| Oracle® TopLink Developer's Guide 10g Release 3 (10.1.3.1.0) Part Number B28218-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® TopLink Developer's Guide 10g Release 3 (10.1.3.1.0) Part Number B28218-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
This chapter includes deployment information on the following TopLink applications:
For more information, see the following:
Build the JAR file (see "Java Applications") and place it on the classpath.
For more information on accessing TopLink from your client application, see Chapter 75, "Acquiring and Using Sessions at Run Time".
After you build the WAR and JAR files (see "JavaServer Pages and Servlet Applications"), build them into an EAR file for deployment. To deploy the EAR to your JSP servlet server, copy the EAR to a commonly used directory. You may also need to use server-specific deployment tools. For more information, see the server documentation.
For more information on accessing TopLink from your client application, see "Loading a Session From sessions.xml With an Alternative Class Loader".
After you build the WAR and JAR files (see "Session Bean Applications"), build them into an EAR file for deployment. To deploy the EAR file to your J2EE server, copy the EAR to a commonly used directory. You may also need to use server-specific deployment tools. For more information, see the server documentation.
For more information on accessing TopLink from your client application, see "Loading a Session From sessions.xml With an Alternative Class Loader".
Optionally, you may also consider "Hot Deployment of EJB".
After you build the WAR and JAR files (see "CMP Applications"), build them into an EAR file for deployment. To deploy the EAR file to your J2EE server, copy the EAR to a commonly used directory. You may also need to use server-specific deployment tools. For more information, see the server documentation.
This section describes the following:
For additional information on server-specific configuration, see Chapter 7, "Integrating TopLink With an Application Server ".
Optionally, you may also consider "Hot Deployment of EJB".
The most efficient way to deploy a CMP application to OC4J is using Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g. For more information, see Oracle Application Server Administrator's Guide.
When you deploy a CMP application to OC4J, the following happens:
OC4J performs a partial EJB conformance check on the beans and their associated interfaces.
OC4J builds the internal OC4J classes that manage security and transactions, as well as the RMI stubs and skeletons that enable client access to the beans.
TopLink builds concrete bean subclasses and EJB finder method implementations.
TopLink CMP support includes integration for BEA WebLogic Server. To enable TopLink CMP for BEA WebLogic entity beans, use the WebLogic EJB Compiler (ejbc) to compile the EJB JAR file, as follows:
Run ejbc from the command line. Include the EJB JAR file as a command line argument. ejbc creates an EJB JAR file that contains the original classes as well as all required generated classes and files.
When you run ejbc, the following happens:
ejbc performs a partial EJB conformance check on the beans and their associated interfaces.
ejbc builds the internal BEA WebLogic classes that manage security and transactions, as well as the RMI stubs and skeletons that enable client access to the beans.
TopLink builds concrete bean subclasses and EJB finder method implementations.
For more information about running ejbc, see the BEA WebLogic Server documentation.
When you start ejbc, it processes the data in a series of stages. If errors occur while running ejbc, attempt to determine which stage causes the problem. Common problems include the following:
Bean classes that do not conform with the EJB specification
Classes missing from the classpath (all domain classes, required TopLink classes, and all required BEA WebLogic classes must be on the classpath)
Java compiler (javac) problems, often caused by using an incorrect version of the JDK
A failure when generating the RMI stubs and skeletons (a failure of RMI compiler (rmic))
Refer to Chapter 15, "Troubleshooting Application Deployment" for additional information.
TopLink CMP support includes an integration for IBM WebSphere application server 4.0. Use the following procedure to deploy your application to WebSphere applicaton server:
Use the TopLink Deploy Tool for WebSphere to compile the EJB JAR file. For more information, see "Using the WebSphere Deploy Tool".
Start the WebSphere Administration Server.
Start the Administration Console and deploy the compiled JAR file.
For more information about deploying the JAR file, see the IBM WebSphere application server documentation.
|
Note: When you deploy an application that contains an entity bean, set up a data source and associate it with the bean. For more information about how to create and associate data sources, see the IBM WebSphere application server documentation. |
It is not necessary to deploy the EJB JAR file in WebSphere Studio Application Developer (WSAD), because deployment is carried out using the Deploy Tool (see "Using the WebSphere Deploy Tool").
You can start the bean in either the WebSphere application server or in WSAD.
To start the bean in IBM WebSphere application server, do the following:
Select the application that contains the entity beans.
Right-click and choose Start.
A message dialog box appears if the bean starts successfully. If an error occurs, consult Part V, "Troubleshooting a TopLink Application" for troubleshooting information.
To start the bean in WSAD, do the following:
Right-click the EJB project, and choose Run on Server.
To view the status of the process, open the Console tab of the Server view.
After you build the WAR and JAR files, build them into an EAR file for deployment. To deploy the EAR file to your J2EE server, copy the EAR to a commonly used directory. You may also need to use server-specific deployment tools. For more information, see the server documentation.
For additional information on server-specific configuration, see Chapter 7, "Integrating TopLink With an Application Server ".
Optionally, you may also consider "Hot Deployment of EJB".
Many J2EE containers support hot deployment, a feature that enables you to deploy EJB on a running server. Hot deployment allows you to do the following:
Deploy newly developed EJB to a running production system.
Remove (undeploy) deployed EJB from a running server.
Modify (redeploy) the behavior of deployed EJB by updating the bean class definition.
The client receives deployment exceptions when attempting to access undeployed or re-deployed bean instances. The client application must catch and handle the exceptions.
How you configure hot deployment of EJB depends on the type of J2EE application you are deploying:
For more information about hot deployment, see the J2EE container documentation.
When you take advantage of hot deployment in a CMP application, consider the following:
You must deploy all related beans (all beans that share a common TopLink project) within the same EJB JAR file. Because TopLink views deployment on a project level, deploy all the project beans (rather than just a portion of them) to maintain consistency across the project.
When you redeploy a bean, you automatically reset its TopLink project. This flushes all object caches and rolls back any active object transactions associated with the project.
When you take advantage of hot deployment in a non-CMP application, you must refresh the TopLink session using the SessionManager method getSession with the appropriate arguments (see "Refreshing a Session When the Class Loader Changes".
If you do not use this SessionManager method, then your application is responsible for destroying or refreshing the session when a hot deployment (or hot redeployment) occurs.
TopLink integration for IBM WebSphere application server includes a deployment tool that helps you deploy your projects to WebSphere. The Deploy Tool for WebSphere is a graphical tool that makes project deployment to WebSphere easier to configure and execute. The Deploy Tool also includes a command-line option that lets you deploy your project while bypassing the graphical interface element of the tool.
You can use the Deploy Tool on its own (see "Using the Deploy Tool on its Own") or with the WebSphere Studio Application Developer (see "Using the Deploy Tool With WebSphere Studio Application Developer").
To deploy a JAR file, use this procedure:
Start the WebSphere Deploy Tool by executing the appropriate <TOPLINK_HOME>/bin/wasDeployTool script: on Windows, execute wasDeployTool.cmd; on UNIX, execute wasDeployTool.sh.
The WebSphere Deploy Tool dialog box appears (see Figure 10-1).
Figure 10-1 The Deploy Tool Set Up for Use with WSAD
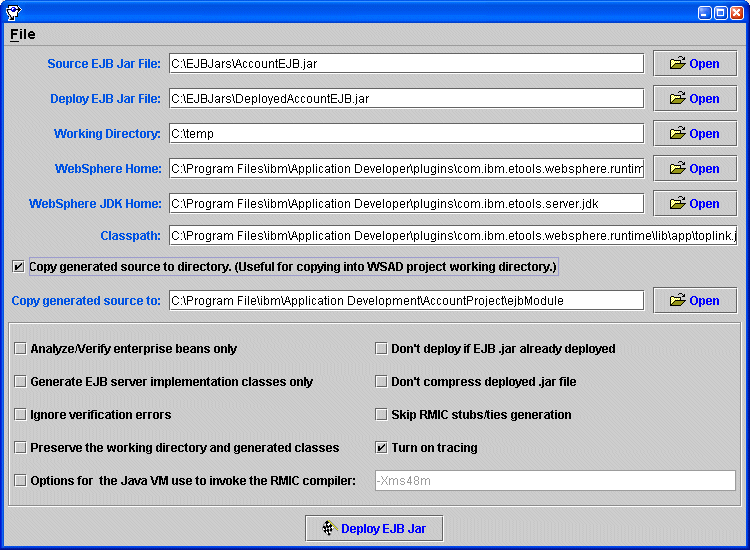
Enable the Copy generated source to directory option to save a copy of the generated code in the specified directory. This is a quick and efficient way to copy the files into a WSAD project working directory.
Enable the Turn on tracing option if you want to see the details of the process.
Click Deploy EJB.
The Deploy tool is compatible with the WSAD.
To deploy from the Deploy Tool to WSAD, do the following:
Select the EJB Project in WSAD and choose to generate Deploy and RMIC Code.
Export the EJB Project to an EJB JAR file, making sure that the TopLink project and toplink-ejb-jar.xml files are included in the EJB JAR file.
Start the WebSphere Deploy Tool by executing the appropriate <TOPLINK_HOME>/bin/wasDeployTool script: on Windows, execute wasDeployTool.cmd; on UNIX, execute wasDeployTool.sh.
The WebSphere Deploy Tool dialog appears (see Figure 10-1).
Choose the EJB Project working directory so that TopLink overrides the WSAD deploy code with the TopLink deploy code.
If the source is copied to a directory other than the WSAD EJB Project directory, manually copy the source files to the WSAD EJB Project under the ejbModule directory of the project.
Enter appropriate directories in the fields of the Deploy Tool.
Choose Deploy EJB JAR to create the deployed EJB JAR file.
Choose Rebuild all from the Project menu to compile the deploy code to incorporate CMP.
The most common error you might encounter when you use the Deploy Tool is the NoClassDefFoundError exception. To resolve this error condition, add the required resources to the Classpath. The Turn on tracing option also helps to debug errors during deployment code generation.
When an obscure error appears during the generating stub phase, copy the Java command and run it at the command prompt. This gives a more detailed error message.
See Chapter 7, "Integrating TopLink With an Application Server " for additional information.