|
Oracle TopLink Developer's Guide
10g Release 3 (10.1.3) B13593-01 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
|
Oracle TopLink Developer's Guide
10g Release 3 (10.1.3) B13593-01 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
If you plan to use a coordinated cache (see "Understanding Cache Coordination"), you can configure how, and under what conditions, a coordinated cache propagates changes for a given descriptor.
Table 28-13 summarizes which descriptors support cache isolation configuration.
Table 28-15 Descriptor Support for Cache Coordination Change Propagation Configuration
| Descriptor | Using TopLink Workbench
|
Using Java
|
|---|---|---|
|
Relational DescriptorsFoot 1 |
|
|
|
Object-Relational Descriptors |

|
|
|
EIS DescriptorsFoot 2 |
|
|
|
XML Descriptors |

|

|
Footnote 1 Relational class descriptors only (see "Relational Class Descriptors").
Footnote 2 EIS root descriptors only (see "EIS Root Descriptors").
This configuration overrides the default cache coordination change propagation configuration defined at the project level (see "Configuring Cache Coordination Change Propagation at the Project Level").
To complete your coordinated cache configuration, see "Configuring a Coordinated Cache".
|
Note: If you configure a descriptor as isolated (see "Configuring Cache Isolation at the Descriptor Level"), it cannot participate in a coordinated cache. |
To specify the coordinated cache change propagation options, use this procedure:
Select the descriptor in the Navigator.
Select the Caching tab in the Editor. The Caching tab appears.
Figure 28-27 Caching Tab, Coordination Options
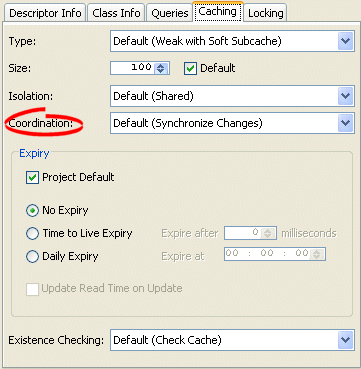
Complete the Coordination options on the Caching tab.
Use the following information to enter data in the Coordination field:
| Coordination Option | Description | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
| None | For both existing and new instances, do not propagate a change notification. | Infrequently read or changed objects. |
| Synchronize Changes | For an existing instance, propagate a change notification that contains each changed attribute.
For a new instance, propagate an object creation (along with all the new instance's attributes) only if the new instance is related to other existing objects that are also configured with this change propagation option. |
Frequently read or changed objects that contain few attributes or in cases where only a few attributes are frequently changed.
Objects that have many or complex relationships. |
| Synchronize Changes and New Objects | For an existing instance, propagate a change notification that contains each changed attribute.
For a new instance, propagate an object creation (along with all the new instance's attributes). |
Frequently read or changed objects that contain few attributes or in cases where only a few attributes are frequently changed.
Objects that have few or simple relationships. |
| Invalidate Changed Objects | For an existing instance, propagate an object invalidation that marks the object as invalid in all other sessions. This tells other sessions that they must update their cache from the data source the next time this object is read.
For a new instance, no change notification is propagated. |
Frequently read or changed objects that contain many attributes in cases where many of the attributes are frequently changed. |
Use a descriptor amendment method (see "Configuring Amendment Methods") to invoke ClassDescriptor method setCacheSynchronizationType passing in one of the following parameters:
ClassDescriptor.DO_NOT_SEND_CHANGES
ClassDescriptor.SEND_OBJECT_CHANGES
ClassDescriptor.SEND_NEW_OBJECTS_WITH_CHANGES
ClassDescriptor.INVALIDATE_CHANGED_OBJECTS