| Oracle® TopLink Developer's Guide 10g Release 3 (10.1.3.1.0) Part Number B28218-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® TopLink Developer's Guide 10g Release 3 (10.1.3.1.0) Part Number B28218-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
How you package the components of your application depends on the type of application and how you plan to deploy it.
This section describes TopLink-specific details applicable to the common packaging strategies used for the following types of application:
For information, see the following:
For non-J2EE Java applications, it is common to package the application in a single JAR file as Figure 9-1 shows.
Figure 9-1 Packaging a non-J2EE Java Application

This JAR contains the TopLink files and domain objects required by the application, including:
project.xml File (or the compiled project class file if you are not using XML files for deployment)
The mapped classes required by the application, in a fully-resolved directory structure
When you create the JAR file, the JAR building utility automatically creates a directory structure within the JAR. Ensure that the sessions.xml file and the project.xml file (or project class file) appear at the root of the JAR file. Ensure that the class directory structure starts at the root of the JAR.
If you do not store the project.xml or sessions.xml files at the root of the JAR file, see "Packaging With TopLink Metadata File Resource Paths".
For simple J2EE applications without EJB, it is common to package the application in an Enterprise Archive (EAR) file made up of various J2EE application component archives as Figure 9-2 shows.
Figure 9-2 Packaging a J2EE JSP or Servlet Application Without EJB

The component archives with TopLink dependencies include the following:
The domain JAR contains the TopLink files and domain objects required by the application, including:
project.xml File (or the compiled Project class file, if you are not using XML files for deployment)
The mapped classes required by the application, in a fully resolved directory structure
When you create the JAR file, the JAR building utility automatically creates a directory structure within the JAR. Ensure that the sessions.xml file and the project.xml file (or project.class file) appear at the root of the JAR file. Also ensure that the class directory structure starts at the root of the JAR.
If you do not store the project.xml or sessions.xml files at the root of the JAR file, see "Packaging With TopLink Metadata File Resource Paths".
For J2EE applications with session beans, it is common to package the application in an Enterprise Archive (EAR) file made up of various J2EE application component archives as Figure 9-3 shows.
Figure 9-3 Packaging a J2EE Application With Session Beans
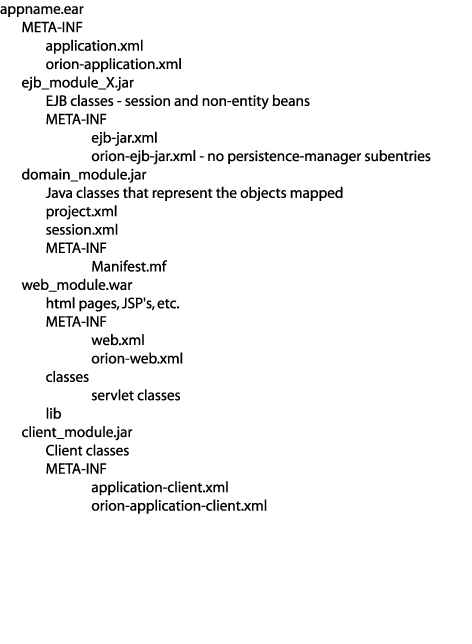
The component archives with TopLink dependencies include the following:
The domain JAR contains the TopLink files and domain objects required by the application, including the following:
project.xml File (or the compiled project.class file if you are not using XML files for deployment)
The mapped classes required by the application, in a fully-resolved directory structure
When you create the JAR file, the JAR building utility automatically creates a directory structure within the JAR. Ensure that the sessions.xml file and the project.xml file (or project.class file) appear at the root of the JAR file. Also ensure that the class directory structure starts at the root of the JAR.
If you do not store the project.xml or sessions.xml files at the root of the JAR file, see "Packaging With TopLink Metadata File Resource Paths".
In this type of application, the EJB JAR contains session beans. Consequently, its orion-ejb-jar.xml file does not contain persistence-manager or pm-properties entries. These entries apply only to CMP applications.
For J2EE applications that use CMP to persist entity beans, it is common to package the application in an Enterprise Archive (EAR) file made up of various J2EE application component archives as Figure 9-4 shows.
Figure 9-4 Packaging a J2EE Application With Entity Beans With Container-Managed Persistence
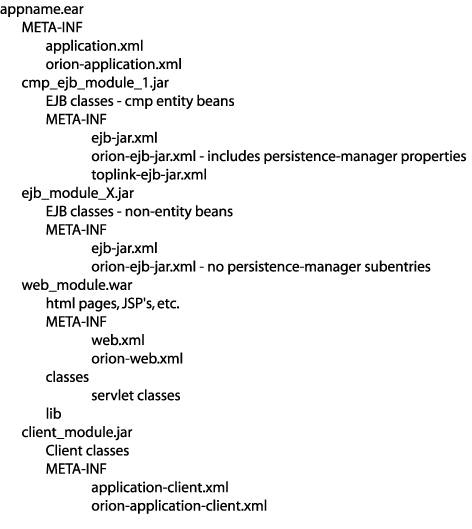
The component archives with TopLink dependencies include the following:
In this type of application, the EJB JAR file specifically service both non-entity and entity EJB. It includes the following:
The home and remote, and all implementation code for all mapped beans in the application.
All mapped non-EJB classes from the TopLink Workbench project
The home and remote, and all implementation code for any session beans included in the application.
Helper classes that contain TopLink amendment methods, and any other classes the application requires.
For example, an instance of oracle.toplink.ejb.cmp.DeploymentCustomization (for more information, see customization-class in Table 8-3 in "Configuring persistence-manager Entries").
Store the following XML files in the EJB JAR \meta-inf directory:
|
Note: If you do not use XML files for deployment, include your compiledoracle.toplink.sessions.Project file at the root of the EJB JAR (not in the \meta-inf directory). |
Because the EJB JAR contains both session and entity beans, if you are using OC4J or BEA WebLogic (WLS), the <J2EE-Container>-ejb-jar.xml file must contain persistence-manager and pm-properties entries. For more information, see "Configuring persistence-manager Entries".
You must persist all of the entity beans to the same data source. For a CMP application, TopLink does not support the session broker functionality (see "Session Broker and Client Sessions").
For J2EE applications that use BMP to persist entity beans, it is common to package the application in an Enterprise Archive (EAR) file made up of various J2EE application component archives as Figure 9-5 shows.
Figure 9-5 Packaging a J2EE Application With Entity Beans With Bean-Managed Persistence

The component archives with TopLink dependencies include the following:
The domain JAR contains the TopLink files and domain objects required by the application, including the following:
project.xml File (or the compiled project.class file if you are not using XML files for deployment)
The mapped classes required by the application, in a fully resolved directory structure
When you create the JAR file, the JAR building utility automatically creates a directory structure within the JAR. Ensure that the sessions.xml file and the project.xml file (or project.class file) appear at the root of the JAR file. Also ensure that the class directory structure starts at the root of the JAR.
If you do not store the project.xml or sessions.xml files at the root of the JAR file, see "Packaging With TopLink Metadata File Resource Paths".
In this type of application, the EJB JAR file specifically services both session and entity beans. It includes the following:
The home and remote, and all implementation code for all mapped beans in the application
All mapped non-EJB classes from the TopLink Workbench project
The home and remote, and all implementation code for any session beans included in the application
Helper classes that contain TopLink amendment methods, and any other classes the application requires
Store the following XML files in the EJB JAR \meta-inf directory:
Because the EJB JAR does not contain entity beans with container-managed persistence, its orion-ejb-jar.xml file must not contain persistence-manager or pm-properties entries.
For more information, see "Configuring persistence-manager Entries".
If you do not store the project.xml or sessions.xml files at the root of the JAR file, then you must provide the full resource path to the files when accessing them. Ensure that you use "/" in resources paths, not "\". Using "\" will not work in Java.
For example, in the jar element, reference the project.xml and sessions.xml files as follows:
<jar>/myapp/ordersys/persist/sessions.xml <jar>/myapp/ordersys/persist/project.xml
In the sessions.xml file, reference the project.xml as follows:
myapp/ordersys/persist/project.xml
To acquire the session, use the following:
SessionManager.getManager().getSession(
new XMLSessionConfigLoader("myapp/ordersys/persist/sessions.xml"),
"OrdersysSession",
getClass().getClassLoader()
);
For more information about acquiring sessions at run time, see "Acquiring a Session From the Session Manager".