| Oracle® TopLink Developer's Guide 10g Release 3 (10.1.3.1.0) Part Number B28218-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® TopLink Developer's Guide 10g Release 3 (10.1.3.1.0) Part Number B28218-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
This chapter describes how to configure an XML mapping.
Table 63-1 lists the types of XML mappings that you can configure and provides a cross-reference to the type-specific chapter that lists the configurable options supported by that type.
Table 63-1 Configuring XML Mappings
Table 63-2 lists the configurable options shared by two or more XML mapping types.
For more information, see the following:
Table 63-2 lists the configurable options shared by two or more XML mapping types. In addition to the configurable options described here, you must also configure the options described for the specific XML Mapping Types, as shown in Table 63-1.
Table 63-2 Common Options for XML Mappings
| Option | Type | TopLink Workbench | Java |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Basic |
 |
 |
|
"Configuring Reference Descriptor" |
Basic |
 |
 |
|
"Configuring Container Policy" |
Advanced |
 |
 |
|
"Configuring Method Accessing" |
Advanced |
 |
 |
|
"Configuring Read-Only Mappings" |
Advanced |
 |
 |
|
"Configuring Maps to Wildcard" |
Advanced |
 |
|
|
"Configuring a Serialized Object Converter" |
Advanced |
 |
 |
|
"Configuring a Type Conversion Converter" |
Advanced |
 |
 |
|
"Configuring an Object Type Converter" |
Advanced |
 |
 |
|
"Configuring a Simple Type Translator" |
Advanced |
 |
 |
|
"Configuring the Use of a Single Node" |
Advanced |
 |
 |
For XML attributes that reference other descriptors (instead of a schema element), you must select a specific reference descriptor.
Table 63-3 summarizes which XML mappings support reference descriptor configuration.
Table 63-3 XML Mapping Support for Reference Descriptor Configuration
| XML Mapping | Using TopLink Workbench |
Using Java |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
XML Composite Direct Collection Mapping |
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
|
XML Composite Collection Mapping |
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
To specify a reference descriptor for an XML mapping that references another descriptor (instead of a schema element), use this procedure.
Select the mapped attribute in the Navigator. Its properties appear in the Editor.
Click the General tab. The General tab appears.
Figure 63-1 General Tab, Reference Descriptor Field
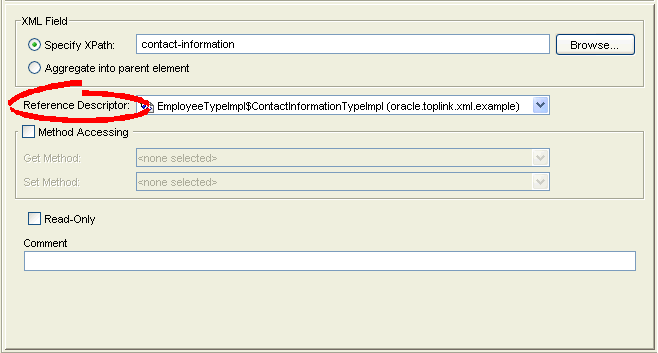
If this XML attribute refers to another descriptor (instead of a schema element), use the Reference Descriptor field to select a descriptor in the project.
This attribute applies only to TopLink Workbench. Use this option to solve "No XPath specified" problems (see "Using the Problems Window") for an XML mapping that does not need an XPath (see "Configuring XPath") for it maps to a wildcard.
If the XML mapping is owned by an anyType descriptor (see "Configuring for Complex Type of anyType"), it cannot map to a wildcard, and you must specify an XPath.
Table 63-4 summarizes which XML mappings support maps to wildcard configuration.
Table 63-4 XML Mapping Support for Maps to Wildcard Configuration
| XML Mapping | Using TopLink Workbench | Using Java |
|---|---|---|
|
|
 |
 |
|
XML Composite Direct Collection Mapping |
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
XML Composite Collection Mapping |
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
To specify a map a schema element using the xs:any declaration, use this procedure.
Select the mapped attribute in the Navigator. Its properties appear in the Editor.
Figure 63-2 Mapping Tab, Maps to Wildcard Option
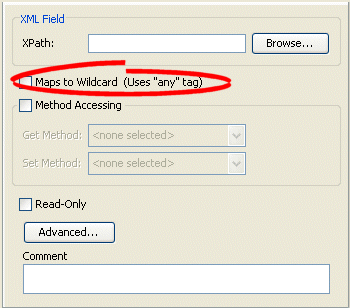
If the XML mapping is not owned by an anyType descriptor (see "Configuring for Complex Type of anyType") and maps to a wildcard, then you do not need to specify an XPath (see "Configuring XPath"). Select the Maps to Wildcard (uses "any" tag) option to clear the missing XPath neediness message.
If the XML mapping is owned by an anyType descriptor, it cannot map to a wildcard and you must specify an XPath. Deselect the Maps to Wildcard (Uses "any" tag) option and ensure that you specify an XPath.