8 Creating an Analysis Task
Once you have captured a SQL workload that you want to analyze into a SQL tuning set, you can run SQL Performance Analyzer to analyze the effects of a system change on SQL performance. To run SQL Performance Analyzer, you must first create a SQL Performance Analyzer task. A task is a container that encapsulates all of the data about a complete SQL Performance Analyzer analysis. A SQL Performance Analyzer analysis comprises of at least two SQL trials and a comparison. A SQL trial encapsulates the execution performance of a SQL tuning set under specific environmental conditions and represents a particular test execution or explain plan operation performed by SQL Performance Analyzer when testing a system change. When creating a SQL Performance Analyzer task, you will need to select a SQL tuning set as its input source. The SQL tuning set remains constant in the SQL Performance Analyzer task and is executed in isolation during each SQL trial. Thus, performance differences between trials are caused by environmental differences. For more information, see "Creating a SQL Performance Analyzer Task".
This chapter described how to create a SQL Performance Analyzer task and contains the following topics:
Note:
The primary interface for running SQL Performance Analyzer is Oracle Enterprise Manager. If for some reason Oracle Enterprise Manager is unavailable, you can run SQL Performance Analyzer using theDBMS_SQLPA PL/SQL package.Tip:
Before running SQL Performance Analyzer, capture the SQL workload to be used in the performance analysis into a SQL tuning set on the production system, then transport it to the test system where the performance analysis will be performed, as described in "Capturing the SQL Workload".Creating an Analysis Task Using Enterprise Manager
There are two types of workflow available in Oracle Enterprise Manager for creating a SQL Performance Analyzer task:
-
Parameter change workflow
Use the parameter change workflow to determine how a database initialization parameter change will affect SQL performance, as described in "Using the Parameter Change Workflow".
-
Guided workflow
Use the guided workflow to compare SQL performance for all types of system changes other than a database initialization parameter change, as described in "Using the Guided Workflow".
Using the Parameter Change Workflow
The Parameter Change workflow enables you to test the performance effect on a SQL workload when you change the value of a single environment initialization parameter. For example, you can compare SQL performance when the sort area size is increased from 1 MB to 2 MB.
After you select a SQL tuning set and a comparison metric, SQL Performance Analyzer creates a task and performs a trial with the initialization parameter set to the original value. A task is a container for the results of SQL replay trials. A SQL trial captures the execution performance of a SQL tuning set under specific environmental conditions. SQL Performance Analyzer then performs a second trial with the parameter set to the changed value. Any regression or change in performance are reported in a system-generated SQL Performance Analyzer report.
Note:
To create an analysis task for other types of system changes, use the guided workflow instead, as described in "Using the Guided Workflow".To create a SQL Performance Analyzer task using the parameter change workflow:
-
On the Software and Support page, under Real Application Testing, click SQL Performance Analyzer.
The SQL Performance Analyzer page appears. A list of existing SQL Performance Analyzer tasks are displayed.
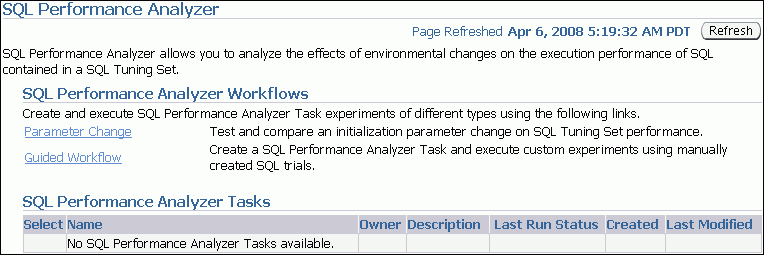
Description of the illustration spa.gif
-
On the SQL Performance Analyzer page, click Parameter Change.
The Parameter Change page appears.

Description of the illustration spa_param_change.gif
-
In the Task Name field, enter the name of the task.
-
In the SQL Tuning Set field, enter the name of the SQL tuning set that contains the SQL workload to be analyzed.
Alternatively, click the search icon to search for a SQL tuning set using the Search and Select: SQL Tuning Set window.
The selected SQL tuning set now appears in the SQL Tuning Set field.
-
In the Description field, optionally enter a description of the task.
-
In the Creation Method list, determine how the SQL trial is created and what contents are generated by performing one of the following actions:
-
Select Execute SQLs.
The SQL trial generates both execution plans and statistics for each SQL statement in the SQL tuning set by actually running the SQL statements.
-
Select Generate Plans.
The SQL trial invokes the optimizer to create execution plans only without actually running the SQL statements.
-
-
In the Per-SQL Time Limit list, determine the time limit for SQL execution during the trial by performing one of the following actions:
-
Select Unlimited.
The execution will run each SQL statement in the SQL tuning set to completion and gather performance data. Collecting execution statistics provides greater accuracy in the performance analysis but takes a longer time. Using this setting is not recommended because the task may be stalled by one SQL statement for a prolonged period of time.
-
Select Customize and enter the specified number of seconds, minutes, or hours.
-
-
In the Parameter Change section, complete the following steps:
-
In the Parameter Name field, enter the name of the initialization parameter whose value you want to modify, or click the Search icon to select an initialization parameter using the Search and Select: Initialization Parameters window.
-
In the Base Value field, enter the current value of the initialization parameter.
-
In the Changed Value field, enter the new value of the initialization parameter.
-
-
In the Comparison Metric list, select the comparison metric to use for the analysis:
-
If you selected Generate Plans in Step 6, then select Optimizer Cost.
-
If you selected Execute SQLs in Step 6, then select one of the following options:
-
Elapsed Time
-
CPU Time
-
Buffer Gets
-
Disk Reads
-
Direct Writes
-
Optimizer Cost
-
To perform the comparison analysis by using more than one comparison metric, perform separate comparison analyses by repeating this procedure using different metrics.
-
-
In the Schedule section:
-
In the Time Zone list, select your time zone code.
-
Select Immediately to start the task now, or Later to schedule the task to start at a time specified using the Date and Time fields.
-
-
Click Submit.
A confirmation message appears.
In the SQL Performance Analyzer Tasks section, the status of this task is displayed. To refresh the status icon, click Refresh. After the task completes, the Last Run Status icon changes to a check mark.
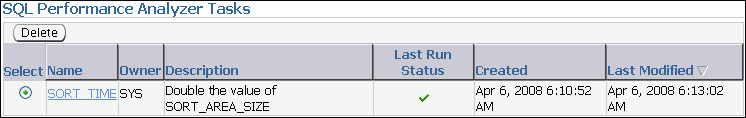
Description of the illustration spa_spa_tasks.gif
-
In the SQL Performance Analyzer Tasks section, select the task and click the link in the Name column.
The SQL Performance Analyzer Task page appears.
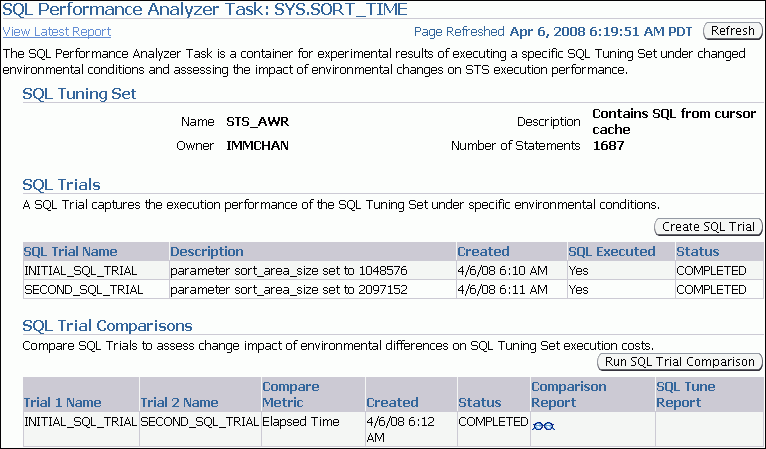
Description of the illustration spa_task.gif
This page contains the following sections:
-
SQL Tuning Set
This section summarizes information about the SQL tuning set, including its name, owner, description, and the number of SQL statements it contains.
-
SQL Trials
This section includes a table that lists the SQL trials used in the SQL Performance Analyzer task.
-
SQL Trial Comparisons
This section contains a table that lists the results of the workload comparisons
-
-
Click the icon in the Comparison Report column.
The SQL Performance Analyzer Task Result page appears.
-
Review the results of the performance analysis, as described in "Reviewing the SQL Performance Analyzer Report Using Oracle Enterprise Manager".
-
In cases when regression are identified, click the icon in the SQL Tune Report column to view a SQL tuning report.
Using the Guided Workflow
The guided workflow enables you to test the performance effect of any types of system changes on a SQL workload, as listed in "SQL Performance Analyzer".
Note:
To create an analysis task to test database initialization parameter changes, use the simplified parameter change workflow instead, as described in "Using the Parameter Change Workflow".To create a SQL Performance Analyzer task using the guided workflow:
-
On the Software and Support page, under Real Application Testing, click SQL Performance Analyzer.
The SQL Performance Analyzer page appears. A list of existing SQL Performance Analyzer tasks are displayed.
-
On the SQL Performance Analyzer page, click Guided Workflow.
The Guided Workflow page appears.
The guided workflow enables you to test the performance effect on a SQL workload when you perform any type of system changes, as described in "SQL Performance Analyzer".
This page lists the required steps in the SQL Performance Analyzer task in sequential order. Each step must be completed in the order displayed before the next step can begin.

Description of the illustration spa_guided_workflow.gif
-
On the Guided Workflow page, click the Execute icon for the Step 1: Create SQL Performance Analyzer Task based on SQL Tuning Set.
The Create SQL Performance Analyzer Task page appears.
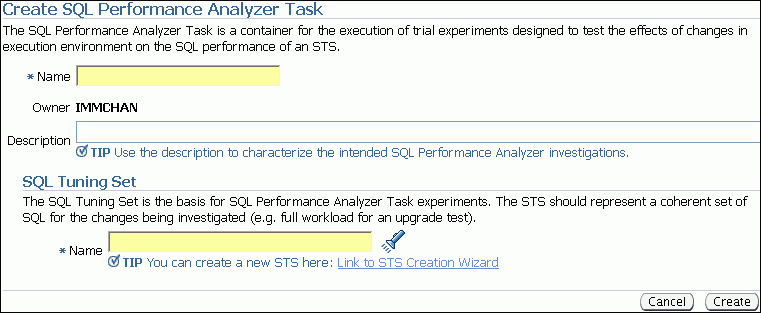
Description of the illustration spa_create_task.gif
-
In the Name field, enter the name of the task.
-
In the Description field, optionally enter a description of the task.
-
Under SQL Tuning Set, in the Name field, enter the name the SQL tuning set that contains the SQL workload to be analyzed.
Alternatively, click the search icon to select a SQL tuning set from the Search and Select: SQL Tuning Set window.
-
Click Create.
The Guided Workflow page appears.
The Status icon of this step has changed to a check mark and the Execute icon for the next step is now enabled.
-
Once the analysis task is created, you can build the pre-change performance data by executing the SQL statements stored in the SQL tuning set, as described in Chapter 9, "Creating a Pre-Change SQL Trial".
Creating an Analysis Task Using APIs
This section describes how to create a new SQL Performance Analyzer task by using the DBMS_SQLPA.CREATE_ANALYSIS_TASK function. A task is a database container for SQL Performance Analyzer execution inputs and results.
Tip:
Before proceeding, capture the SQL workload to be used in the performance analysis into a SQL tuning set on the production system, then transport it to the test system where the performance analysis will be performed, as described in "Capturing the SQL Workload".Call the CREATE_ANALYSIS_TASK function to prepare the analysis of a SQL tuning set using the following parameters:
-
Set
task_nameto specify an optional name for the SQL Performance Analyzer task. -
Set
sqlset_nameto the name of the SQL tuning set. -
Set
sqlset_ownerto the owner of the SQL tuning set. The default is the current schema owner. -
Set
basic_filterto the SQL predicate used to filter the SQL from the SQL tuning set. -
Set
order_byto specify the order in which the SQL statements will be executed.You can use this parameter to ensure that the more important SQL statements will be processed and not skipped if the time limit is reached.
-
Set
top_sqlto consider only the top number of SQL statements after filtering and ranking.
The following example illustrates a function call:
VARIABLE t_name VARCHAR2(100);
EXEC :t_name := DBMS_SQLPA.CREATE_ANALYSIS_TASK(sqlset_name => 'my_sts', -
task_name => 'my_spa_task');
Once the analysis task is created, you can build the pre-change performance data by executing the SQL statements stored in the SQL tuning set, as described in Chapter 9, "Creating a Pre-Change SQL Trial".
See Also:
Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference to learn more about theDBMS_SQLPA.CREATE_ANALYSIS_TASK function