%ROWTYPE Attribute
The %ROWTYPE attribute lets you declare a record that represents a row in a table or view. For each column in the referenced table or view, the record has a field with the same name and data type. To reference a field in the record, use record_name.field_name. The record fields do not inherit the constraints or default values of the corresponding columns.
If the referenced item table or view changes, your declaration is automatically updated. You need not change your code when, for example, columns are added or dropped from the table or view.
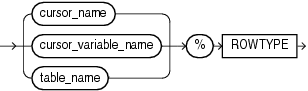
Description of the illustration rowtype_attribute.gif
Keyword and Parameter Descriptions
An explicit cursor previously declared within the current scope.
A PL/SQL strongly typed cursor variable, previously declared within the current scope.
A database table or view that must be accessible when the declaration is elaborated.
-
Example 2-14, "Using %ROWTYPE to Declare a Record that Represents a Table Row"
-
Example 2-15, "Declaring a Record that Represents a Subset of Table Columns"
-
Example 2-16, "Declaring a Record that Represents a Row from a Join"
-
Example 2-17, "Assigning One Record to Another, Correctly and Incorrectly"
-
Example 5-7, "Specifying Collection Element Types with %TYPE and %ROWTYPE"
-
Example 5-20, "Assigning Values to VARRAYs with Complex Data Types"
-
Example 6-24, "Cursor Variable Returning a %ROWTYPE Variable"
-
Example 6-25, "Using the %ROWTYPE Attribute to Provide the Data Type"