Siebel Life Sciences Guide > Importing Data > Administrator Procedures >
Importing Data with Siebel EIM
Siebel EIM manages the exchange of data between Siebel database tables and other corporate databases. This section provides information specific to Siebel Life Sciences and supersedes information in Siebel Enterprise Integration Manager Administration Guide. For general information on Siebel EIM, read Siebel Enterprise Integration Manager Administration Guide.
Stages of the Data Import Process
The data import process with Siebel EIM uses two stages, as shown in Figure 12.
- The data is first copied from external data tapes (or other provided media) into the interface tables for the Siebel Industry Application (SIA), using a native database data-loading utility (such as SQL* Loader).
For information about the interface tables and their relationships to base tables in the Siebel application database, read Data and Related Interface Tables. For further details on Siebel Industry Application interface tables, such as the contents of each table, read Interface Tables Reference for Siebel Industry Applications.
- Using EIM, you transfer the data from the interface tables to predefined destination columns in the base tables of the Siebel Life Sciences database. The EIM process uses a configuration file (
default.ifb).
For general information about default.ifb and instructions on using Siebel EIM, read Siebel Enterprise Integration Manager Administration Guide.
Figure 12. Process Flow From an External Database to the SIA Database
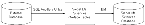
|
Recommended Import Order
To correctly establish the relationships between dependent data elements, the data should be imported in the order recommended below. In general, reference data such as therapeutic classes, competitive metrics, and competitive issues should be imported first, followed by employee and product data (internal products, external products, and medical specialties), followed by contacts data. Syndicated data should be loaded last.
The following list shows the recommended import order for all data types specific to Siebel Life Sciences.
- Reference data (therapeutic classes, competitive metrics, and so on)
- Employees
- Broadcast messages
- Products (both internal and external)
- Leads
- Medical specialties
- Insurance plans
- Accounts
- Opportunities
- Formularies
- Contacts
- Contact ratings and rankings
- Quotes
- Documents
- Proposal templates
- Forecasts
- Fulfillment data
- Call lists
- Objectives
- Marketing campaigns
- Product consumption
- Service requests
- Product defects
- Activities and appointments
- Notes
- File attachments
- Syndicated data
Data and Related Interface Tables
The process for importing syndicated data takes advantage of the fact that syndicated data is read-only. Because the row ID on the S_SYND_DATA table is never referred to anywhere else in the Siebel data model, it can be populated with dummy values that differ from usual row IDs. The application administrator uses SQL*Loader to populate the ID field with a unique sequential value, a process which provides either full or partial table-level extraction. Using views in the Syndicated Data Administration screen, you can define complex routing rules for syndicated data.
Table 19 shows the relationships between the data, interface tables, and base tables.
Table 19. Data and Related Interface Tables
Data
|
Interface Table
|
Base Table
|
Table Description
|
Account Details
|
EIM_ACCNT_DTL
|
S_ORG_EXT
|
Organization
|
S_ORG_EXT_LSX
|
1:1 Extension table for Account Types
|
S_ORG_EXT_X
|
1:1 Account Best Times to Visit
|
Activities
|
EIM_ACTIVITY
|
S_EVT_ACT
|
Activities
|
EIM_ACTIVITY1
|
S_EVT_ACT
|
Activities Only User Key
|
S_ACT_SIGN
|
Signatures
|
EIM_ACTIVITY2
|
S_EVT_ACT
|
Activities Only User Key
|
S_ACT_PRDINT
|
Activity Products
|
S_ACT_ISS
|
Activity Issues
|
S_ACT_PROD_ISS
|
Issues for Activity Products
|
Addresses
|
EIM_ADDR_ORG
|
S_ADDR_ORG
|
Account Addresses including Bricks
|
Agreements and Contracts
|
EIM_AGREEMENT
|
S_DOC_AGREE
|
Agreements and Contracts
|
EIM_AGREE_LS
|
S_DOC_AGREE
|
Contracts
|
S_AGREE_PAY
|
Contract Payments
|
EIM__ENTLMNT
|
S_ENTLMNT
|
Entitlements and Contract Price Group
|
S_ENTLMNT_ITEM
|
Price Group Products
|
S_ENTLMNT_FEE
|
Nonproduct Fees
|
S_ENTLMNT_ITEM_FEE
|
Product Fee Price Group
|
Brick
|
EIM_AREA_LS
|
S_AREA_LS
|
Bricks
|
Chat and Discussions
|
EIM_DISCN_LS
|
S_TOPIC_LS
|
Chat/Discussion Topics
|
S_TOPIC_CON_LS
|
Chat User Registration
|
S_MESG_BRD_LS
|
Message Board
|
Clinical
|
EIM_CL_ACT_LS
|
S_EVT_ACT
|
Clinical Activity Columns
|
EIM_CL_DSGN_LS
|
S_CL_DSGN_LS
|
Clinical Designs
|
EIM_CL_PGM_LS
|
S_CL_PGM_LS
|
Clinical Programs
|
S_CL_PGM_ATT_LS
|
Clinical Program Attachments
|
S_CL_PGM_APP_LS
|
Clinical Program Applications
|
EIM_CL_PTCL_LS
|
S_CL_PTCL_LS
|
Clinical Protocols
|
S_CL_PTCL_LSXM
|
1:M Protocol Extension Table
|
S_CL_PTL_ATT_LS
|
Clinical Protocol Attachments
|
S_CL_PTL_POS_LS
|
Clinical Protocol Positions
|
S_CPTCL_DSGN_LS
|
Clinical Protocol Designs
|
EIM_CL_SUBJ_LS
|
S_CL_SUBJ_LS
|
Clinical Subjects
|
S_CL_SUBJ_ST_LS
|
Clinical Subject Status
|
S_CL_SJ_CSNT_LS
|
Clinical Subject Consent
|
S_CL_SBJ_ATT_LS
|
Clinical Subject Attachments
|
EIM_PTL_SITE_LS
|
S_PTCL_SITE_LS
|
Clinical Protocol Sites
|
S_PTL_ST_POS_LS
|
Clinical Protocol Site Positions
|
S_PTL_ST_ATT_LS
|
Clinical Protocol Site Attachments
|
S_PTL_ST_CON_LS
|
Clinical Protocol Site Contacts
|
S_PS_STMPVER_LS
|
Clinical Protocol Site Template Versions
|
S_CL_ACT_EXC_LS
|
Clinical Protocol Site Activity Exceptions
|
S_CL_PYMNT_LS
|
Clinical Payments
|
EIM_SBJ_TMPL_LS
|
S_SUBJ_TMPL_LS
|
Subject Templates
|
S_SBJTMP_VER_LS
|
Subject Template Versions
|
EIM_TMPL_PLNITM
|
S_TMPL_PLAN_ITEM
|
Subject Template Visits
|
Companies
|
EIM_ACCOUNT
|
S_ORG_EXT
|
Organization
|
S_ACCNT_POSTN
|
Position for Account
|
S_ADDR_ORG
|
Account Addresses
|
S_ORG_REL
|
Account Affiliations
|
EIM_ACCOUNT1
|
S_ORG_EXT
|
Organization Only User Key
|
S_ACCNT_CLS_RNK
|
Account Ratings and Rankings
|
S_ACCNT_MED_PROC
|
Account Medical Procedures
|
S_ACCNT_MED_SPEC
|
Account Medical Specialties
|
Contacts
|
EIM_CONTACT
|
S_CONTACT
|
Contacts
|
S_ADDR_PER
|
Contact Addresses
|
S_CONTACT_REL
|
Contact Affiliations
|
S_PER_ORG_UNIT
|
Contact to Account Affiliations and Roles
|
S_STATE_LIC_LS
|
Contact State Licenses
|
EIM_CONTACT1
|
S_CONTACT
|
Contacts Only User Key
|
S_POSTN_CON
|
Contact Positions
|
S_CON_ADDR
|
Contact Address Usage
|
EIM_CON_DTL
|
S_CONTACT
|
Contacts Only User Key
|
S_CONTACT_LSX
|
1:1 Contacts Extension Table
|
S_CONTACT_LSXM
|
1:M Contacts Extension Table
|
Formularies
|
EIM_FRMULRY_LS
|
S_FORMULARY
|
Formulary Opportunities
|
S_FRMULRY_PROD
|
Formulary Products
|
Industry
|
EIM_INDUSTRY
|
S_INDUST
|
Account and Contact Types
|
Insurance Plans
|
EIM_INS_PLAN_LS
|
S_INS_PLAN
|
Insurance Plans
|
Medical Education
|
EIM_ME_EVT_LS
|
S_ME_EVT_LS
|
MedEd Events
|
S_ME_EVT_POS_LS
|
MedEd Event Positions
|
S_ME_EVT_PRD_LS
|
MedEd Event Products
|
S_ME_EVT_INV_LS
|
MedEd Event Invitees
|
EIM_ME_PLN_LS
|
S_ME_PLN_LS
|
MedEd Plans
|
S_ME_PLN_MDF_LS
|
MedEd Plan Funds
|
S_ME_PLN_PRD_LS
|
MedEd Plan Products
|
EIM_ME_SES_LS
|
S_ME_SES_LS
|
MedEd Sessions
|
S_ME_SES_PRD_LS
|
MedEd Session Products
|
S_ME_SES_INV_LS
|
MedEd Session Invitees
|
S_ME_SES_LIT_LS
|
MedEd Session Literature
|
S_ME_SES_MAT_LS
|
MedEd Session Materials
|
Medical Procedures
|
EIM_PROC_LS
|
S_MED_PROC
|
Medical Procedures
|
Medical Specialties
|
EIM_SPEC_LS
|
S_MED_SPEC
|
Medical Specialties
|
Objectives
|
EIM_ACCT_SRC
|
S_ACCNT_SRC
|
Target Accounts for Objectives
|
EIM_CONTACT2
|
S_CONTACT
|
Contacts Only User Key
|
S_CAMP_CON
|
Target Contacts for Objective
|
EIM_SRC
|
S_SRC
|
Objectives
|
S_SRC_POSTN
|
Objective Positions
|
Products
|
EIM_PROD_INT
|
S_PROD_INT
|
Products-Details, Samples, Markets, Lots, and Promotional Items
|
EIM_PROD_INT1
|
S_PROD_INT
|
Products
|
S_PROD_POSTN
|
Personal Product List
|
S_PROD_REL
|
Product Relations
|
Samples
|
EIM_SAMPLE_LS
|
S_SAMPLE_TXN
|
Sample Transactions
|
S_MPL_TXN_ITEM
|
Sample Transaction Item
|
EIM_POSITION
|
S_POSTN
|
Positions
|
S_STOCK_POSTN
|
Stock Inventory by Position
|
S_STOCK_PERIOD
|
Stock Period
|
Signature Disclaimers
|
EIM_SIGNDIC_LS
|
S_SIGN_DISC_LS
|
Signature Disclaimers
|
Syndicated Data
|
EIM_SYN_DATA_LS
|
S_SYND_DATA
|
Syndicated Data
|
For further information, see Interface Tables Reference for Siebel Industry Applications. That book lists the contents of each table referred to in Table 19:
- Specific data and file attachments that Siebel EIM can process.
- Names of the interface tables.
- Target base tables mapped to the interface tables.
- Any secondary tables associated with the target tables (where data from the interface tables might ultimately reside).