|
Oracle TopLink Developer's Guide
10g Release 3 (10.1.3) B13593-01 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
|
Oracle TopLink Developer's Guide
10g Release 3 (10.1.3) B13593-01 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
XML direct mappings map a Java attribute directly to XML text nodes. You can use an XML direct mapping in the following scenarios:
See Chapter 67, "Configuring an XML Direct Mapping" for more information.
|
Note: Do not confuse an XML direct mapping with a relational direct-to-XMLType mapping (see "Direct to XMLType Mapping").
|
This section describes using an XML direct mapping when:
Given the XML schema in Example 65-2, Figure 65-1 illustrates an XML direct mapping to a simple text node in a corresponding XML document. Example 65-3 shows how to configure this mapping in Java.
Example 65-2 Schema for XML Direct Mapping to Simple Text Node
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <xsd:element name="phone-number" type="xsd:string"/> </xsd:schema>
Figure 65-1 XML Direct Mapping to Simple Text Node
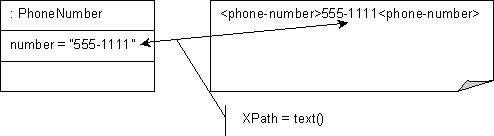
Given the XML schema in Example 65-4, Figure 65-2 illustrates an XML direct mapping to individual text nodes in a sequence in a corresponding XML document. Example 65-5 shows how to configure this mapping in Java.
Example 65-4 Schema for XML Direct Mapping to a Text Node in a Simple Sequence
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <xsd:element name="customer" type="customer-type"/> <xsd:complexType name="customer-type"> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="first-name" type="xsd:string"/> <xsd:element name="last-name" type="xsd:string"/> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:schema>
Example 65-5 Java for XML Direct Mapping to a Text Node in a Simple Sequence
XMLDirectMapping firstNameMapping = new XMLDirectMapping();
firstNameMapping.setAttributeName("firstName");
firstNameMapping.setXPath("first-name/text()");
XMLDirectMapping lastNameMapping = new XMLDirectMapping();
lastNameMapping.setAttributeName("lastName");
lastNameMapping.setXPath("last-name/text()");
Given the XML schema in Example 65-6, Figure 65-3 illustrates an XML direct mapping to a text node in a subelement in a corresponding XML document. Example 65-7 shows how to configure this mapping in Java.
Example 65-6 Schema for XML Direct Mapping to a Text Node in a Subelement
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <xsd:element name="customer" type="customer-type"/> <xsd:complexType name="customer-type"> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="personal-info"> <xsd:complexType> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="first-name" type="xsd:string"/> <xsd:element name="last-name" type="xsd:string"/> <xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:element> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:schema>
Example 65-7 Java for XML Direct Mapping to a Text Node in a Subelement
XMLDirectMapping firstNameMapping = new XMLDirectMapping();
firstNameMapping.setAttributeName("firstName");
firstNameMapping.setXPath("personal-info/first-name/text()");
XMLDirectMapping lastNameMapping = new XMLDirectMapping();
lastNameMapping.setAttributeName("lastName");
lastNameMapping.setXPath("personal-info/last-name/text()");
Given the XML schema in Example 65-8, Figure 65-4 illustrates an XML direct mapping to a text node by position in a corresponding XML document. Example 65-9 shows how to configure this mapping in Java.
Example 65-8 Schema for XML Direct Mapping to Text Node by Position
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <xsd:element name="customer" type="customer-type"/> <xsd:complexType name="customer-type"> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="name" type="xsd:string" maxOccurs="2"/> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:schema>
Example 65-9 Java for XML Direct Mapping to Text Node by Position
XMLDirectMapping firstNameMapping = new XMLDirectMapping();
firstNameMapping.setAttributeName("firstName");
firstNameMapping.setXPath("name[1]/text()");
XMLDirectMapping lastNameMapping = new XMLDirectMapping();
lastNameMapping.setAttributeName("lastName");
lastNameMapping.setXPath("name[2]/text()");
Given the XML schema in Example 65-8, Figure 65-4 illustrates an XML direct mapping to a text node by position in a corresponding XML document. Example 65-9 shows how to configure this mapping in Java.
In most cases, TopLink can determine the target format in the XML document. However, there are cases where you must specify which one of a number of possible targets TopLink should use. For example, a java.util.Calendar could be marshalled to a schema date, time, or dateTime node, or a byte[] could be marshalled to a schema hexBinary or base64Binary node.
Given the XML schema in Example 65-8, Figure 65-4 illustrates an XML direct mapping to a text node by position in a corresponding XML document. Example 65-9 shows how to configure this mapping in Java.
Example 65-12 Schema for XML Direct Mapping to a Specified Schema Type
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <xsd:element name="customer" type="customer-type"/> <xsd:complexType name="customer-type"> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="picture" type="xsd:hexBinary"/> <xsd:element name="resume" type="xsd:base64Binary"/> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:schema>
Example 65-13 Java for XML Direct Mapping to a Specified Schema Type
XMLDirectMapping pictureMapping = new XMLDirectMapping();
pictureMapping.setAttributeName("picture");
pictureMapping.setXPath("picture/text()");
XMLField pictureField = (XMLField) pictureMapping.getField();
pictureField.setSchemaType(XMLConstants.HEX_BINARY_QNAME);
XMLDirectMapping resumeMapping = new XMLDirectMapping();
resumeMapping.setAttributeName("resume");
resumeMapping.setXPath("resume/text()");
XMLField resumeField = (XMLField) resumeMapping.getField();
resumeField.setSchemaType(XMLConstants.BASE_64_BINARY_QNAME);
Given the XML schema in Example 65-14, Figure 65-7 illustrates an XML direct mapping to an xsd:list type in a corresponding XML document when you represent the list in your object model as a String of white space delimited tokens. Example 65-15 shows how to configure this mapping in Java.
Example 65-14 Schema for XML Direct Mapping to a List Field
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <xsd:element name="employee" type="employee-type"/> <xsd:complexType name="employee-type"> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="tasks" type="tasks-type"/> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> <xsd:simpleType name="tasks-type"> <xsd:list itemType="xsd:string"/> </xsd:simpleType> </xsd:schema>
Figure 65-7 XMLDirect Mapping to a List Field
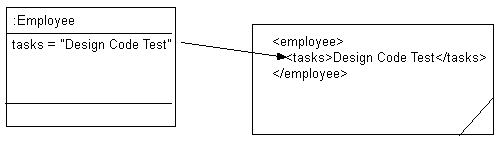
Given the XML schema in Example 65-16, Figure 65-8 illustrates a Java class that can be mapped to a corresponding XML document. Note the shoeSize attribute in this class: when using a union field, the corresponding attribute must be able to store all possible values.
Example 65-16 Schema for XML Direct Mapping to a Union Field
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <xsd:element name="customer" type="customer-type"/> <xsd:complexType name="customer-type"> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="shoe-size" type="size-type"/> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> <xsd:simpleType name="size-type"> <xsd:union memberTypes="xsd:decimal xsd:string"/> </xsd:simpleType> </xsd:schema>
Figure 65-8 Java Class for XML Direct Mapping to a Union Field

Figure 65-9 illustrates an XML direct mapping to a union field in an XML document that conforms to the schema in Example 65-16. When TopLink unmarshalls the XML document, it tries each of the union types until it can make a successful conversion. The first schema type in the union is xsd:decimal. Because "10.5" is a valid decimal, TopLink converts the value to the appropriate type. If the Object attribute is specific enough to trigger an appropriate value, TopLink will use that type instead. Otherwise, TopLink uses a default (in this case BigDecimal). You can override this behavior in Java code.
Figure 65-10 illustrates an XML direct mapping to union field in another XML document that conforms to the schema in Example 65-16. In this document, the value "M" is not a valid xsd:decimal type so the next union type is tried. The next union type is xsd:string and a conversion can be done.
Example 65-17 shows how to configure this mapping in Java.
Example 65-17 Java for XML Direct Mapping to a Union Type
XMLDirectMapping shoeSizeMapping = new XMLDirectMapping();
shoeSizeMapping.setAttributeName("shoeSize");
XMLUnionField shoeSizeField = new XMLUnionField();
shoeSizeField.setXPath("shoe-size/text()");
shoeSizeField.addSchemaType(XMLConstants.DECIMAL_QNAME);
shoeSizeField.addSchemaType(XMLConstants.STRING_QNAME);
shoeSizeMapping.setField(shoeSizeField);
To override the default conversion, use the XMLUnionField method addConversion:
shoeSizeField.addConversion(XMLConstants.DECIMAL_QNAME, Float.class);
Given the XML schema in Example 65-18, Figure 65-11 illustrates an XML direct mapping to a union of lists in a corresponding XML document. Example 65-19 shows how to configure this mapping in Java.
Example 65-18 Schema for XML Direct Mapping to Union of Lists
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <xsd:element name="vacation" type="unionOfLists"/> <xsd:simpleType name="unionOfLists"> <xsd:union memberTypes="xsd:double"> <xsd:simpleType> <xsd:list itemType="xsd:date"/> </xsd:simpleType> <xsd:simpleType> <xsd:list itemType="xsd:integer"/> </xsd:simpleType> </xsd:union> </xsd:simpleType> </xsd:schema>
Note that in this example, valid XML documents contain either all xsd:double, all xsd:date, or all xsd:integer values.
Given the XML schema in Example 65-20, Figure 65-12 illustrates a Java class that can be mapped to a corresponding XML document. Example 65-27 shows how to configure this mapping in Java.
Example 65-20 Schema for XML Direct Mapping to a Union of Unions
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <xsd:element name="vacation" type="unionOfUnions"/> <xsd:simpleType name="unionOfUnions"> <xsd:union> <xsd:simpleType> <xsd:union> <xsd:simpleType> <xsd:list itemType="xsd:date"/> </xsd:simpleType> <xsd:simpleType> <xsd:list itemType="xsd:integer"/> </xsd:simpleType> </xsd:union> </xsd:simpleType> <xsd:simpleType> <xsd:union> <xsd:simpleType> <xsd:list itemType="xsd:string"/> </xsd:simpleType> <xsd:simpleType> <xsd:list itemType="xsd:float"/> </xsd:simpleType> </xsd:union> </xsd:simpleType> </xsd:union> </xsd:simpleType> </xsd:schema>
Example 65-21 Java for XML Direct Mapping to a Union of Unions
XMLDirectMapping vacationMapping = new XMLDirectMapping();
vacationMapping.setAttributeName("vacation");
XMLUnionField vacationField = new XMLUnionField();
vacationField.setXPath("vacation/text()");
vacationField.addSchemaType(XMLConstants.DATE_QNAME);
vacationField.addSchemaType(XMLConstants.INTEGER_QNAME);
vacationField.addSchemaType(XMLConstants.STRING_QNAME);
vacationField.addSchemaType(XMLConstants.FLOAT_QNAME);
vacationMapping.setField(vacationField);
If the type of a node is not defined in your XML schema, you can configure an XML direct mapping to use the xsi:type attribute to provide type information.
Given the XML schema fragment in Example 65-22, Figure 65-13 illustrates a Java class that can be mapped to a corresponding XML document.
Example 65-22 Schema for XML Direct Mapping with Simple Type Translator
... <xs:element name="area-code" type="anySimpleType"/> <xs:element name="number" type="anySimpleType"/> ...
Figure 65-13 Java Class for XML Direct Mapping with Simple Type Translator

Figure 65-14 illustrates an XML direct mapping with a simple type translator in an XML document that conforms to the schema in Example 65-22.
Figure 65-14 XML Direct Mapping with a Simple Type Translator

Example 65-23 shows how to configure this mapping in Java.
Example 65-23 Java for XML Direct Mapping with Simple Type Translator
XMLDirectMapping numberMapping = new XMLDirectMapping();
numberMapping.setAttributeName("number");
numberMapping.setXPath("number/text()");
XMLField numberField = (XMLField) numberMapping.getField();
numberField.setIsTypedTextField(true);
For more information, see "Simple Type Translator".