| Oracle® Collaboration Suite Concepts Guide 10g Release 1 (10.1.2) Part Number B25491-03 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Collaboration Suite Concepts Guide 10g Release 1 (10.1.2) Part Number B25491-03 |
|
|
View PDF |
Oracle Collaboration Suite 10g Content Services is a database-centric content management application that provides users with a comprehensive, integrated solution for file and document lifecycle management and business process automation. All Oracle Content Services content is stored in an Oracle database.
This chapter discusses basic concepts that you should understand when using Oracle Content Services. Topics include the following:
The following sections describe the key features of Oracle Content Services:
Users log in to a single Site and can then see only the contents of that Site, regardless of whether they are members of other Sites. A user can only be logged in to one Site at a time. A Site folder can contain Containers, Libraries, or a combination of the two.
A Container is a special kind of folder that can contain other Containers or Libraries. Containers let Oracle Content Services administrators organize the folder hierarchy in a logical way. For example, Containers could be created for geographical regions or by department. Only Container Administrators can create and delete Containers. Containers can have default folder configuration settings that are inherited by Libraries created in the Container. In addition, a Container can be configured to disallow the creation of Libraries, or to limit who can create Libraries by enforcing a workflow for that Container.
Libraries are the first level in the folder hierarchy where content is added. Members must be added to a Library, and only Configuration Administrators and members of a particular Library can see that Library inside of a Container or the Site folder. Libraries and Personal Libraries are the only folders that contain a trash folder. Libraries can contain files and folders, and have a quota associated with them.
There are two types of administration for Oracle Content Services: system administration and application administration.
The System administration manages the Oracle Content Services domain by starting and stopping the nodes, services, and servers, tuning the system to ensure reliability and performance, creating, modifying, and deleting sites, as well as registering custom workflows. System Administration uses the Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Application Server Control for Oracle Collaboration Suite to manage Oracle Content Services.
Application administration involves managing users, quota, Libraries, categories, content, and records at the Site and Container level. Application administration is divided into multiple administrator roles that can be assigned at the Site level only, or at both the Site and Container level.
A single user can act in multiple roles. In addition, each role has a different set of access privileges.
See "About File Sharing and Access" in the online help for Oracle Content Services and Oracle Content Services Application Administrator's Guide for detailed information about administration levels and roles in Oracle Content Services. See Oracle Content Services Administrator's Guide for more information about administering Oracle Content Services.
Oracle Content Services provides users with control over access to their work. Users can specify who may access any file, folder, or Library they manage. Oracle Content Services also contains a type of folder called a Container; Containers are accessible to all users. See Oracle Content Services Folder Hierarchy for more information.
If enabled, all Oracle Content Services users have a Personal Library. Each user has complete control over access to this Library.
By default, a file, folder, or Container inherits its sharing settings from its parent folder. An administrator of the file, folder, or Container can change inherited sharing settings.�
Access Roles
Oracle Content Services security is based on roles. Oracle Content Services includes a set of default access roles that administrators can assign to users.
See "About File Sharing and Access" in the online help for Oracle Content Services and the Oracle Content Services Application Administrator's Guide for detailed information about roles.
Oracle Content Services user groups let users communicate and collaborate efficiently. Users can create a group for the members of a project team, a special interest group, or any other collection of users.
Any Oracle Content Services user can create a new group, or search for and request to be added to existing groups.
These groups are not Oracle Internet Directory groups. They are logical groupings that users can create within an Oracle Content Services Site to streamline collaborative work in Oracle Content Services.
Oracle Content Services provides reports that allow users to generate dynamic views of information. Oracle Content Services provides the following reports:
My Recent Files: The My Recent Files report displays a list of the user's most recently accessed files.
Locked Files: The Locked Files report displays all files that the user has locked.
Checked-Out Files: The Checked-Out Files report displays all files that the user has checked out.
My Requests: The My Requests report displays a filtered list of workflow requests.
Quota is the measurement of storage use in Oracle Content Services. Each Library is allocated a quota by the Quota Administrator. The contents of each Library, including its Trash folder, count against the Library's allocated quota. When the Library's quota is exceeded, Library members cannot store additional content in the Library. The Library's administrators can, however, request that the Quota Administrator increase the Library's quota.
Oracle Content Services provides a user interface for the Quota Administrator to view and change quotas, as well as a facility to browse or search for a Library by name. The Quota Administrator can view the allocated and used quota, and change the allocated quota for any Library.
See "About Folder and Library Management" in the online help for Oracle Content Services for detailed information.
Oracle Content Services users can customize account preferences from the User Preferences pages. Users can change the following options:
The number of files to list in My Recent Files
The default document language and character set
Their FTP password
Users can set their user preferences (or accept the default values) when they first log in to Oracle Content Services.
See "User Preferences" in the online help for Oracle Content Services for detailed information.
Users can conduct simple or advanced searches. A simple search searches for specified text in file names. Advanced searching lets users add, refine, and combine search criteria.
Users can also refine the search by using a Category Search to find files, based on their associated categories, and the attribute values of those categories. See Categories for more information.
See "Search Options" in the online help for Oracle Content Services for detailed information.
By associating Categories with files or folders and modifying the attributes of a Category, users can organize and classify their information. Users can also search for files by Category and a Category's attributes. The Oracle Content Services Category Administrator creates Categories.
Users can categorize files, folders, and links, by applying Categories to them on the File or Folder Properties window. Users that have been granted the permission to add, modify, or delete category information on a folder can also specify one or more required Categories for folders. Users must enter information for these Categories when uploading or checking in files.
See "About Categories" in the online help for Oracle Content Services for detailed information.
Users can retain a history of file modifications by creating and saving one or more versions of a file. Oracle Content Services lets users manage file versions with check-in/check-out functionality. The check-out functionality can only be performed on versioned files. To create a new version manually, users can check out a file. This locks the file and prevents other users from seeing changes by other users until the file is checked back in, which versions the file. Users can also set folders to version files automatically when they update files.
If automatic versioning is enabled, any overwrite operation creates a version of the overwritten document.
Users that have been granted Manager role on a folder can enable versioning for their folders, and set the versioning type: automatic or manual. The Version History table has a Type column, and the Version Properties page has a Version Type parameter that specifies whether a version is an automatic or manual version.
See "About Versioning" in the online help for Oracle Content Services for detailed information.
When users lock a file, they obtain exclusive access to that file. Other Oracle Content Services users are unable to edit the content and properties of the locked file. Users can lock a file manually, and files are locked automatically when they are edited through a client application, when the files are checked out, or when they are part of a review process. If a versioned file is locked, its version history is also locked.
See "About File Management," "About Workflow," and "About Review Processes" in the online help for Oracle Content Services for detailed information.
Users can submit files for review to a specified set of reviewers. These reviewers fall into two categories: Approvers, who can approve or reject the file, or reviewers, who can view the file but cannot approve or reject it.
Oracle Workflow is the key component of a review process in Oracle Content Services. Using a review process, any Library member can submit for review one or more files to other members of their Library. A review process ends in the approval or rejection of these files, or the process can expire or be canceled prior to their approval or rejection. Members can be either approvers or reviewers of a review process:
Users can also specify that files approved in a review process be automatically moved to a new location, copied to a new location, versioned, or deleted.
When you complete the review process, the initiator is notified of the approval or rejection of the review process.
See "About Review Processes" and "About Workflow" in the online help for Oracle Content Services for detailed information.
The System Administrator can create custom review processes, also called workflow processes, to use in Oracle Content Services. A workflow designer, a person with the necessary skills to design a workflow process in Oracle JDeveloper, creates the custom workflow process. Then, the Instance Administrator registers the custom workflow process with Oracle Content Services.
See "Review Processes and Workflow" in the online help for Oracle Content Services for detailed information.
Oracle Content Services includes user-initiated and automatic workflows. Automatic workflows can be initiated upon the occurrence of events within Oracle Content Services. These workflows can be configured so that the event (such as a check in or copy) does not complete until the workflow is satisfied. They can also be started after the event completes, which provides functions such as user notification. Workflows can also invoke the Oracle Application Server Web Services APIs, which allow further custom automation of business processes and application functions.
|
Note: Oracle BPEL Process Manager must be licensed separately. |
Oracle BPEL Process Manager is used by Oracle Content Services to provide the capability to create custom flows that automate the processes that are unique to your organization.
Custom BPEL workflows can be defined in Oracle BPEL Process Manager, then registered for use in Oracle Content Services. Custom workflows are only available to the default Site in Oracle Content Services; additional Sites cannot use the custom workflows.
Oracle BPEL Process Manager provides a framework for easily designing, deploying, monitoring, and administering processes based on BPEL standards.
The Business Process Execution Language (BPEL) is an XML-based language for enabling task-sharing across multiple enterprises using a combination of Web services. BPEL is based on the XML Schema, simple object access protocol (SOAP), and Web services description language (WSDL). Using BPEL, users can design a business process that integrates a series of discrete services into an end-to-end process flow.
The Oracle BPEL Process Manager consists of:
A Designer tool that runs in JDeveloper to graphically create the flows required for automating the various business process of an organization
A highly scalable run-time server that is deployed in Oracle Application Server
A management console for deploying, testing, and debugging BPEL flows running in the BPEL server
A Worklist application for managing user tasks
See Oracle BPEL Process Manager Developer's Guide for more information about BPEL and Oracle BPEL Process Manager
Using Oracle Drive or Microsoft Web Folders, a user can open and edit an Oracle Content Services file and save changes directly back to Oracle Content Services. When a user opens a file from Oracle Drive or Microsoft Web Folders to edit, the file is automatically locked in Oracle Content Services. Any changes made to the file are automatically saved in Oracle Content Services. When the user closes the file, it is automatically unlocked in Oracle Content Services.
Edit-in-place is available from the Content Services Web client when Oracle Drive is running.
See Using Protocol Servers to Access Oracle Content Services for more information about Oracle Drive and Microsoft Web Folders, and "Editing Files in Place" in the online help for Oracle Content Services for detailed information about the edit-in-place feature.
Oracle Content Services can integrate with Symantec Antivirus Scan Engine. When virus scanning is enabled, Oracle Content Services scans for viruses when a file is downloaded from Oracle Content Services (this includes opening the file in an application). Virus checking can also be invoked manually to scan files already in Oracle Content Services.
If a file contains a virus, the file is put into quarantine. While in quarantine, the document can be deleted or overwritten, but cannot be opened.
Every Library has a Trash folder, located in the top-level folder of the Library. When users delete files and folders from a Library, the files and folders are moved to the Trash folder. These can then be deleted from the Trash folder manually.
See "About File Management" in the online help for Oracle Content Services for detailed information.
Records management is the systematic and comprehensive control of the creation, capture, maintenance, filing, use, and disposition of records.
Oracle Records Management is a records management application that ships with Oracle Content Services.
Record Administrators can perform the following:
Define File Plans. A File Plan is a hierarchical set of subjects or business activities.
Search and browse records.
Define, classify, and manage records.
Oracle Drive is a desktop client for Oracle's WebDAV servers, such as Oracle Content Services and Oracle Portal. Oracle Drive allows you to access Oracle WebDAV files and file properties through a mapped drive in Windows Explorer, as well as from any Windows application's Open and Save As dialogs. You can also use Oracle Drive's offline and synchronization capabilities to manage files when you are disconnected from the network. Oracle Drive also allows you to back up the files on your hard disk to a server. When you reconnect to your network, Oracle Drive synchronizes all file changes between a local computer and the Oracle WebDAV server, ensuring that the contents of selected local folders and remote folders match.
See Using Protocol Servers to Access Oracle Content Services and the online help for Oracle Content Services for more information.
|
Note: Oracle Drive is for Microsoft Windows operating systems only. |
Oracle Content Services includes the Oracle Content Services Web client, an interactive and rich Web interface that makes Oracle Content Services content easily accessible from any Web browser. Using the Dynamic HTML capabilities of Oracle UIX 3.0, this thin client provides users of Oracle Content Services with a user experience similar to thick client applications, employing a dynamic tree view, right-clicking, pull-down menus as well as drag and drop. In addition to its standard mode, the Oracle Content Services Web client can be launched in an accessible mode designed expressly for users of assistive technology such as JAWS.
Figure 4-2 Oracle Content Services Web client
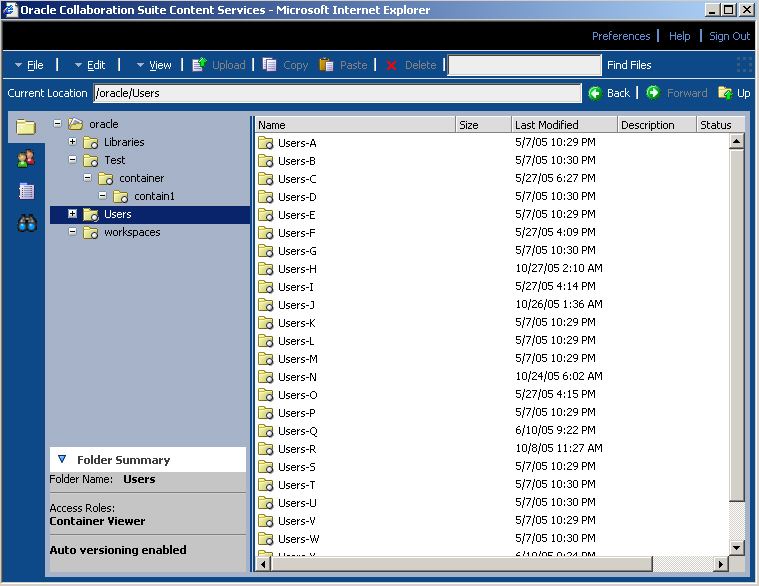
A link in Oracle Content Services is a navigational shortcut that points to a folder, file, file version, Library, or Container. Users can open, copy, move, and delete links, as long as the links are unlocked. Moving or overwriting the target item does not break the link.
A link inherits its security settings from the folder where it is created. Users cannot create versions of a link.
|
Note: The feature described in this section was added to Oracle Collaboration Suite in the Oracle Collaboration Suite Cumulative Patchset 10.1.2.3. If you are using a previous version or patchset of Oracle Collaboration Suite, the feature described is not available. |
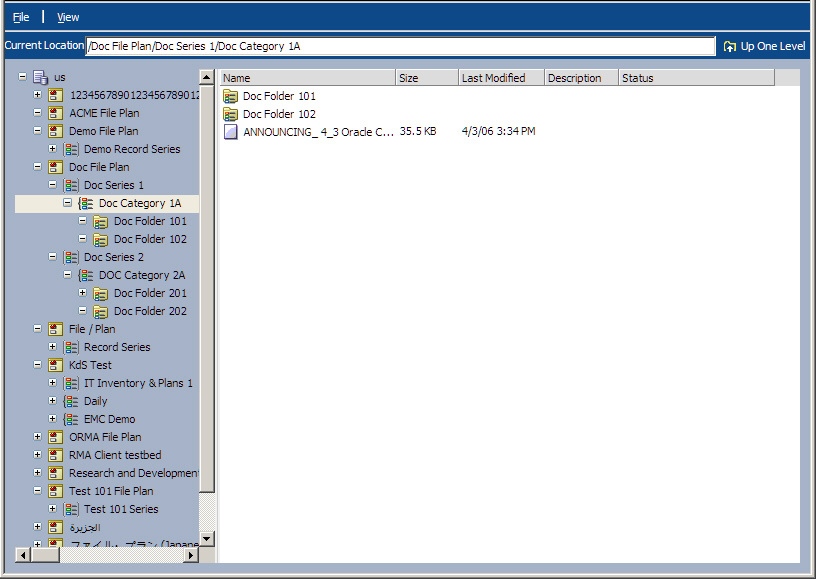
Oracle Records Management is a records management application that ships with Oracle Content Services. In order to use Oracle Records Management, you must be running Oracle Content Services. Through Oracle Records Management, administrators can set records management properties for any folder in which a user might store data. Some records management tasks, such as declaring records, are performed through Oracle Content Services. Other records management tasks, such as managing file plans, record series, record categories, and record folders, are performed through Oracle Records Management.
Figure 4-3 Oracle Records Management Web client
|
Note: The feature described in this section was added to Oracle Collaboration Suite in the Oracle Collaboration Suite Cumulative Patchset 10.1.2.3. If you are using a previous version or patchset of Oracle Collaboration Suite, the feature described is not available. |
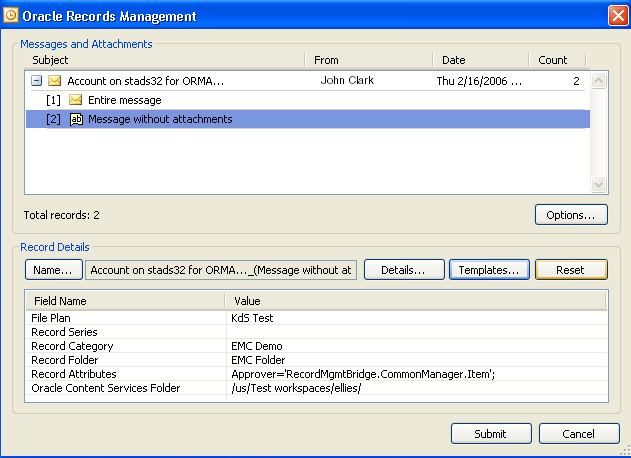
Oracle Records Management Add-In for Outlook is an add-in enabling Microsoft Outlook users to transform any Outlook message into a Record and then submit that Record to Oracle Content Services. Oracle Records Management Add-In for Outlook also enables you to manage records and organize templates from within Outlook by selecting an option from the Records Management menu, which is accessible from the Actions menu, the toolbar, or by right-clicking a message.
Figure 4-4 Oracle Records Management Add-In for Outlook
Users can connect to Oracle Content Services using protocols appropriate to their platform. For example, Windows users can use Oracle Drive or connect using Web Folders and UNIX users can connect using FTP. Users on all platforms can connect using HTTP for Web browser-based access.
Oracle Content Services supports the following protocols:
HTTP, the Hypertext Transfer Protocol, is used for Web browser-based access.
FTP, the File Transfer Protocol, is used for file transfers across Wide Area Networks such as the Internet.
The FTP protocol sends unencrypted passwords over the network. For this reason, users must create an FTP password for greater security. See the Oracle Content Services chapter of Oracle Collaboration Suite Security Guide for more information about FTP passwords.
In addition to FTP, Secure FTP (FTPS) is supported. You can access Oracle Content Services using either implicit or explicit FTPS. Because FTPS does not send unencrypted passwords over the network, an FTP password is not necessary.
WebDAV, Web-based Distributed Authoring and Versioning, is an HTTP-related protocol that is designed for Wide Area Networks such as the Internet. Currently, the most widespread WebDAV client is the Web Folders extension to Windows Explorer, also known as Network Places in Windows 2000/XP.
Oracle Drive provides users with SMB-like drive mapping capabilities, but uses WebDAV as the actual file protocol.