Constant
A constant holds a value that does not change.
A constant declaration specifies its name, data type, and value, and allocates storage for it. The declaration can also impose the NOT NULL constraint.

Description of the illustration constant_declaration.gif
Description of the illustration datatype.gif
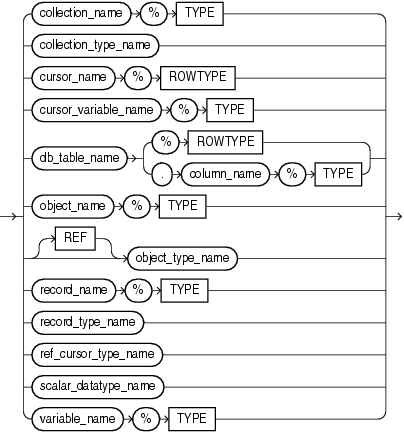
Keyword and Parameter Descriptions
A collection (associative array, nested table, or varray) previously declared within the current scope.
A user-defined collection type defined using the data type specifier TABLE or VARRAY.
The name of the constant. For naming conventions, see Identifiers.
An explicit cursor previously declared within the current scope.
A PL/SQL cursor variable previously declared within the current scope.
A database table or view that must be accessible when the declaration is elaborated.
A database table and column that must be accessible when the declaration is elaborated.
The value to be assigned to the constant when the declaration is elaborated. The value of expression must be of a data type that is compatible with the data type of the constant.
A constraint that prevents the program from assigning a null value to the constant. Assigning a null to a variable defined as NOT NULL raises the predefined exception VALUE_ERROR.
An instance of an object type previously declared within the current scope.
A user-defined or %ROWTYPE record previously declared within the current scope.
A field in a user-defined or %ROWTYPE record previously declared within the current scope.
A user-defined record type that is defined using the data type specifier RECORD.
A user-defined cursor variable type, defined using the data type specifier REF CURSOR.
Represents a record that can hold a row from a database table or a cursor. Fields in the record have the same names and data types as columns in the row.
A predefined scalar data type such as BOOLEAN, NUMBER, or VARCHAR2. Includes any qualifiers for size, precision, and character or byte semantics.
Represents the data type of a previously declared collection, cursor variable, field, object, record, database column, or variable.
Constants are initialized every time a block or subprogram is entered. Whether public or private, constants declared in a package specification are initialized only once for each session.
You can define constants of complex types that have no literal values or predefined constructors, by invoking a function that returns a filled-in value. For example, you can make a constant associative array this way.