| Oracle® TopLink Developer's Guide 10g Release 3 (10.1.3.1.0) Part Number B28218-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® TopLink Developer's Guide 10g Release 3 (10.1.3.1.0) Part Number B28218-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
This chapter explains how transactions are implemented in TopLink, including the following:
A database transaction is a set of operations (create, read, update, or delete) that either succeed or fail as a single operation. The database discards, or rolls back, unsuccessful transactions, leaving the database in its original state. Transactions may be internal (that is, provided by TopLink) or external (that is, provided by a source external to the application, such as an application server).
In TopLink, transactions are contained in the unit of work object. You acquire a unit of work from a session (see "Acquiring a Unit of Work") and using its API, you can control transactions directly or through a Java 2 Enterprise Edition (J2EE) application server transaction controller such as the Java Transaction API (JTA).
Transactions execute in their own context, or logical space, isolated from other transactions and database operations.
The transaction context is demarcated; that is, it has a defined structure that includes:
A begin point, where the operations within the transaction begin. At this point, the transaction begins to execute its operations.
A commit point, where the operations are complete and the transaction attempts to formalize changes on the database.
The degree to which concurrent (parallel) transactions on the same data are allowed to interact is determined by the level of transaction isolation configured. ANSI/SQL defines four levels of database transaction isolation as shown in Table 97-1. Each offers a trade-off between performance and resistance from the following unwanted actions:
Dirty read: a transaction reads uncommitted data written by a concurrent transaction.
Nonrepeatable read: a transaction rereads data and finds it has been modified by some other transaction that was committed after the initial read operation.
Phantom read: a transaction reexecutes a query and the returned data has changed due to some other transaction that was committed after the initial read operation.
Table 97-1 Transaction Isolation Levels
| Transaction Isolation Level | Dirty Read | Nonrepeatable Read | Phantom Read |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Read Uncommitted |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Read Committed |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Repeatable Read |
No |
No |
Yes |
|
Serializable |
No |
No |
No |
As a transaction is committed, the database maintains a log of all changes to the data. If all operations in the transaction succeed, the database allows the changes; if any part of the transaction fails, the database uses the log to roll back the changes.
Like any transaction, a unit of work transaction provides the following:
Unit of work operations occur within a unit of work context, in which writes are isolated from the database until commit time. The unit of work executes changes on copies, or clones, of objects in its own internal cache, and if successful, applies changes to objects in the database and the session cache.
In a standalone TopLink application, your application demarcates transactions using the unit of work.
If your application includes a J2EE container that provides container-managed transactions, your application server demarcates transactions using its own transaction service. You configure TopLink to integrate with the container's transaction service by specifying a TopLink external transaction controller.
A TopLink external transaction controller class integrates the unit of work with an application server's transaction service. Using an external transaction controller, your application can participate in transactions that span multiple data sources and that are managed by the application server. The external transaction controller coordinates messages and callbacks between the application server's transaction service and the unit of work.
When you configure your application to use an external transaction controller (see "Configuring the Server Platform"), the unit of work executes as part of an external transaction. The unit of work still manages its own internal operations, but it waits for the external transaction to tell it to write changes back to the database and to the session cache.
Note that because the transaction happens outside of the unit of work context and is controlled by the application server's transaction service, errors can be more difficult to diagnose and fix because exceptions may occur outside of your application code, for example, during application server initiated call-backs.
You can integrate the unit of work with the following:
The Java Transaction API (JTA) is the application programming interface you use to interact with a transaction manger.
Using JTA, your application can participate in a distributed transaction. A transaction manager that implements JTA provides transaction management and connection pooling and enables your application to interact with multiple data sources transparently by using JTA.
For more information, see "Integrating the Unit of Work With an External Transaction Service".
The CORBA Object Transaction Service (OTS) specification is part of the Common Object Request Brokers Architecture (CORBA) Object Services model and is the standard for Object Request Broker (ORB) implementations. Some servers implement the Java APIs for the OTS rather than for JTA (see "JTA Controlled Transactions").
Use TopLink OTS support with the unit of work to directly access the Java OTS interfaces of servers that do not support JTA.
To integrate your application with an OTS transaction service, you must configure your application to use a custom server platform (see "Configuring the Server Platform").
For more information, see "Integrating the Unit of Work With an External Transaction Service".
Entity beans that use container-managed persistence may participate in transactions that are either client demarcated or container demarcated.
A client demarcated transaction occurs when a client of an entity bean directly sets up transaction boundaries using the javax.transaction.UserTransaction interface.
A container demarcated transaction occurs when the container automatically wraps an invocation on an EJB in a transaction based upon the transaction attributes supplied in the EJB deployment descriptor.
In transactions involving EJB, TopLink waits until the transaction begins its two-phase commit process before updating the database. This allows for the following:
SQL optimizations that ensure only changed data is written to the data source
Proper ordering of updates to allow for database constraints
For more information, see "Integrating the Unit of Work With CMP".
The unit of work does not directly participate in database transaction isolation. Because the unit of work may execute queries outside the database transaction (and, by interacting with the cache, outside the database itself), the database does not have control over this data and its visibility.
However, by default, TopLink provides a degree of transaction isolation regardless of what database transaction isolation has been configured on the underlying database.
Each unit of work instance operates on its own copy (clone) of registered objects (see "Clones and the Unit of Work"). In this case, because the unit of work provides an API that allows querying to be done on object changes within a unit of work (see "Using Conforming Queries and Descriptors"), the unit of work provides read committed operations.
Optimistic locking, optimistic read locking, or pessimistic locking can be used to further manage concurrency (see "Locking and the Unit of Work").
Changes are committed to the database only when the unit of work commit method is called (either directly or by way of an external transaction controller).
For detailed information on configuring and using TopLink to achieve a particular level of transaction isolation and transaction isolation level limitations, see "Database Transaction Isolation Levels".
This section introduces transaction concepts unique to TopLink, including the following:
The TopLink unit of work simplifies transactions and improves transactional performance. It is the preferred method of writing to a database in TopLink because it performs the following:
Sends a minimal amount of SQL to the database during the commit by updating only the exact changes down to the field level
Reduces database traffic by isolating transaction operations in their own memory space
Optimizes cache coordination, in applications that use multiple caches, by passing change sets (rather than objects) between caches
Isolates object modifications in their own transaction space to allow parallel transactions on the same objects
Ensures referential integrity and minimizes deadlocks by automatically maintaining SQL ordering
Orders database insert, update, and delete operations to maintain referential integrity for mapped objects
Resolves bidirectional references automatically
Frees the application from tracking or recording its changes
Simplifies persistence with persistence by reachability (see "Associating a New Source to an Existing Target Object")
TopLink uses the unit of work as follows:
The client application acquires a unit of work from a session object.
The client application queries TopLink to obtain a cache object it wants to modify, and then registers the cache object with the unit of work.
The unit of work registers the object according to the object's change policy. For more information about how change policy affects registration, see "Unit of Work and Change Policy".
By default, as each object is registered, the unit of work accesses the object from the session cache or database and creates a backup clone and working clone (see "Clones and the Unit of Work"). The unit of work returns the working clone to the client application.
The client application modifies the working object returned by the unit of work.
The client application (or external transaction controller) commits the transaction.
The unit of work calculates the change set for each registered object according to the object's change policy. For more information about how change policy affects change set calculation, see "Unit of Work and Change Policy".
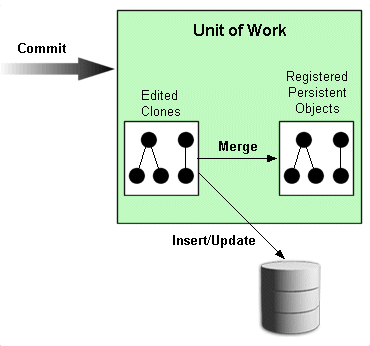
By default, at commit time, the unit of work compares the working clones to the backup clones and calculates the change set (that is, determines the minimum changes required). The comparison is done with a backup clone so that concurrent changes to the same objects will not result in incorrect changes being identified. The unit of work then attempts to commit any new or changed objects to the database.
If the commit transaction succeeds, the unit of work merges changes into the shared session cache. Otherwise, no changes are made to the objects in the shared cache. For more details, see "Commit and Rollback Transactions".
If there are no changes, the unit of work does not start a new transaction.
Figure 97-1 The Life Cycle of a Unit of Work
Example 97-1 shows the default life cycle in code.
Example 97-1 Unit of Work Life Cycle
// The application reads a set of objects from the database Vector employees = session.readAllObjects(Employee.class); // The application specifies an employee to edit . . . Employee employee = (Employee) employees.elementAt(index); try { // Acquire a unit of work from the session UnitOfWork uow = session.acquireUnitOfWork(); // Register the object that is to be changed. Unit of work returns a clone // of the object and makes a backup copy of the original employee Employee employeeClone = (Employee)uow.registerObject(employee); // Make changes to the employee clone by adding a new phoneNumber. // If a new object is referred to by a clone, it does not have to be // registered. Unit of work determines it is a new object at commit time PhoneNumber newPhoneNumber = new PhoneNumber("cell","212","765-9002"); employeeClone.addPhoneNumber(newPhoneNumber); // Commit the transaction: unit of work compares the employeeClone with // the backup copy of the employee, begins a transaction, and updates the // database with the changes. If successful, the transaction is committed // and the changes in employeeClone are merged into employee. If there is an // error updating the database, the transaction is rolled back and the // changes are not merged into the original employee object uow.commit(); } catch (DatabaseException ex) { // If the commit fails, the database is not changed. The unit of work should // be thrown away and application-specific action taken } // After the commit, the unit of work is no longer valid. Do not use further
The unit of work tracks changes for a registered object based on the change policy you configure for the object's descriptor. If there are no changes, the unit of work will not start a new transaction.
Table 97-2 lists the change policies that TopLink provides.
Table 97-2 TopLink Change Policies
| Change Policy | Applicable to... |
|---|---|
|
Deferred Change Detection Policy |
Wide range of object change characteristics. The default change policy. |
|
Object-Level Change Tracking Policy |
Objects with few attributes or with many attributes and many changed attributes. |
|
Attribute Change Tracking Policy |
Objects with many attributes and few changed attributes. The most efficient change policy. The default change policy for EJB 3.0 persistent or 2.n CMP on OC4J. |
For more information, see "Configuring Change Policy".
The DeferredChangeDetectionPolicy is the change policy that all persistent objects use by default.
This option provides good unit of work commit performance for a wide range of object change characteristics.
When you register in a unit of work an object whose descriptor is configured with a DeferredChangeDetectionPolicy (see "Configuring Deferred Change Detection Policy"), a backup clone is made of the object (see "Clones and the Unit of Work") and at commit time, the unit of work computes changes by making an attribute-by-attribute comparison between the backup clone and the original object.
This change policy is applicable to all mapping types.
The ObjectChangeTrackingPolicy optimizes the unit of work commit transaction by including objects in the change set calculation only if at least one attribute has changed.
This option provides improved unit of work commit performance for objects with few attributes, or with many attributes and many changed attributes.
When you register in a unit of work an object whose descriptor is configured with ObjectChangeTracking change policy, a backup clone is made of the object and at commit time, the unit of work computes changes by comparing the backup to the current object if and only if at least one attribute is changed (if the object's hasChanges method returns true). If a registered object has no changes, the unit of work does not compare it to the backup clone.
This change policy is applicable to a subset of mapping types (see "Change Policy Mapping Support").
TopLink provides different levels of support for this change policy depending on the EBJ version and application server you are using:
For CMP applications deployed to an application server for which TopLink provides CMP integration (see "Application Server Support"), when you configure a descriptor for an entity bean with container-managed persistence with an ObjectChangeTrackingPolicy, TopLink code generates a concrete subclass to implement the TopLink ChangeTracker interface at deploy time (see "Configuring Object Change Tracking Policy").
|
Note: The preceding paragraph is also true for applications that use EJB 3.0 persistence. |
The AttributeChangeTrackingPolicy optimizes the unit of work commit transaction by tracking all object changes at the attribute level. This eliminates two unit of work operations: backup clone creation and change detection through comparison.
This option provides improved unit of work commit performance for objects with many attributes, and few changed attributes. Generally, this is the most efficient change policy.
This change policy is applicable to a subset of mapping types (see "Change Policy Mapping Support").
|
Note: You cannot use theAttributeChangeTrackingPolicy if you are using any instance of FieldsLockingPolicy (see "Optimistic Field Locking Policies"). |
TopLink provides different levels of support for this change policy depending on the EBJ version and application server you are using:
For plain Java objects or application servers other than OC4J, to use the AttributeChangeTrackingPolicy with a class, you must configure the class's descriptor with an AttributeChangeTrackingPolicy and you must implement the ChangeTracker interface in that class (see "Configuring Attribute Change Tracking Policy").
When using CMP on OC4J, if you want to benefit from this performance enhancement, configure your descriptors with the default DeferredChangeDetectionPolicy and allow TopLink to automatically apply an AttributeChangeTrackingPolicy. If you configure your project's descriptors with any other change policy, TopLink will honor that configuration and not apply an AttributeChangeTrackingPolicy.
When you deploy a TopLink-enabled CMP application to OC4J, for each mapped class configured with the default DeferredChangeDetectionPolicy, TopLink uses code generation to automatically override this configuration with an AttributeChangeTrackingPolicy and to make the class implement the required interfaces.
TopLink supports alternative change tracking policies (policies other than DeferredChangeDetectionPolicy) for attributes that use any of the following mapping types:
Transformation Mapping (immutable mappings only)
EIS Transformation Mapping (immutable mappings only)
TopLink uses the DeferredChangeDetectionPolicy (see "Deferred Change Detection Policy") for attributes that use any other type of mapping.
When using the DefrerredChangeDetectionPolicy or the ObjectLevelChangeTrackingPolicy (see "Deferred Change Detection Policy"), the unit of work maintains two copies of the original objects registered with it:
Working clones
Backup clones
After you change the working clones and the transaction is committed, the unit of work compares the working clones to the backup clones, and writes any changes to the database. The unit of work uses clones to allow parallel units of work (see "Nested and Parallel Units of Work") to exist, a requirement in multiuser three-tier applications.
The TopLink cloning process is efficient in that it clones only the mapped attributes of registered objects, and stops at indirection objects unless you trigger the indirection. For more information, see "Configuring Indirection".
You can customize the cloning process using the descriptor's copy policy. For more information, see "Configuring Copy Policy".
Never use a clone after committing the unit of work that the clone is from (even if the transaction fails and rolls back). A clone is a working copy used during a transaction and as soon as the transaction is committed (successful or not), the clone must not be used. Accessing an uninstantiated clone value holder after a unit of work commit transaction will raise an exception. The only time you can use a clone after a successful commit transaction is when you use the advanced API described in "Resuming a Unit of Work After Commit".
You can use TopLink to create the following:
For additional information and examples on using nested and parallel units of work, see "Using a Nested or Parallel Unit of Work".
You can nest a unit of work (the child) within another unit of work (the parent). A nested unit of work does not commit changes to the database. Instead, it passes its changes to the parent unit of work, and the parent attempts to commit the changes at commit time. Nesting units of work lets you break a large transaction into smaller isolated transactions, and ensures that:
Changes from each nested unit of work commit or fail as a group.
Failure of a nested unit of work does not affect the commit or rollback transaction of other operations in the parent unit of work.
Changes are presented to the database as a single transaction.
You can modify the same objects in multiple unit of work instances in parallel because the unit of work manipulates copies of objects. TopLink resolves any concurrency issues when the Units of Work commits the changes.
When a unit of work transaction is committed, it either succeeds, or fails and rolls back. A commit transaction can be initiated by your application or by a J2EE container.
At commit time, the unit of work compares the working clones and backup clones to calculate the change set (that is, to determine the minimum changes required). Changes include updates to or deletion of existing objects, and the creation of new objects. The unit of work then begins a database transaction, and attempts to write the changes to the database. If all changes commit successfully on the database, the unit of work merges the changed objects into the session cache. If any one of the changes fail on the database, the unit of work rolls back any changes on the database, and does not merge changes into the session cache.
The unit of work calculates commit order using foreign key information from one-to-one and one-to-many mappings. If you encounter constraint problems during a commit transaction, verify your mapping definitions. The order in which you register objects with the registerObject method does not affect the commit order.
When your application uses JTA, the unit of work commit transaction acts differently than in a non-JTA application. In most cases, the unit of work attaches itself to an external transaction. If no transaction exists, the unit of work creates a transaction. This distinction affects commit activity as follows:
If the unit of work attaches to an existing transaction, the unit of work ignores the commit call. The transaction commits the unit of work when the entire external transaction is complete.
If the unit of work starts the external transaction, the transaction treats the unit of work commit call as a request to commit the external transaction. The external transaction then calls its own commit code on the database.
In either case, only the external transaction can call commit on the database because it owns the database connection.
For more information, see "Integrating the Unit of Work With an External Transaction Service".
A unit of work commit transaction must succeed or fail as a unit. Failure in writing changes to the database causes the unit of work to roll back the database to its previous state. Nothing changes in the database, and the unit of work does not merge changes into the session cache.
In a JTA environment, the unit of work does not own the database connection. In this case, the unit of work sends the rollback call to the external transaction rather than the database, and the external transaction treats the rollback call as a request to roll the transaction back.
For more information, see "Integrating the Unit of Work With an External Transaction Service".
You cannot modify the primary key attribute of an object in a unit of work. This is an unsupported operation and doing so will result in unexpected behaviour (exceptions or database corruption).
To replace one instance of an object with unique constraints with another, see "Using the Unit of Work setShouldPerformDeletesFirst Method".
By default, the unit of work performs change set calculation efficiently for a wide range of object change characteristics. However, there are various ways you can use the unit of work to enhance application performance.
One way to improve performance is to consider using an alternative change policy (see "Unit of Work and Change Policy").
For more performance options, see "Unit of Work Optimization".
You do not instantiate an instance of oracle.toplink.sessions.UnitOfWork. Rather, you acquire a unit of work from an instance of oracle.toplink.sessions.Session or from another unit of work.
For more information on creating sessions, see "Creating Sessions".
For more information on acquiring a unit of work, see "Acquiring a Unit of Work".
For more information on using the basic API of the unit of work, see "Using Basic Unit of Work API".
For more information on using the advanced API of the unit of work, see "Using Advanced Unit of Work API".
The unit of work extends the interface oracle.toplink.sessions.Session, and implements all the usual session API. When using session API from a unit of work, you should consider the following:
A unit of work offers the same set of database access methods as a regular session.
When called from a unit of work, these methods access the objects in the unit of work, register the selected objects automatically, and return clones.
Although this makes it unnecessary for you to call the registerObject and registerAllObjects methods, be aware of the restrictions on registering objects described in "Creating an Object" and "Associating a New Source to an Existing Target Object".
As with regular sessions, you use the readObject and readAllObjects methods to read objects from the database.
For information on locking API generic to all sessions, see:
For information on locking API specific to a unit of work, see "Using Optimistic Read Locking With forceUpdateToVersionField".
Throughout the chapters in this part, the following object model and schema are used in the examples provided. The example object model appears in Figure 97-2 and the example entity-relationship (data model) diagram appears in Figure 97-3.