CASE Statement
The CASE statement chooses from a sequence of conditions, and execute a corresponding statement.
The simple CASE statement evaluates a single expression and compares it to several potential values.
The searched CASE statement evaluates multiple Boolean expressions and chooses the first one whose value is TRUE.
The CASE statement is appropriate when a different action is to be taken for each alternative.
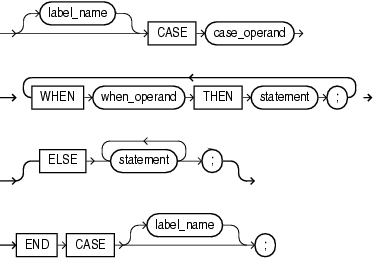
Description of the illustration simple_case_statement.gif
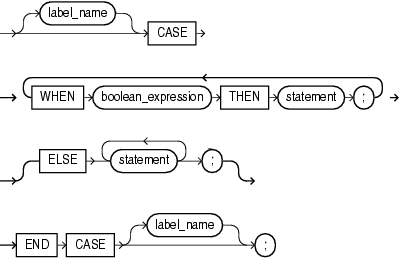
Description of the illustration searched_case_statement.gif
(statement ::=, boolean_expression ::=)
Keyword and Parameter Descriptions
An expression whose value is used to select one of several alternatives. Its value can be of any PL/SQL type except BLOB, BFILE, an object type, a PL/SQL record, an index-by table, a varray, or a nested table.
WHEN { when_operand | boolean_expression } THEN statement
The when_operands or boolean_expressions are evaluated sequentially. If the value of a when_operand equals the value of case_operand, or if the value of a boolean_expression is TRUE, the statement associated with that when_operand or boolean_expression executes, and the CASE statement ends. Subsequent when_operands or boolean_expressions are not evaluated.
The value of a when_operand can be of any PL/SQL type other than BLOB, BFILE, an object type, a PL/SQL record, an index-by table, a varray, or a nested table.
Caution:
Thestatements can modify the database and invoke nondeterministic functions. There is no fall-through mechanism, as there is in the C switch statement.ELSE statement [statement ]...
In the simple CASE statement, the statements execute if and only if no when_operand has the same value as case_operand.
In the searched CASE statement, the statements execute if and only if no boolean_expression has the value TRUE.
If you omit the ELSE clause, and there is no match (that is, no when_operand has the same value as case_operand, or no boolean_expression has the value TRUE), the system raises a CASE_NOT_FOUND exception.
See Also:
-
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for information about the
NULLIFfunction -
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for information about the
COALESCEfunction