome</local-home> <local>myEjb.HelloLocal</local> <ejb-class>myEjb.HelloBean</ejb-class> <session-type>Stateful</session-type> <transaction-type>Container</transaction-type> </session> </enterprise-beans> <assembly-descriptor> </assembly-descriptor> </ejb-jar>
Create a JAR file named myapp-ejb.jar (for example) with the standard J2EE structure to hold the EJB components. Here are the JAR file contents:
META-INF/ META-INF/MANIFEST.MF META-INF/ejb-jar.xml myEjb/ myEjb/HelloBean.class myEjb/HelloLocalHome.class myEjb/HelloLocal.class
(The MANIFEST.MF file is created automatically by the JAR utility.)
To deploy the application, create a standard application deployment descriptor, application.xml. This file describes the modules in the application.
<?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE application PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD J2EE Application 1.3//EN" "http://java.sun.com/dtd/application_1_3.dtd"> <application> <display-name>Servlet_calling_ejb_example</display-name> <module> <web> <web-uri>myapp-web.war</web-uri> <context-root>/myapp</context-root> </web> </module> <module> <ejb>myapp-ejb.jar</ejb> </module> </application>
The <context-root> element is required, but in an OC4J standalone environment it is ignored. The context path is actually specified through the root attribute of the appropriate <web-app> element in http-web-site.xml, as shown in "Deployment Configuration" below. For consistency, and to avoid confusion, use the same setting for <context-root> as for the <web-app> root attribute.
Finally, create an EAR file named myapp.ear (for example) with the standard J2EE structure to hold the application components. Here are the EAR file contents:
META-INF/ META-INF/MANIFEST.MF META-INF/application.xml myapp-ejb.jar myapp-web.war
(The MANIFEST.MF file is created automatically by the JAR utility.)
To deploy the application, the following entry is added to the server.xml file in the OC4J configuration files directory, specifying the appropriate path information:
<application name="myapp" path="your_path/lib/myapp.ear" />
If you use the admin.jar -deploy option to deploy the application, this entry is made automatically. (See "Using admin.jar to Deploy the EAR File".)
The next step is to bind the Web module to a Web site. You will need the following entry in the Web site XML file (typically http-web-site.xml in OC4J standalone) in the OC4J configuration files directory:
<web-app application="myapp" name="myapp-web" root="/myapp" />
If you use the admin.jar -bindWebApp option after deploying the application, this entry is made automatically. (See "Using admin.jar to Bind the Web Application".)
According to the configuration of this example, you can invoke the servlet as follows, assuming a host myhost. By default, OC4J standalone uses port 8888.
http://myhost:8888/myapp/DoubleHello
The context path, myapp, is according to the relevant <web-app> element root setting in the Web site XML file. The servlet path, DoubleHello, is according to the relevant <url-pattern> element in the web.xml file.
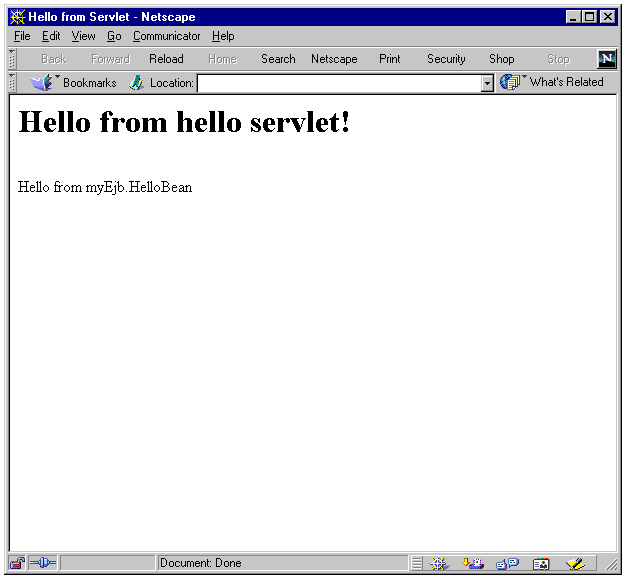
Figure 4-3, which follows, shows the application output to a Web browser. The output from the servlet is printed in H1 format at the top, then the output from the EJB is printed in text format below that.
This section adapts the preceding HelloServlet/HelloBean example for remote lookup within the same application, where the servlet and EJB are in the same application but on different tiers. The discussion highlights use of the orion-application.xml file remote flag, which determines where EJBs are deployed and searched for, and necessary changes to the code and descriptor files.
In this example, the default ApplicationInitialContextFactory is used for the JNDI context, as in the preceding local lookup example. An alternative would be to use RMIInitialContextFactory, as discussed in the next example, "EJB Remote Lookup Outside the Application".
In OC4J, to perform a remote EJB lookup within the same application but on different tiers (where the same application has been deployed to both tiers), you must set the EJB remote flag appropriately on each tier. When this flag is set to "true", beans will be looked up on a remote server instead of the EJB service being used on the local server.
The remote flag is an attribute in the <ejb-module> subelement of an <orion-application> element in the orion-application.xml file. The default setting is remote="false". Here is an example of setting it to "true":
<orion-application ... > ... <ejb-module remote="true" ... /> ... </orion-application>
The suggested steps are illustrated in Figure 4-4 and described below.
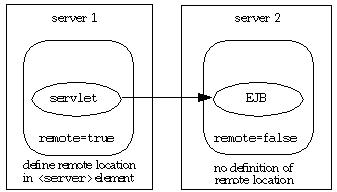
remote flag value of "false". If you provide an orion-application.xml file, it is suggested that it either have the remote flag explicitly set to "false", or no remote flag setting at all, in which case its value is "false" by default. If you do not provide orion-application.xml, OC4J generates the file automatically with the remote flag disabled.
remote="true" in the orion-application.xml file for your application on server 1, the servlet tier. Given this setting, the servlet will not look for EJBs on server 1.
remote="false" in the orion-application.xml file for your application on server 2, the EJB tier. Given this setting, the servlet will look for EJBs on server 2.
<server> element in the rmi.xml file on server 1 to specify the remote host, server 2, where the servlet will look for the EJB. This includes the host name and port as well as a user name and password for authentication:
<rmi-server ... > ... <server host="remote_host" port="remote_port" username="user_name" password="password" /> ... </rmi-server>
If there are <server> elements for multiple remote servers, the OC4J container will search all of them for the target EJB.
|
Note:
In the |
check-for-updates flag is enabled
admin.jar -updateConfig option
See "Key OC4J Flags for Development" for information about check-for-updates and -updateConfig.
|
Note:
Remember that this discussion assumes an OC4J standalone environment during development. In an Oracle Application Server environment, any configuration must be through Enterprise Manager or the Servlet EJB calls in an Oracle Application Server environment are discussed in the Oracle Application Server Containers for J2EE Enterprise JavaBeans Developer's Guide. |
This section has code for a servlet-EJB sample using remote lookup of an EJB component within the same application. This includes servlet code, EJB code, and EJB interface code. Note the bold passages in particular.
This section contains the servlet code. In this example, the code and configuration are fundamentally the same as in the local lookup example, aside from two differences:
javax.rmi.PortableRemoteObject.narrow() static method to ensure that objects can be cast to the desired type. This was not required in the local lookup example, but is mandatory for any remote lookup.
Again, the default ApplicationInitialContextFactory is used for the JNDI initial context factory, the java:comp syntax is used for the lookup, and the web.xml file is searched for EJB references.
This example assumes that the rmi.xml file on the servlet tier has been set up to specify the host, port, user name, and password for the remote lookup, as shown in the preceding section, "Use of the Remote Flag". With this assumption, there is no need to set up a JNDI context (URL, user name, and password) in the servlet code.
package myServlet; // Step 1: Import the EJB package. import myEjb.*; import java.io.*; import javax.servlet.*; import javax.servlet.http.*; import javax.naming.*; // for JNDI import javax.rmi.*; // for RMI, including PortableRemoteObject import javax.ejb.CreateException; import java.rmi.RemoteException; public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { response.setContentType("text/html"); PrintWriter out = response.getWriter(); out.println("<html><head><title>Hello from Servlet</title></head>"); // Step 2: Print a message from the servlet. out.println("<body><h1>Hello from hello servlet!</h1></body>"); // Step 3: Create an output string, with an error default. String s = "If you see this message, the ejb was not invoked properly!!"; // Step 4: Use JNDI to look up the EJB home interface. try { InitialContext ic = new InitialContext(); Object homeObject = ic.lookup("java:comp/env/ejb/HelloBean"); HelloHome hh = (HelloHome) PortableRemoteObject.narrow(homeObject,HelloHome.class); // Step 5: Create the EJB local interface object. HelloRemote hr = (HelloRemote) PortableRemoteObject.narrow(hh.create(),HelloRemote.class); // Step 6: Invoke the helloWorld() method on the local object. s = hr.helloWorld(); } catch (NamingException ne) { System.out.println("Could not locate the bean."); } catch (CreateException ce) { System.out.println("Could not create the bean."); } catch (RemoteException ce) { System.out.println("Error during execution of remote call."); } catch (Exception e) { // Unexpected exception; send back to client for now. throw new ServletException(e); } // Step 7: Print the message from the EJB. out.println("<br>" + s); out.println("</html>"); } }
The EJB code for a remote lookup within the same application is very similar to that for a local lookup, but adds a RemoteException. The home and remote EJB interface code is also shown below.
package myEjb; import javax.ejb.*; public class HelloBean implements SessionBean { public String helloWorld () { return "Hello from myEjb.HelloBean"; } public void ejbCreate () throws CreateException {} public void ejbRemove () {} public void setSessionContext (SessionContext ctx) {} public void ejbActivate () {} public void ejbPassivate () {} }
Here is the code for the home interface. Extend EJBHome (instead of EJBLocalHome as when local interfaces are used). Also, a RemoteException is added.
package myEjb; import java.rmi.RemoteException; import javax.ejb.EJBHome; import javax.ejb.CreateException; public interface HelloHome extends EJBHome { public HelloRemote create () throws RemoteException, CreateException; }
Here is the code for the remote interface. Extend EJBObject (instead of EJBLocalObject as when local interfaces are used). As with the home interface above, the use of RemoteException is added.
package myEjb; import java.rmi.RemoteException; import javax.ejb.EJBObject; public interface HelloRemote extends EJBObject { public String helloWorld () throws RemoteException; }
This section highlights web.xml and ejb-jar.xml entries to use with remote interfaces. You can compare the highlighted passages to parallel passages in the local interface example.
|
Note:
The
The |
The remote flag must also be set appropriately in orion-application.xml on each host, as discussed in "Use of the Remote Flag".
The contents of web.xml for this example are as follows. Note the <ejb-ref> element and its <home> and <remote> subelements, for use of remote interfaces.
<?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE WEB-APP PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN" "http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd"> <web-app> <display-name>HelloServlet</display-name> <description> HelloServlet </description> <servlet> <servlet-name>ServletCallingEjb</servlet-name> <servlet-class>myServlet.HelloServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>ServletCallingEjb</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/DoubleHello</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <welcome-file-list> <welcome-file> index.html </welcome-file> </welcome-file-list> <ejb-ref> <ejb-ref-name>ejb/HelloBean</ejb-ref-name> <ejb-ref-type>Session</ejb-ref-type> <home>myEjb.HelloHome</home> <remote>myEjb.HelloRemote</remote> </ejb-ref> </web-app>
For this example, the contents of ejb-jar.xml are as follows. Note the <home> and <remote> elements, for the use of remote interfaces.
<?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE ejb-jar PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Enterprise JavaBeans 2.0//EN" "http://java.sun.com/dtd/ejb-jar_2_0.dtd"> <ejb-jar> <enterprise-beans> <session> <description>Hello Bean</description> <ejb-name>ejb/HelloBean</ejb-name> <home>myEjb.HelloHome</home> <remote>myEjb.HelloRemote</remote> <ejb-class>myEjb.HelloBean</ejb-class> <session-type>Stateful</session-type> <transaction-type>Container</transaction-type> </session> </enterprise-beans> <assembly-descriptor> </assembly-descriptor> </ejb-jar>
This section adapts the preceding HelloServlet/HelloBean example for remote lookup to a different application (deployed to a different OC4J instance), highlighting necessary changes to the code and descriptor files.
Instead of using the default JNDI initial context factory, ApplicationInitialContextFactory, this example uses RMIInitialContextFactory.
The remote flag discussed in the preceding section, "EJB Remote Lookup within the Same Application", is not relevant.
This section has code for a servlet-EJB sample using remote lookup outside the application. This includes servlet code, EJB code, and EJB interface code. Note the bold passages in particular.
This section contains the servlet code. In this scenario, the specification of URL, user, and password must be in the servlet code. (In the example of a remote lookup within the same application, there is an assumption that this information is specified in the rmi.xml file.) A step is added to the servlet code here to set up the JNDI environment for the lookup. In this code, the following are static fields of the javax.naming.Context interface, which is implemented by the javax.naming.InitialContext class:
INITIAL_CONTEXT_FACTORY setting specifies the initial context factory to use, RMIInitialContextFactory in this case.
SECURITY_PRINCIPAL setting specifies the identity of the principal (user name) for authenticating the caller to the service.
SECURITY_CREDENTIALS setting specifies the password of the principal for authenticating the caller to the service.
PROVIDER_URL setting specifies the URL, or a comma-delimited list of URLs, for the lookup. The information after the port number corresponds to the application name as defined in the server.xml file, "myapp" in this example.
When RMIInitialContextFactory is used, there is no java:comp syntax in the JNDI lookup of the remote EJB component you wish to connect to, and the lookup must use the EJB name as specified in the ejb-jar.xml file. The web.xml file is not accessed, so any EJB references there will be ignored for the lookup.
package myServlet; // Step 1: Import the EJB package. import myEjb.*; import java.io.*; import java.util.*; import javax.servlet.*; import javax.servlet.http.*; import javax.naming.*; // for JNDI import javax.rmi.*; // for RMI, including PortableRemoteObject import javax.ejb.CreateException; import java.rmi.RemoteException public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { response.setContentType("text/html"); PrintWriter out = response.getWriter(); out.println("<html><head><title>Hello from Servlet</title></head>"); // Step 2: Print a message from the servlet. out.println("<body><h1>Hello from hello servlet!</h1></body>"); //Step 2.5: Set up JNDI properties for remote call Hashtable env = new Hashtable(); env.put(Context.INITIAL_CONTEXT_FACTORY, "com.evermind.server.rmi.RMIInitialContextFactory"); env.put(Context.SECURITY_PRINCIPAL, "admin"); env.put(Context.SECURITY_CREDENTIALS, "welcome"); env.put(Context.PROVIDER_URL, "ormi://myhost:port/myapp"); // Step 3: Create an output string, with an error default. String s = "If you see this message, the ejb was not invoked properly!!"; // Step 4: Use JNDI to look up the EJB home interface. try { InitialContext ic = new InitialContext(env); Object homeObject = ic.lookup("ejb/HelloBean"); HelloHome hh = (HelloHome) PortableRemoteObject.narrow(homeObject, HelloHome.class); // Step 5: Create the EJB remote interface. HelloRemote hr = (HelloRemote) PortableRemoteObject.narrow(hh.create(), HelloRemote.class); // Step 6: Invoke the helloWorld() method on the remote object. s = hr.helloWorld(); } catch (NamingException ne) { System.out.println("Could not locate the bean."); } catch (CreateException ce) { System.out.println("Could not create the bean."); } catch (RemoteException ce) { System.out.println("Error during execution of remote call."); } catch (Exception e) { // Unexpected exception; send back to client for now. throw new ServletException(e); } // Step 7: Print the message from the EJB. out.println("<br>" + s); out.println("</html>"); } }
|
Notes:
|
The EJB code for a remote lookup outside the application, including the bean code and the interface code, is the same as for a remote lookup within the application, including the use of RemoteException.
package myEjb; import javax.ejb.*; public class HelloBean implements SessionBean { public String helloWorld () { return "Hello from myEjb.HelloBean"; } public void ejbCreate () throws CreateException {} public void ejbRemove () {} public void setSessionContext (SessionContext ctx) {} public void ejbActivate () {} public void ejbPassivate () {} }
Here is the code for the home interface:
package myEjb; import java.rmi.RemoteException; import javax.ejb.EJBHome; import javax.ejb.CreateException; public interface HelloHome extends EJBHome { public HelloRemote create () throws RemoteException, CreateException; }
Here is the code for the remote interface.
package myEjb; import java.rmi.RemoteException; import javax.ejb.EJBObject; public interface HelloRemote extends EJBObject { public String helloWorld () throws RemoteException; }
This section highlights ejb-jar.xml entries that are specific to remote lookup. These entries are the same as for remote lookup within the application. You can compare the highlighted passages to parallel passages in the other examples.
Because RMIInitialContextFactory is used in the servlet for the JNDI initial context factory, the web.xml file is not relevant.
|
Note:
The
The |
The contents of ejb-jar.xml are as follows. Note the <home> and <remote> elements, for use of remote interfaces.
<?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE ejb-jar PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Enterprise JavaBeans 1.12//EN" "http://java.sun.com/dtd/ejb-jar_2_0.dtd"> <ejb-jar> <enterprise-beans> <session> <description>Hello Bean</description> <ejb-name>ejb/HelloBean</ejb-name> <home>myEjb.HelloHome</home> <remote>myEjb.HelloRemote</remote> <ejb-class>myEjb.HelloBean</ejb-class> <session-type>Stateful</session-type> <transaction-type>Container</transaction-type> </session> </enterprise-beans> <assembly-descriptor> </assembly-descriptor> </ejb-jar>
Complete the following steps:
PROVIDER_URL in the servlet code.
|
|
 Copyright © 2002, 2003 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|