| Oracle® Business Intelligence Applications Installation and Configuration Guide Version 7.9.4 E10742-01 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
| Oracle® Business Intelligence Applications Installation and Configuration Guide Version 7.9.4 E10742-01 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
This chapter describes how to configure Oracle Financial Analytics for particular sources to meet your business needs.
This chapter contains the following topics:
Oracle Financial Analytics consists of the following:
Oracle General Ledger and Profitability Analytics. The General Ledger Analytics application provides information to support your enterprise's balance sheet and provides a detailed analysis on the overall health of your company. The default configuration for the General Ledger Analytics application is based on what is identified as the most-common level of detail or granularity. However, you can configure and modify the extracts to best meet your business requirements.
The Profitability Analytics application provides cost analysis, revenue trends, and sales performance to provide an accurate picture of profit and loss. The information found in the Profitability Analytics application pertains to data found in the revenue and expense account groupings of your financial statements and chart of accounts. The Profitability Analytics application is designed to provide insight into your enterprise's revenue and profitability information, which ties into your accounts receivable. The default configuration for the Profitability Analytics application is based on what is identified as the most-common level of detail, or granularity. However, the extracts are configurable and you can modify the extracts to meet your business requirements. The Profitability Analytics application provides cost analysis, revenue trends, and profitability analysis at the products and customer level, and the income statement at the company and business divisions level.
Oracle Payables Analytics. The Oracle Payables Analytics application provides information about your enterprise's accounts payable information and identifies the cash requirements to meet your obligations.
The information found in the Oracle Payables Analytics application pertains to data found exclusively under Accounts Payable (AP) in your financial statements and chart of accounts. Analysis of your payables allows you to evaluate the efficiency of your cash outflows. The need for analysis is increasingly important because suppliers are becoming strategic business partners with the focus on increased efficiency for just in time, and quality purchasing relationships.
The default configuration for the Oracle Payables Analytics application is based on what is identified as the most- common level of detail, or granularity. However, you can configure or modify the extracts to best meet your business requirements.
Oracle Receivables Analytics. The Oracle Receivables Analytics application provides information to support your credit and collection activities, and to monitor and identify potential, receivables problems.
The information found in the Oracle Receivables Analytics application pertains to data found exclusively in the Accounts Receivable (AR) account grouping of your financial statements and chart of accounts. Each day that your receivables are past the due date represents a significant, opportunity-cost to your company. Keeping a close eye on the trends, and clearing of AR is one way to assess the efficiency of your sales operations, the quality of your receivables, and the value of key customers.
The default configuration for the Oracle Receivables Analytics application is based on what is identified as the most-common level of detail or granularity. However, you may configure and modify the extracts to best meet your business requirements.
This section contains configuration steps that you need to perform on Oracle Financial Analytics before you do a full data load, and contains the following topics:
Section 10.2.1, "Configuration Steps for Financial Analytics For All Source Systems"
Section 10.2.2, "Configuration Steps for Financial Analytics For Oracle EBS"
Section 10.2.3, "Configuration Steps for Financial Analytics For PeopleSoft"
Section 10.2.4, "Configuration Steps for Financial Analytics For Universal"
Section 10.2.5, "Configuration Steps for Controlling Your Data Set"
This section contains configuration steps before you do a full data load that apply to all source systems.
|
Note: For configuration steps that apply to all analytics modules (for example, Oracle Financial Analytics, Oracle HR Analytics, Oracle Sales Analytics, see Chapter 8, "Configuring Common Areas and Dimensions"). |
This section contains configuration steps before you do a full data load that apply to Oracle EBS, and contains the following topics:
Section 10.2.2.2, "How to Map Oracle General Ledger Natural Accounts to Group Account Numbers"
Section 10.2.2.3, "How to do Group Account correction for Oracle Application"
If you modify or extend a seeded list of values, you must configure the CSV files for Oracle Financial Analytics by mapping values from your source systems to the domain values.
The following three sections explains how to extract the lists of values from your source system, which you then compare with the seeded values. If the lists of values are different to the seeded values, you need to follow the instructions to configure the Domain Values and CSV Worksheet Files.
Table 10-3 lists the CSV worksheet files and the domain values for Financial Analytics and Oracle EBS in the $pmserver\LkpFiles folder.
Table 10-1 Domain Values and CSV Worksheet Files for Oracle Financial Analytics and Oracle EBS
| Worksheet File Name | Description | Session |
|---|---|---|
|
domainValues_Xact_Types_DocTypes_ora12.csv |
List the Transaction types and the corresponding domain values for the Oracle EBS R12 application. For more information about updating the values in this file, see Section 10.2.2.4, "How to configure domainValues_Xact_Types_DocTypes_ora12.csv for Oracle General Ledger and Profitability Analytics"). |
SDE_ORA_TransactionTypeDimension_GLCOGSDerive |
|
domainValues_Xact_Types_DocTypes_ora11i.csv |
List the Transaction types and the corresponding domain values for the Oracle EBS 11i application. For more information about updating the values in this file, see Section 10.2.2.5, "How to configure domainValues_Xact_Types_DocTypes_ora11i.csv for Oracle General Ledger and Profitability Analytics"). |
SDE_ORA_TransactionTypeDimension_GLCOGSDerive |
|
Note: It is critical that the General Ledger Account Numbers are mapped to the Group Account Numbers (or domain values) as the metrics in the General Ledger reporting layer uses these values. For a list of domain values for General Ledger Account Numbers, see Oracle Business Analytics Warehouse Naming Conventions and Domain Values. |
You can categorize your Oracle General Ledger accounts into specific group account numbers. The group account number is used during data extraction as well as front-end reporting. The GROUP_ACCT_NUM field in the GL account dimension table W_GL_ACCOUNT_D denotes the nature the nature of the General Ledger accounts (for example, cash account, payroll account). Refer to the master_code column in the file_group_acct_names_ora.csv file for values you can use. For a list of the Group Account Number domain values, see Oracle Business Analytics Warehouse Naming Conventions and Domain Values. The mappings to General Ledger Accounts Numbers are important for both Profitability analysis and General Ledger analysis (for example, Balance Sheets).
The logic for assigning the accounts is located in the file_group_acct_codes_ora.csv file. The table below shows an example configuration of the file_group_acct_codes_ora.csv file.
Table 10-2 Example configuration of file_group_acct_codes_ora.csv
| COA ID | FROM ACCT | TO ACCT | GROUP_ACCT_NUM |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
101010 |
101099 |
CA |
|
1 |
131010 |
131939 |
FG INV |
|
1 |
152121 |
152401 |
RM INV |
|
1 |
171101 |
171901 |
WIP INV |
|
1 |
173001 |
173001 |
PPE |
|
1 |
240100 |
240120 |
ACC DEPCN |
|
1 |
261000 |
261100 |
INT EXP |
|
1 |
181011 |
181918 |
CASH |
|
1 |
251100 |
251120 |
ST BORR |
In the table above, in the first row, all accounts within the account number range from 101010 to 101099 that have a Chart of Account (COA) ID equal to 1 are assigned to Current Asset. Each row maps all accounts within the specified account number range and within the given chart of account ID.
If you need to create a new group of account numbers, you can create new rows in the file_group_acct_names_EBS.csv file. You can then assign GL accounts to the new group of account numbers in the file_group_acct_codes_ora11i.csv file.
You also need to add a new row in the file_grpact_fstmt.csv file. This file specifies the relationship between a Group Account Number and a Financial Statement Item Code. You must map the new Group Account Number to one of the following Financial Statement Item codes:
AP
AR
COGS
REVENUE
TAX
OTHERS
These Financial Statement Item codes correspond to the following six base fact tables in the Financial Analytics product.
AP base fact (W_AP_XACT_F)
AR base fact (W_AR_XACT_F)
Revenue base fact (W_GL_REVN_F)
Cost of Goods Sold base fact (W_GL_COGS_F)
Tax base fact (W_TAX_XACT_F)
GL Journal base fact (W_GL_OTHER_F)
By mapping your GL accounts against the Group Account Numbers and then associating the Group Account Number to a Financial Statement Item code, you have indirectly associated the GL account numbers to Financial Statement Item codes as well.
Financial Statement Item codes are internal codes used by ETL process to process the GL journal records during the GL reconciliation process against the subledgers. When the ETL process reconciles a GL journal record, it looks at the Financial Statement Item code associated with the GL account that the journal is charging against, and then uses the value of the Financial Statement item code to decide which base fact the GL journal should reconcile against. For example, when processing a GL journal that charges to a GL account which is associate to 'AP' Financial Statement Item code, then the ETL process will try to go against AP base fact table (W_AP_XACT_F), and try to locate the corresponding matching AP accounting entry. If that GL account is associated with the 'REVENUE' Financial Statement Item code, then the ETL program will try to go against the Revenue base fact table (W_GL_REVN_F), and try to locate the corresponding matching Revenue accounting entry.
|
Note: When you specify the Group Account Number, you must capitalize the letters and use the values in themaster_code column of the file_group_acct_names_ora.csv file. |
To map Oracle General Ledger account numbers to Group Account Numbers
Open the file_group_acct_names_ora.csv file with a text editor in the $pmserver\srcfiles folder.
Edit the fields in the following table:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| COA ID | The ID of the General Ledger chart of account. |
| FROM ACCT and TO ACCT | The natural account range. This is based on the natural account segment of your GL accounts. |
| GROUP_ACCT_NUM | This field denotes the nature of the Oracle General Ledger accounts. For example, Cash account, Payroll account, and so on. Refer to the file_group_acct_names_ora.csv file for values you can use. |
|
Note: It is important that you do not edit any other fields in the CSV files. |
Save and close the CSV file.
Note: Refer to the section Section 10.2.2.2, "How to Map Oracle General Ledger Natural Accounts to Group Account Numbers" for general concepts about Group Account Number and Financial Statement Item Code.
When a user mistakenly maps a GL natural account number to an incorrect Group Account Number, incorrect accounting entries might be inserted into the fact table. For example, natural account 1210 is classified as belonging to 'AR' Group Account Number when it should be classified as having 'AP' Group Account Number. When this happens, the ETL program will get all the journal lines charging to account 100 and try to reconcile these journal lines against subledger accounting records in the AR fact table (W_AR_XACT_F). Since these journal lines did not come from AR, the ETL program will not be able to find the corresponding matching subledger accounting records for these journal lines. In this case, the ETL program will insert 'Manual' records into the AR fact table because it thinks that these GL journal lines are 'Manual' journal entries created directly in GL system charging against the AR accounts. This entire process is call GL Reconciliation process.
In order to revert these 'Manual' entries in the AR fact, you will need to utilize the 'Group Account Number Cleanup' program provided in Oracle BI Applications. This program will revert the 'Manual' entries in the fact table (in this case, AR fact table); and then try to do the GL reconciliation process again. This time, the ETL program will try to look for the corresponding matching subledger accounting records in the AP fact (W_AP_XACT_F); provided that you've re-assign the natural account 1210 to the 'AP' group account number in the file_group_acct_codes_ora.csv file.
To do Group Account correction:
Correct the mapping of GL Natural account to the group account in the input 'csv' file Òfile_group_acct_codes_ora.csvÓ.
For example, before correction, a CSV file has the following values:
CHART OF ACCOUNTS ID = 101
FROM ACCT = 1110
TO ACCT = 1110
GROUP_ACCT_NUM = CASH
After correction, if the account '1210' originally belonged to the 'AP' Group Acct Num and after correcting the GL Natural account to the group account, the CSV file would have the following values:
CHART OF ACCOUNTS ID = 101
FROM ACCT = 1210
TO ACCT = 1210
GROUP_ACCT_UM = AR
In the DAC, do the following:
Navigate to the appropriate container.
Go to 'Design' and open up the 'Subject Areas' tab.
Open up the 'Financials – General Ledger' subject area and verify which of the following configuration tag is marked as 'inactive':
- Financials – Calculate GL Balance
- Oracle – Extract GL Balance
Out of the box, 'Financials – Calculate GL Balance' should be marked as inactive.
Open up the 'Financials – Group Account Number Cleanup' subject area and make sure the followings is configured:
- If in step 3, 'Financials – Calculate GL Balance' is marked as 'inactive', then the configuration tag 'Financials – Calculate GL Balance Reverse' should be marked as 'inactive' as well.
- If in step 3, 'Oracle – Extract GL Balance' is marked as 'inactive', then the configuration tag 'Financials – Calculate GL Balance Reverse' should be unmarked in the 'inactive' check box.
If you need to make any change in step b above, then you need to reassemble the 'Financials – Group Account Number Clean Up' subject area and then redesign the one of these execution plans, depending on which version of Oracle EBS you have:
Financials – Group Account Number Clean Up ORA1158
Financials – Group Account Number Clean Up ORA1159
Financials – Group Account Number Clean Up ORA11510
Financials – Group Account Number Clean Up R12
Depending on the Oracle EBS version you have, run the corresponding Group Account Cleanup execution plan:
Financials – Group Account Number Clean Up ORA1158
Financials – Group Account Number Clean Up ORA1159
Financials – Group Account Number Clean Up ORA11510
Financials – Group Account Number Clean Up R12
This section explains how to configure domainValues_Xact_Types_DocTypes_ora12.csv for Oracle General Ledger and Profitability Analytics, Release 12.
To configure domainValues_ Xact_Types_DocTypes_psft.csv for PeopleSoft Receivables:
Identify the Entry Types in your Oracle Inventory Application by using the following SQL:
select mtt.transaction_type_id, mtt.description from mtl_transaction_types mtt;
This query gives the transaction type codes in your Oracle Inventory Application and their corresponding descriptions.
Open the domainValues_Xact_Types_DocTypes_ora12.csv file using a text editor in the $pmserver\lkpfiles folder.
Look for only the rows in the file which has xact_cat_code = 'COGS' or xact_cat_code = 'DEFERRED_COGS'. From among these records, look for those with W_XACT_TYPE_CODE = 'DELIVERY' or 'RETURN'. The column XACT_TYPE_CODE will contain the entry type codes from Oracle Inventory application, and the column W_XACT_TYPE_CODE is the corresponding domain value to which this entry type code will be mapped to.
Map the entry type codes returned by the query above from your Oracle Inventory Application to the domain values.
Make sure the entry type codes go into the XACT_TYPE_CODE column in the file. Note that it is not necessarily a one-to-one mapping between the domain values and the entry types. For example, you can have multiple entry types mapped into the DELIVERY/RETURN domain value. Be careful not to map the same entry type to two different domain values.
Save and close the file.
In Informatica Designer, open the mapping SDE_ORA_GLCOGSFact in the folder SDE_ORAxxx_adapter.
Open the mapplet mplt_BC_ORA_GLCOGSFact contained inside this mapping.
Open the source qualifier SQ_MTL_TRANSACTION_ACCOUNTS.
Modify the sql so that it extracts the additional transaction type ids, from step 1, that need to be extracted.
Make the same change in Informatica Workflow Manager to the SQL Override in the full load sessions SDE_PSFT_ARTransactionFact_Item_Full and SDE_PSFT_ARTransactionFact_ItemActivity_Full".
This section explains how to configure domainValues_Xact_Types_DocTypes_ora11i.csv for Oracle General Ledger and Profitability Analytics, Release 11i.
To configure domainValues_Xact_Types_DocTypes_ora11i.csv for Oracle General Ledger and Profitability Analytics:
Identify the Entry Types in your Oracle Inventory Application by using the following SQL:
select mtt.transaction_type_id, mtt.description from mtl_transaction_types mtt;
This query gives the transaction type codes in your Oracle Inventory Application and their corresponding descriptions.
Open the domainValues_Xact_Types_DocTypes_ora11i.csv file using a text editor in the $pmserver\lkpfiles folder.
Look for only the rows in the file which has xact_cat_code = 'COGS'. From among these records, look for those with W_XACT_TYPE_CODE = 'DELIVERY' or 'RETURN'. The column XACT_TYPE_CODE will contain the entry type codes from Oracle Inventory application, and the column W_XACT_TYPE_CODE is the corresponding domain value to which this entry type code will be mapped to.
Map the entry type codes returned by the query above from your Oracle Inventory Application to the domain values.
Make sure the entry type codes go into the XACT_TYPE_CODE column in the file. Note that it is not necessarily a one-to-one mapping between the domain values and the entry types. For example, you can have multiple entry types mapped into the DELIVERY/RETURN domain value. Be careful not to map the same entry type to two different domain values.
Save and close the file.
In Informatica Designer, open the mapping SDE_ORA_GLCOGSFact in the folder SDE_ORAxxx_adapter.
Open the mapplet mplt_BC_ORA_GLCOGSFact contained inside this mapping.
Open the source qualifier SQ_MTL_TRANSACTION_ACCOUNTS.
Modify the sql so that it extracts the additional transaction type ids, from step 1, that need to be extracted.
Make the same change in Informatica Workflow Manager to the full load sessions that correspond to these mappings: SDE_ORA_GLCOGSFact_Full.
This section contains configuration steps before you do a full data load that apply to PeopleSoft, and contains the following topics:
If you modify or extend a seeded list of values, you must configure the CSV files for Oracle Financial Analytics by mapping values from your source systems to the domain values.
The section Section 10.2.3.2, "How to configure domainValues_ Xact_Types_DocTypes_psft.csv for PeopleSoft Receivables" explains how to extract the lists of values from your source system, which you then compare with the seeded values. If the lists of values are different to the seeded values, you need to follow the instructions to configure the Domain Values and CSV Worksheet Files.
Table 10-3 lists the CSV worksheet files and the domain values for Financial Analytics and PeopleSoft in the $pmserver\LkpFiles folder.
Table 10-3 Domain Values and CSV Worksheet Files for Oracle Financial Analytics
| Worksheet File Name | Description | Session |
|---|---|---|
|
domainValues_Xact_Types_DocTypes_psft.csv |
List the Transaction types and the corresponding domain values for the PeopleSoft application. For more information about updating the values in this file, see Section 10.2.3.2, "How to configure domainValues_ Xact_Types_DocTypes_psft.csv for PeopleSoft Receivables"). |
SDE_PSFT_TransactionTypeDimension_ARDerive |
This section explains how to configure domainValues_ Xact_Types_DocTypes_psft.csv for PeopleSoft Receivables.
To configure domainValues_ Xact_Types_DocTypes_psft.csv for PeopleSoft Receivables:
Identify the Entry Types in your PeopleSoft Receivables Application by using the following SQL:
SELECT DISTINCT ENTRY_TYPE, DESCR FROM PS_ENTRY_TYPE_TBL
This query gives the entry type codes in your PeopleSoft Receivables Application and their corresponding descriptions.
Open the domainValues_ Xact_Types_DocTypes_psft.csv file using a text editor in the $pmserver\lkpfiles folder.
Look for only the rows in the file that have xact_cat_code = 'RECEIVABLE' and W_XACT_TYPE_CODE = 'ORIGINAL' or 'APPLICATION'. The column XACT_SUBTYPE_CODE will contain the entry type codes from PeopleSoft Receivables and the columns W_XACT_TYPE_CODE and W_XACT_SUBTYPE_CODE are the corresponding domain values these entry type codes will be mapped to.
Copy the TYPE column to the XACT_TYPE_CODE column in the file.
The data must be copied starting from the 2nd line. The first line is the column header.
Map the entry type codes returned by the query above from your PeopleSoft Receivable Application to the domain values.
Make sure the entry type codes go into the XACT_TYPE_CODE column in the file. Note that it is not necessarily a one-to-one mapping between the domain values and the entry types. For example, you can have multiple entry types mapped into the ORIGINAL/INVOICE domain value. Be careful not to map the same entry type to two different domain values.
Save and close the file.
In Informatica Designer, open mapplets mplt_BC_PSFT_ARTransactionFact_Item and mplt_BC_PSFT_ARTransactionFact_ItemActivity in the SDE_PSFTxx_adapter folder.
Open the source qualifier transformation.
At the end of the SQL, there is a "IN" clause that should include all the entry type codes that map into W_XACT_TYPE_CODE = 'ORIGINAL' in the csv file prepared above.
Make the same change in Informatica Workflow Manager to the SQL Override in the full load sessions SDE_PSFT_ARTransactionFact_Item_Full and SDE_PSFT_ARTransactionFact_ItemActivity_Full".
Oracle BI Application computes GL Balances based on the GL Journals extracted into the data warehouse. It assumes that the beginning balance is zero and calculates the ending GL Balance for a month by adding up all the GL Journals from the beginning of time to that month (for Balance Sheet Accounts) or from the beginning of the year to that month (for Non-Balance Sheet Accounts). But since it assumes the beginning balance is zero, there is a problem if you want to extract Journals from your PeopleSoft system only from a certain year. For example, if you have 10 years worth of Journals in the OLTP system and you extract only last 3 years data into the data warehouse, the GL Balance computed will not take into account the first 7 years' journals, and hence the balance will not be correct.
To address the issue, Oracle BI Applications provides a facility for you to enter a beginning balance for every account. So instead of starting from zero, the GL Balance computation will start from this beginning balance number and start adding up journals to it to calculate ending GL Balances. The facility is through the universal adapter for the GL Journals Staging table, W_GL_OTHER_FS. There is a csv file, file_gl_other.csv, in the srcfiles directory of the informatica server. In this file, you enter a beginning balance for each GL Account and that will be automatically loaded into the staging table W_GL_OTHER_FS. Note that the file needs to be ready before the first full load ETL is started.
To insert beginning GL Balances
Open the file_gl_other.csv file using a text editor in the $pmserver\lkpfiles folder.
Populate the following columns:
GL_ACCOUNT_ID - FK to GL Account dimension
DOC_STATUS_ID - FK to Status dimension. Set this to "ACCT_DOC_STATUS~~POSTED" for all rows.
POSTED_ON_DT - Posted Date in YYYYMMDDHH24MISS format. Set this to the date for which you are entering beginning balances. For example, you are decide to extract journals from Jan 01 of 2005, set this date to 20050101000000.
ACCT_PERIOD_END_DT - Accounting Period Date in YYYYMMDDHH24MISS format. Set this to the date for which you are entering beginning balances. For example, you are decide to extract journals from Jan 01 of 2005, set this date to 20050101000000.
OTHER_DOC_AMT - Amount in document currency.
OTHER_LOC_AMT - Amount in local/Business Unit currency
GLOBAL1_EXCHANGE_RATE - Exchange rate for Doc Currency to Global1 Currency Code
GLOBAL2_EXCHANGE_RATE - Exchange rate for Doc Currency to Global2 Currency Code
GLOBAL3_EXCHANGE_RATE - Exchange rate for Doc Currency to Global3 Currency Code.
BALANCE_ID - Give a unique value for this row
Save and close the file.
In Informatica Designer, open mapplets mplt_BC_PSFT_ARTransactionFact_Item and mplt_BC_PSFT_ARTransactionFact_ItemActivity in the SDE_PSFTxx_adapter folder.
Open the source qualifier transformation.
At the end of the SQL, there is a "IN" clause that should include all the entry type codes that map into W_XACT_TYPE_CODE = 'ORIGINAL' in the csv file prepared above.
Make the same change in Informatica Workflow Manager to the SQL Override in the full load sessions SDE_PSFT_ARTransactionFact_Item_Full and SDE_PSFT_ARTransactionFact_ItemActivity_Full".
This section contains configuration steps before you do a full data load that apply to Universal.
Not applicable to Oracle BI Applications Version 7.9.4.
This section contains additional configuration steps for Oracle Financial Analytics, and contains the following topics:
Section 10.2.5.1, "Configuration Steps for Financial Analytics For All Source Systems"
Section 10.2.5.2, "Configuration Steps for Financial Analytics For Oracle EBS"
Section 10.2.5.3, "Configuration Steps for Financial Analytics For PeopleSoft"
Section 10.2.5.4, "Configuration Steps for Financial Analytics Chain For Universal"
This section contains additional configuration steps that apply to all source systems, and contains the following topics:
This section explains how to control the lengths of the aging buckets in the AP and AR aging snapshot tables. These tables are:
W_AP_AGING_INVOICE_A
W_AR_AGING_INVOICE_A
W_AP_AGING_SUPPLIER_A
W_AR_AGING_CUSTOMER_A
In these four tables, outstanding AP/AR balance information is broken out into rows. Each row represents the outstanding balance information for a particular aging bucket. Four aging buckets are provided out-of-the-box, with the following durations:
Bucket 1: 0 – 30 days
Bucket 2: 31 – 60 days
Bucket 3: 61 – 90 days
Bucket 4: 90+ days
Use the DAC to configure the lengths of these aging buckets, as described below.
To configure the length of aging buckets
Click on the 'Tasks' tab.
Query for the following tasks
PLP_APSnapshotInvoiceAging
PLP_ARSnapshotInvoiceAging
For each of these tasks, click on the 'Parameters' tab and update the parameters with names starting with '$$BUCKET'.
Save your work.
These aging tables are snapshot tables. You can also control how many historic month end snapshots you want to keep in these tables (the default value is 24 months). You can increase or decrease the number by adjusting the $$HISTORY_MONTHS parameter.
This section contains additional configuration steps that apply to Oracle EBS, and contains the following topics:
Section 10.2.5.2.1, "How to Configure How GL Balances Is Populated in Oracle EBS"
Section 10.2.5.2.2, "How to Configure Oracle Profitability Analytics Transaction Extracts"
Section 10.2.5.2.3, "How to Configure Cost Of Goods Extract (Oracle EBS 11i-specific)"
Section 10.2.5.2.4, "How to Configure the General Ledger Account Hierarchies"
Section 10.2.5.2.7, "How to Configure AP Balance ID for Oracle Payables Analytics"
Section 10.2.5.2.9, "How to Configure the AR Adjustments Extract for Oracle Receivables Analytics"
Section 10.2.5.2.10, "How to Configure the AR Schedules Extract"
Section 10.2.5.2.13, "How to Specify the Ledger or Set of Books for which GL Data is Extracted"
Section 10.2.5.2.14, "How to Setup Drill Down in Oracle BI Answers from General Ledger to Subledger"
Oracle BI Applications provides two ways to populate the GL balances (stored in the W_GL_BALANCE_F table), as follows:
By extracting the GL balances directly from Oracle General Ledger, as follows:
In DAC, for the Subject Area 'Financials – General Ledger', in the 'Configuration Tag' tab, make sure that the tag 'Oracle – Extract GL Balance' is unchecked for the 'Inactive' checkbox.
Make sure the tag 'Financials – Calculate GL Balance is checked in the 'Inactive' checkbox.
Click Assemble to redesign the subject area.
After the subject area has been redesigned, redesign the execution plans that contain this subject area.
By calculating the GL balances based on the records in the W_GL_OTHER_F table, which stores all journal lines, as follows:
In DAC, for the Subject Area 'Financials – General Ledger', in the 'Configuration Tag' tab, make sure that the tag 'Financials – Calculate GL Balance' is unchecked for the 'Inactive' checkbox.
Make sure the tag 'Oracle – Extract GL Balance' is checked in the 'Inactive' checkbox.
Click Assemble to redesign the subject area.
After the subject area has been redesigned, redesign the execution plans that contain this subject area.
There are two separate transaction extracts for Oracle General Ledger and Profitability Analytics—General Ledger Revenue and General Ledger COGS. By default, the Oracle General Ledger Analytics application extracts only Completed revenue and COGS that have been posted to the general ledger. Completed revenue transactions are those where the RA_CUSTOMER_TRX_ALL.COMPLETE_FLAG = Y. If you want to extract incomplete revenue transactions, you can remove the filter in the Business Component.
To modify the extract filter for Oracle General Ledger and Profitability Analytics Revenue
In PowerCenter Designer, open the appropriate Oracle Applications folder (for example, SDE_ORA11510_adapter).
In Mapplet Designer, open the mplt_BC_ORA_GLRevenueFact mapplet.
Double-click the Source Qualifier to open the Edit Transformations window, and click the Properties tab.
In the User Defined Join field and in the SQL Query field, remove the statement:
AND RA_CUSTOMER_TRX_ALL.COMPLETE_FLAG = Y
Validate and save your changes to the repository.
For customers of EBS 11i, 11.5.8, 11.5.9, and 11.5.10, the Oracle General Ledger Analytics application extracts only COGS transactions that have been posted to the general ledger, by default. All COGS transactions that have been transferred satisfy the following condition— MTL_TRANSACTION_ACCOUNTS.GL_BATCH_ID <> -1. If you want to extract all transactions, you can remove the filter in the Business Component mapplet. You need to modify the Business Component mapplet for both the regular extract mapplet as well as the primary extract mapplet. This does not apply to EBS R12; by default all transactions are extracted. The following section applies only to EBS 11i customers.
To modify the extract filter for General Ledger COGS
In PowerCenter Designer, open the appropriate Oracle Applications folder (for example, SDE_ORA11510_adapter).
In Mapplet Designer, open mplt_BC_ORA_GLCOGSFact.
Double-click the Source Qualifier to open the Edit Transformations window, and click the Properties tab.
In the User Defined Join field and in the SQL Query field, remove the statement:
AND MTL_TRANSACTION_ACCOUNTS.GL_BATCH_ID <> -1
In Mapplet Designer, open mplt_BC_ORA_GLCOGSFact_PRIMARY.
Double-click the Source Qualifier to open the Edit Transformations window, and click the Properties tab.
In the User Defined Join field and in the SQL Query field, remove the statement:
AND MTL_TRANSACTION_ACCOUNTS.GL_BATCH_ID <> -1
Validate and save your changes to the repository.
Make appropriate changes to the sql in the informatica session, "SDE_ORA_GLCOGSFact_Full", which is present in the corresponding folder in Workflow Manager.
If you customized the mapping SDE_ORA_GLCOGSFact to extract from Oracle EBS versions 11.5.8, 11.5.9, or 11.5.10, modify the domain values file domainValues_Xact_Types_DocTypes_ora11i.csv.
To extract from Oracle EBS version R12, modify the file domainValues_Xact_Types_DocTypes_ora12.csv.
The are two ways to set up hierarchies in Oracle Financial Analytics:
Using General Ledger Accounting Flexfield Value Sets Definitions
Using the Financial Statement Generator (FSG) Report Definition
Whichever method you choose to set up General Ledger Account hierarchies, you store the hierarchy information in the W_HIERARCHY_D table.
As an example, the hierarchy for US Acct might have the following structure:
Node A has child nodes B and C.
Node B has child nodes D and E.
Node C has child nodes F and G.
Node D has child nodes H and I.
Node F has child nodes J and K.
The figure below shows the example hierarchy for US Acct.
The table below shows how the hierarchy US Acct would be stored in the W_HIERARCHY_D table as follows:
Oracle EBS supports up to 30 segments in which to store accounting flex fields. Flex fields are flexible enough to support complex data configurations, for example:
You can store data in any segments.
You can use more or fewer segments per chart of account, as required.
You can specify multiple segments for the same chart of account.
An Example Data Configuration for a Chart of Accounts
A single company might have a US Chart of Account and an APAC Chart of Account with the following data configuration:
Table 10-5 Example Chart of Accounts
| Segment Type | US Chart of Account (4256) value | APAC Chart of Account (4257) value |
|---|---|---|
|
Company |
Stores in segment 3 |
Stores in segment 1 |
|
Natural Account |
Stores in segment 4 |
Stores in segment 3 |
|
Cost Center |
Stores in segment 5 |
Stores in segment 2 |
|
Geography |
Stores in segment 2 |
Stores in segment 2 |
|
Line of Business (LOB) |
Stores in segment 1 |
Stores in segment 4 |
The example shows that in Chart Of Account 4256, Company is stored in the segment3 column in the Oracle EBS table GL_CODE_COMBINATIONS_ALL. In Chart Of Account COA4257, Company is stored in segment1 column in GL_CODE_COMBINATIONS_ALL table. The objective of this configuration file is to make sure that when segment information is extracted into the warehouse table W_GL_ACCOUNT_D, segments with the same nature from different chart of accounts are stored in the same column in W_GL_ACCOUNT_D.
For example, we can store Company segments from COA 4256 and 4257 in segment1 column in W_GL_ACCOUNT_D; and Cost Center segments from COA 4256 and 4257 in segment2 column in W_GL_ACCOUNT_D, and so forth.
About Configuring the ETL Process for GL Accounting Flex fields
Before you run the ETL process for General Ledger Accounts, you need to specify the segments that you want to analyze. To specify the segments that you want to analyze, use the following ETL configuration file:
$PMSERVER/srcfile/file_glacct_segment_configur_ora.csv
In the file_glacct_segment_config_ora11i.csv file, you need to specify the segments of the same type in the same column. For example, you might store all Cost Center segments from all chart of accounts in one column, and all Company segments from all chart of accounts in another column.
For example, you might want to do the following:
Analyze GL account hierarchies using only Company, Cost Center, Natural Account, and LOB.
You are not interested in using Geography for hierarchy analysis.
Store all Cost Center segments from all COAs in ACCOUNT_SEG2_CODE column in W_GL_ACCOUNT_D.
Store all Natural Account segments from all COAs in ACCOUNT_SEG3_CODE column in W_GL_ACCOUNT_D.
Store all LOB segments from all COAs in ACCOUNT_SEG4_CODE column in W_GL_ACCOUNT_D.
In W_GL_BALANCE_A (where you store GL account balances at aggregated level), you want to store GL account balances at Company and Cost Center level instead of at GL Code Combination level.
The screenshot below shows how the file_glacct_segment_config_ora11i.csv would be configured to implement the business requirements specified above.
To Set Up Hierarchies With General Ledger Accounting Flex fields
Use the /srcfile/file_glacct_segment_configur_ora.csv file to specify the segments that you want to analyze.
In the DAC, do the following:
For the Subject Area 'Financials – General Ledger', in the 'Configuration Tag' tab, make sure that:
The tag 'Oracle – Extract Value Set Hierarchies' is unchecked for the 'Inactive' checkbox.
The tag 'Oracle – Extract FSG Hierarchies' is checked in the 'Inactive' checkbox.
Click Assemble to redesign the subject area.
After the subject area has been redesigned, also redesign the execution plans which contain this subject area.
Run the ETL process for General Ledger Accounts.
In the RPD Physical Layer (using the Oracle BI Administration Tool), create additional aliases or change the names of the existing alias against the table W_HIERARCHY_D.
For example, if the existing aliases are numbered 1 to 3, name the new alias Dim_W_HIERARCHY_D_ValueSetHierarchy4, and rename the existing aliases as described in the table below:
| Old alias name | New alias name |
|---|---|
| Dim_W_HIERARCHY_D_ValueSetHierarchy1 | Dim_Company_Hierarchy_D |
| Dim_W_HIERARCHY_D_ValueSetHierarchy2 | Dim_CostCenter_Hierarchy_D |
| Dim_W_HIERARCHY_D_ValueSetHierarchy3 | Dim_NaturalAccount_Hierarchy_D |
Create a new alias against W_HIERARCHY_D and name the new alias Dim_LOB_Hierarchy_D.
In the Physical Layer of the Oracle BI Analytics Warehouse, use the Oracle BI Administration Tool to create joins in the physical layer from the new aliases that you created in the previous step, as follows:
Company Hierarchy will join to the segment column in W_GL_ACCOUNT_D that stores the Company segment.
Dim_Company_Hierarchy_D. HIER20_CODE = W_GL_ACCOUNT_D.ACCOUNT_SEG1_CODE
Dim_Compnay_Hierarchy_D.HIER_CODE = W_GL_ACCOUNT_D.ACCOUNT_SEG1_ATTRIB
Cost Center Hierarchy will join to the segment column in W_GL_ACCOUNT_D that stores the Cost Center segment.
Dim_CostCenter_Hierarchy_D. HIER20_CODE = W_GL_ACCOUNT_D.ACCOUNT_SEG2_CODE
Dim_CostCenter_Hierarchy_D.HIER_CODE = W_GL_ACCOUNT_D.ACCOUNT_SEG2_ATTRIB
Natural Account Hierarchy will join to the segment column in W_GL_ACCOUNT_D, that stores the Natural Account segment.
Dim_NaturalAccount_Hierarchy_D. HIER20_CODE = W_GL_ACCOUNT_D.ACCOUNT_SEG3_CODE
Dim_NaturalAccount_Hierarchy_D.HIER_CODE = W_GL_ACCOUNT_D.ACCOUNT_SEG3_ATTRIB
LOB Hierarchy will join to the segment column in W_GL_ACCOUNT_D that stores the LOB segment.
Dim_LOB_Hierarchy_D. HIER20_CODE = W_GL_ACCOUNT_D.ACCOUNT_SEG4_CODE
Dim_LOB_Hierarchy_D.HIER_CODE = W_GL_ACCOUNT_D.ACCOUNT_SEG4_ATTRIB
|
Note: Hierarchies are linked to HIER20_CODE, because it is leaf node of the hierarchy |
In the Business Model Layer of the Oracle BI Analytics Warehouse, use the Oracle BI Administration Tool to create additional dimensions using the new alias.
For more information about example dimensions that are installed with Oracle BI Applications, refer to the following dimensions in the Oracle Business Analytics Warehouse:
Dim - GL ValueSetHierarchy1
Dim - GL ValueSetHierarchy2
Dim - GL ValueSetHierarchy3
A HIER_CODE filter should be specified in the Business Model Layer to restrain the output of logical table to be one Hierarchy only. To specify a filter in the Business Model Layer to restrain the output of logical table, do the following:
Right click logical table Dim_IncomeStatement_FSGHierarchy_D.
Choose Properties.
Choose the Source tab.
Select "Dim_IncomeStatement_FSGHierarchy_D".
Click Edit.
Choose the Content tab.
Insert the following code into the "use WHERE clause…" text box:
"Oracle Data Warehouse"."Catalog"."dbo"."Dim_W_HIERARCHY_D_FSG1"."HIER_CODE" =1001
In the Business Model Layer of the Oracle BI Analytics Warehouse, use the Oracle BI Administration Tool to create additional hierarchies using the dimensions that you created in the previous step.
For more information about example hierarchies that are installed with Oracle BI Applications, refer to the following hierarchies in the Oracle Business Analytics Warehouse:
GL ValueSetHierarchy1
GL ValueSetHierarchy2
GL ValueSetHierarchy3
In the Presentation Layer of the Oracle BI Analytics Warehouse, use the Oracle BI Administration Tool to drag the new hierarchies into the presentation folder.
|
Note: You can rename the hierarchies in the Presentation Layer if required. |
If you need to define GL account hierarchies based on multiple segments within a chart of accounts, you can use the Financial Statement Generator report definition UI in Oracle EBS to define them.
You should first use the Oracle EBS Financial Statement Generator (FSG) form to define a row set or a column set, then the Oracle BI Application will extract the row set or column set definition and convert them into hierarchies.
Oracle Financial Statement Generator hierarchies are extracted from following EBS source tables:
RG_REPORT_AXIS_CONTENTS
This table defines the relationship between the FSG report axis and GL code combinations. The GL code combinations with segment values within the value range defined for that axis are categorized as children of that axis.
RG_REPORT_AXIS_SETS
This table stores the information for each of the row set or column set you defined. There is one record in this table for each row or column set you defined. Each row includes an axis set identifier, a row or column set name, and a structure identifier to assign a specific chart of accounts to the row set or column set.
RG_REPORT_CALCULATIONS
This table stores formulas for calculating each row or column in the row or column set. An example of a row calculation might be to sum up the amount from the previous five rows. An example of a columns calculation might be to calculate column five by subtracting column four from column three.
For example, in Income Statement, "Net Income" is the calculation result of "Gross Profit from Revenue" minus "Total Expense". When converting to hierarchy, Net Income becomes the parent of "Gross Profit from Revenue" and "Total Expense". Therefore, hierarchy can be derived based on the information in RG_REPORT_CALCULATION.
The diagram below shows an example hierarchy, with the top level Net Income node having two child nodes, Total Expense, and Gross Profit from Revn, and the Total Expense node having two child nodes, Operating Expense, and Depreciation Expense.
The diagram below shows how an income state is derived from a hierarchy.
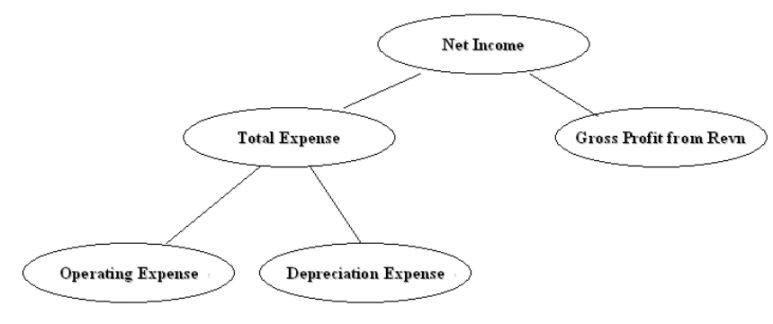
The hierarchy above would be converted into a flattened hierarchy and stored in W_HIERARCHY_D in the following format:
Table 10-6 Example flattened hierarchy stored in W_HIERARCHY_D
| HIER Name | HIER1 | HIER2 | HIER3 | HIER4 | HIER20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Income Statement |
Net Income |
Gross Profit... |
Gross Profit... |
Gross Profit... |
Gross Profit... |
|
Income Statement |
Net Income |
Total Expenses |
Operating Expenses |
Operating Expenses |
Operating Expenses |
|
Income Statement |
Net Income |
Total Expenses |
Depreciation Expense |
Depreciation Expense |
Depreciation Expense |
Fact tables join to the W_HIERARCHY_D table via the General Ledger Account dimension table (W_GL_ACCOUNT_D).
The W_GL_ACCOUNT_D table contains six fields (HIER1_WID, HIER2_WID, HIER3_WID, ...., HIER6_WID), which are foreign keys to the W_HIERARCHY_D.row_wid. Therefore, each General Ledger Code combination can participate in up to six different hierarchies. You can decide which of the six hierarchies to drill on based on the column you use to join to W_HIERARCHY_D.
For example, by using W_GL_ACCOUNT_D.hier3_wid = W_HIERARCHY_D.row_wid. You are essentially drilling using the third hierarchy.
About Configuring the ETL Process for Oracle Financial Statement Generator Report
Before you run the ETL process for General Ledger Accounts, you need to specify the hierarchies that you want to reference. To specify the FSG hierarchies that you want to reference, use the following ETL configuration file:
$PMSERVER/srcfile/file_gl_hierarchy_assignment_ora.csv
In this file, for each chart of accounts, you can specify six FSG hierarchies (using axis_set_id; Axis_set_id is a column from RG_REPORT_AXIS_SETS table. It is the unique ID of a row set or column set) you want to store in the GL account dimension table for the code combinations that belong to that chart of accounts.
The DATASOURCE_NUM_ID field specifies the data source to which the configurations apply. If you have multiple source systems, there might be a chart of accounts across the multiple source systems with the same ID. Therefore, you need to use the DATASOURCE_NUM_ID value to distinguish between them.
For example, we have an Income Statement FSG report and a Balance Sheet FSG report which we want to derive both of their hierarchy structures into OLAP.
Oracle BI Applications assumes that both reports are derived from same set of GL accounts with CHART_OF_ACCOUNTS=101. The axis_set_id of Income Statement is 1001, and for Balance Sheet, it is 1003. The DATASOURCE_NUM_ID for this application is 2.
In addition, for those GL ACCOUNTS that belong to the two reports (by which we used to calculate the reports), we want to associate their HIER1 column (in GL_ACCOUNT_D) with Income Statement hierarchy structure, HIER3 column with Balance Sheet hierarchy structure.
In this case, we would add one row into file_gl_hierarchy_assignment_ora.csv with the following fields set as below:
CHART OF ACCOUNTS - 101
HIER1_AXIS_SET_ID - 1001
HIER3_AXIS_SET_ID - 1003
DATASOURCE_NUM_ID - 2
(Leave the other row values blank.)
This row indicates that for all of the GL Accounts with CHART_OF_ACCOUNTS=101 and DATASOURCE_NUM_ID=2, assigning hierarchies with axis_set_id=1001, null, 1003, null, null, null to HIER1~HIER6 columns respectively. Therefore, after extraction and loading, for those affected GL Account rows, HIER1 column will be the foreign key to Income Statement hierarchy's row ID in W_HIERARCHY_D and HIER3 column will be the foreign key to Balance Sheet hierarchy's row ID in W_HIERARCHY_D.
Note: Financial Analytics will not load those hierarchies with axis_set_id not been specified in file_gl_hierarchy_assignment_ora.csv.
To Set Up Hierarchies With Financial Statement Generator Report Definition:
Use the /srcfile/ file_gl_hierarchy_assignment_ora.csv file to specify the hierarchies you want to reference for each CHART_OF_ACCOUNTS.
In the DAC, do the following:
Navigate to the Subject Area 'Financials – General Ledger'.
In the 'Configuration Tag' tab, make sure that the tag 'Oracle – Extract FSG Hierarchies' is unchecked for the 'Inactive' checkbox.
In the 'Configuration Tag' tab, make sure that the tag 'Oracle – Extract Value Set Hierarchies' is checked in the 'Inactive' checkbox.
Click Assemble to redesign the subject area.
After the subject area has been redesigned, also redesign the execution plans which contain this subject area.
Run the ETL process for General Ledger Accounts.
In the RPD Physical Layer (using the Oracle BI Administration Tool), create additional aliases or change the names of the existing alias against the table W_HIERARCHY_D.
For example, if you want to create an income statement hierarchy, create an additional alias ÒDim_IncomeStatement_FSGHierarchy_DÓ against the table W_HIERARCHY_D.
In the Physical Layer of the Oracle BI Analytics Warehouse, use the Oracle BI Administration Tool to create joins in the physical layer from the new aliases that you created in the previous step, as follows:
Income Statement Hierarchy will join to one of the HIER1~6 columns that you have specified in file file_gl_hierarchy_assignment_ora.csv for Income Statement.
In this case, we join it to HIER1 column.Dim_W_GL_ACCOUNT_D.HIER1_WID = Dim_IncomeStatement_FSGHierarchy_D.ROW_WID
In the Business Model Layer of the Oracle BI Analytics Warehouse, use the Oracle BI Administration Tool to create additional dimensions using the new alias.
For the Income Statement hierarchy case, we create a new logical table ÒDim_IncomeStatement_FSGHierarchy_DÓ, choose ÒDim_IncomeStatement_FSGHierarchy_DÓ in physical layer as source. Mapping ROW_WID, HIER_CODE, and HIER1~HIER20 (both name and code) from physical table to logical key.
Then, set HIER_CODE=1001 (this is the Axis_set_id of Income Statement hierarchy) in logical table to restrain the output of logical table to be Income Statement Hierarchy only (right click logical table ÒDim_IncomeStatement_FSGHierarchy_DÓ – click ÒpropertiesÓ – choose ÒSourceÓ tab – select ÒDim_IncomeStatement_FSGHierarchy_DÓ – click ÒEditÓ button – choose ÒContentÓ tab – fill ("Oracle Data Warehouse"."Catalog"."dbo"."Dim_W_HIERARCHY_D_FSG1"."HIER_CODE" =1001) into Òuse WHERE clause…Ó textbox).
For more information about this process, please refer to the following pre-installed example logical table Dim - FSG Hierarchy 1 in the Oracle Business Analytics Warehouse
In the Business Model Layer of the Oracle BI Analytics Warehouse, use the Oracle BI Administration Tool to create new dimension based on the logical table that you created in the previous step.
Please refer ÒFSG Hierarchy 1Ó as example.
In the Presentation Layer of the Oracle BI Analytics Warehouse, use the Oracle BI Administration Tool to drag the new hierarchies into the presentation folder.
Note: You can rename the hierarchies in the Presentation Layer if required.
The AP Balance ID controls the level at which the balance in W_AP_BALANCE_F is maintained.
This section contains configuration information for Oracle Payables Analytics that is specific to Oracle.
By default, the Accounts Payable (AP) Balance ID is maintained at the following granularity:
SET_OF_BOOKS_ID||'~'||CODE_COMBINATION_ID||'~'||VENDOR_SITE_ID)||'~'||INP_ORG_ID
However, if you want to maintain your AP balance at a different grain, you can redefine the Balance ID value in the applicable mapplets.
To modify the Accounts Payable Balance ID
|
Note: To modify the Accounts Payable Balance ID, you must modify the following mapplets:
|
In PowerCenter Designer, open the appropriate Oracle Applications folder (for example, SDE_ORA11510_adapter).
In Mapplet Designer, open the mapplet (for example, mplt_SA_ORA_APTransactionFact_LiabilityDistribution).
Double-click the Expression transformation to open the Edit Transformations window.
Click the Ports tab to edit the Balance ID definition in the EXT_NU_BALANCE_ID column.
Validate and save your changes to the repository.
Repeat steps 1 to 5 for each mapplet that is listed above.
The AR Balance ID controls the level at which the balance in W_AR_BALANCE_F is maintained.
By default, the AR Balance ID is maintained at the following granularity:
set_of_books_id || '~' || code_combination_id || '~' || customer_id || '~' || customer_site_use_id || '~' transaction_currency_code || '~' || org_id
However, if you want to maintain your AR balance at a different grain, you can redefine the Balance ID value in the applicable mapplets.
To modify the AR Balance ID
|
Note: To modify the AR Balance ID, you must modify the following mapplets:
|
In PowerCenter Designer, open the appropriate Oracle Applications folder (for example, SDE_ORA11510_adapter).
In Mapplet Designer, open the mapplet (for example, mplt_SA_ORA_ARTransactionFact_Adjust).
Double-click the Expression transformation to open the Edit Transformations window.
Click the Ports tab to edit the Balance ID definition in the EXT_NU_AR_BALANCE_ID column.
Validate and save your changes to the repository.
Repeat steps 1 to 5 for each mapplet that is listed above.
By default, Oracle Receivables Analytics extracts only approved adjustment entries against accounts receivable transactions. Approved adjustments are entries where the AR_ADJUSTMENTS_ALL.STATUS = A. If you want to extract additional types of AR adjustment entries, you can remove the filter in the Business Component mapplet. By modifying or removing the filter, you can extract other entries, such as those that require more research, those that are rejected, and those that are not accrued charges.
To modify the extract filter for Accounts Receivable adjustments
In PowerCenter Designer, open the appropriate Oracle Applications folder (for example, SDE_ORA11510_adapter).
In Mapplet Designer, open the mplt_BC_ORA_ARTransactionFact_Adjust mapplet.
Double-click the Source Qualifier to open the Edit Transformations window, and click the Properties tab.
In the SQL Query field and in the User Defined Join field, modify the statement:
AND AR_ADJUSTMENTS_ALL.STATUS = A
Validate and save your changes to the repository.
Repeat Step 2 to Step 4 for the mplt_BC_ORA_ARTransactionFact_AdjustPrimary mapplet.
By default, Oracle Receivables Analytics extracts only completed schedules; that is, transactions where the RA_CUSTOMER_TRX_ALL.COMPLETE_FLAG(+) = Y. If you want to extract additional types of AR schedule entries, you must remove the filter in the Business Component mapplet. By modifying or removing the filter, you can extract other entries, such as those that were marked as incomplete.
To modify the extract filter for Accounts Receivable schedules
In PowerCenter Designer, open the appropriate Oracle Applications folder (for example, SDE_ORA11510_adapter).
In Mapplet Designer, open the mplt_BC_ORA_ARTransactionFact_ARSchedules mapplet.
Double-click the Source Qualifier to open the Edit Transformations window.
In the User Defined Join field and in the SQL Query field, modify the statement:
AND RA_CUSTOMER_TRX_ALL.COMPLETE_FLAG(+) = Y
Validate and save your changes to the repository.
By default, Oracle Receivables Analytics extracts only confirmed, cash-receipt application entries against accounts receivable transactions. Confirmed receipts are entries where the AR_RECEIVABLE_APPLICATIONS_ALL.CONFIRMED_FLAG = Y OR NULL. If you want to extract additional types of cash-receipt application entries, you can remove the filter in the Business Component mapplet. By modifying or removing the filter, you can extract other entries, such as unconfirmed applications.
You must modify both the regular mapplet (mplt_BC_ORA_ARTransactionFact_ReceivableApplication) as well as the primary extract mapplet (mplt_BC_ORA_ARTransactionFact_ReceivableApplicationPrimary).
To modify the extract filter for AR cash receipt application
In PowerCenter Designer, open the appropriate Oracle Applications folder (for example, SDE_ORA11510_adapter).
In Mapplet Designer, open the mplt_BC_ORA_ARTransactionFact_ReceivableApplication mapplet.
Double-click the Source Qualifier to open the Edit Transformations window, and click the Properties tab.
In the User Defined Join field and in the SQL Query field, modify the statement:
AND NVL(AR_RECEIVABLE_APPLICATIONS_ALL.CONFIRMED_FLAG,'Y') = Y
Validate and save your changes to the repository.
Repeat Step 2 to Step 4 for the mplt_BC_ORA_ARTransactionFact_ReceivableApplicationPrimary mapplet.
By default, Oracle Receivables Analytics extracts only confirmed, credit-memo application entries against accounts receivable transactions. Confirmed credit memos are entries where the AR_RECEIVABLE_APPLICATIONS_ALL.CONFIRMED_FLAG = Y OR NULL. If you want to extract additional types of AR credit-memo application entries, you can remove the filter. By modifying or removing the filter, you can extract other entries such as unconfirmed, credit memos.
You must modify both the regular mapplet (mplt_BC_ORA_ARTransactionFact_CreditmemoApplication), as well as the primary extract mapplet (mplt_BC_ORA_ARTransactionFact_CreditmemoApplicationPrimary). Repeat the following procedure for each mapplet.
To modify the extract filter for Accounts Receivable Credit-Memo Application receipts
In PowerCenter Designer, open the appropriate Oracle Applications folder (for example, SDE_ORA11510_adapter).
In Mapplet Designer, open the mplt_BC_ORA_ARTransactionFact_CreditmemoApplication mapplet.
Double-click the Source Qualifier to open the Edit Transformations window, and click the Properties tab.
In the User Defined Join field and in the SQL Query field, modify the statement:
AND NVL(AR_RECEIVABLE_APPLICATIONS_ALL.CONFIRMED_FLAG,'Y') = Y
Validate and save your changes to the repository.
Repeat Step 2 to Step 4 for the mplt_BC_ORA_ARTransactionFact_CreditmemoApplicationPrimary mapplet.
For If you have an Oracle EBS source system, you can specify which set of books or ledgers for which you extract the GL data.
Oracle BI Applications enables you to configure:
The list of ledgers or set of books to extract the GL data
The types of ledgers or set of books to extract the GL data for.
You can use either of these configuration points separately and combine them. When installed out-of-the-box, Oracle BI Applications extract all GL data for all ledgers or set of books.
For Oracle 11i customers, to configure the list of set of books to extract the GL data for, do the following:
Log into DAC and open the source container that you want to configure.
Display the Source System Parameters tab.
Use the Search facility to locate the parameter $$FILTER_BY_SET_OF_BOOKS_ID.
Set the value to 'Y'.
Make sure that you put single quotes around the Y.
Save the changes.
Use the Search facility to locate the parameter $$SET_OF_BOOKS_ID_LIST.
Enter the IDs of the set of books for which you want to extract GL data for.
Specify the list of set of book IDs separated by commas (do not specify single or double quotes).
For example, if you want to extract GL data for set of books with IDs: 101, 207, and 303, then set the value of this parameter to the following:
101, 207, 303
Save the changes.
You can also specify the Set of Books type you want to extract GL data for. In Oracle 11i, there are three set of books types (this is based on the column GL_SETS_OF_BOOKS.mrc_sob_type_code column):
P (Parent)
R (Reporting)
N (None)
For Oracle 11i customers, to configure the types of set of books to extract the GL data for. do the following:
Log into DAC and open the source container that you want to configure.
Display the Source System Parameters tab.
Use the Search facility to locate the parameter $$FILTER_BY_SET_OF_BOOKS_TYPE.
Set the value to 'Y'.
Make sure that you put single quotes around the Y.
Save the changes.
Use the Search facility to locate the parameter $$SET_OF_BOOKS_TYPE_LIST.
Enter the types of set of books for which you want to extract GL data for.
Specify the list of set of book IDs in single quotes and separated by commas.
For example, if you want to extract GL data for all Parent set of books and all Reporting set of books, then set the value of this parameter as follows:
'P', 'R'
Save the changes.
For Oracle 12i customers, to configure the list of ledgers to extract the GL data for, do the following:
Log into DAC and open the source container that you want to configure.
Display the Source System Parameters tab.
Use the Search facility to locate the parameter $$FILTER_BY_LEDGER_ID.
Set the value to 'Y'.
Make sure that you put single quotes around the Y.
Save the changes.
Use the Search facility to locate the parameter $$LEDGER_ID_LIST.
Enter the IDs of ledgers for which you want to extract GL data for.
Specify the list of ledger IDs separated by commas (do not use single quotes).
For example, For example, if you want to extract GL data for ledgers with IDs: 101, 207, and 303, then set the value of this parameter as follows:
101, 207, 303
Save the changes.
You can also specify types of ledgers you want to extract GL data for. In Oracle R12, there are four types of ledgers (this is based on the column GL_LEDGERS.ledger_category_code column):
PRIMARY
SECONDARY
ALC
NONE
For R12 customers, to configure the types of ledgers to extract the GL data for, do the following:
Log into DAC and open the source container that you want to configure.
Display the Source System Parameters tab.
Use the Search facility to locate the parameter $$FILTER_BY_LEDGER_TYPE.
Set the value to 'Y'.
Make sure that you put single quotes around the Y.
Save the changes.
Use the Search facility to locate the parameter $$LEDGER_TYPE_LIST.
Enter the types of ledgers for which you want to extract GL data for.
Specify the list of set of book IDs in single quotes and separated by commas.
For example, if you want to extract GL data for all Primary ledgers and all Secondary ledgers, then simply set the value of this parameter to as follows:
'PRIMARY', 'SECONDARY'
Save the changes.
Oracle BI Applications enables you to trace a GL Journal to the Subledger transaction that created that journal. This ability (or drill down) is achieved through the "Navigation" feature in Oracle BI Answers. This feature is available AP if the source is Oracle EBS 11i and for all subledgers if the source is Oracle EBS R12.
To set up drill down in Oracle BI Answers from General Ledger to Subledger:
Create your subledger request from "Financials - AP Transactions" or "Financials - AR Transactions" catalog as applicable.
In your request, add a filter on the column "GL Journal ID" under the "Document Details" folder and the set the operator of the filter to "Is Prompted".
Build your GL Journal request from the "Financials - GL Detail Transactions" catalog.
To your request, add the column "GL Journal ID" under the "Document Details" folder.
Navigate to the Column Properties of this column, and set the Value Interaction property in the Column Format tab to "Navigate".
Add a navigation target and set the target location to the subledger request you created earlier.
|
Note: For COGS and Revenue, the "GL Journal ID" column is not exposed in any presentation catalogs. It is available in the business model layer of the RPD metadata under the logical tables "Dim - GL COGS Details" and "Dim - GL Revenue Details" respectively. As a workaround, you can create presentation catalogs to report of detail level transactions for COGS and Revenue and expose this column in the presentation catalog and use similar steps are above to setup a drilldown from GL to COGS/Revenue. |
This section contains additional configuration steps that apply to PeopleSoft.
This section describes how to configure Oracle Business Intelligence Applications to use PeopleSoft versions 8.4 and 8.8 as data sources for Financial Analytics, and contains the following topics:
Section 10.2.5.3.1, "About PeopleSoft Trees in Oracle Financial Analytics"
Section 10.2.5.3.2, "GL Account Dimension, Chartfields and Hierarchy for PeopleSoft"
Section 10.2.5.3.5, "General Ledger Chartfield Hierarchy Extraction Customization"
Section 10.2.5.3.6, "Internal Organization Hierarchy Extraction Customization"
Financial Analytics consists of three products: GL and Profitability Analytics, Payables Analytics, and Receivables Analytics. Financial Analytics is referred to in the Oracle Business Intelligence Applications as Financial Analytics. References to Oracle BI Applications can be read as Financial Analytics.
For PeopleSoft, the Oracle Financial Analytics application sources data from a data structure, called PeopleSoft Trees, to get information about the organization's General Ledger hierarchies, Profit hierarchies, Cost Centers' hierarchies, and so on.
PeopleSoft Trees are a flexible, generic way of constructing hierarchical summarization of a particular database fields in PeopleSoft for reporting purposes. Typically, entities such as Chart of Account fields (Account, Dept, and Project, and so on), items, locations, and so on, are organized into user-defined trees.
Table 10-7 lists the PeopleSoft Trees the Oracle Financial Analytics application sources.
Table 10-7 PeopleSoft Trees for Oracle's Siebel Financial Analytics
| PeopleSoft Data Structure | Repository Source Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
PeopleSoft Tree |
ACCTROLLUP |
Account Rollup |
|
PeopleSoft Tree |
AR_BUSINESS_UNITS |
AR Business Unit Roll-Up |
|
PeopleSoft Tree |
DEPARTMENTS |
Manufacturing Departments |
|
PeopleSoft Tree |
OPERUNIT |
Operating Unit |
Table 10-8 lists the mappings and sessions using PeopleSoft Trees.
Table 10-8 List of Mappings And Sessions Using PeopleSoft Trees
| Repository Source Name | Mapping | Session |
|---|---|---|
|
ACCTROLLUP |
M_P_GL_ACCTS_HIERARCHY_EXTRACT |
S_M_P_GL_ACCTS_HIERARCHY_EXTRACT |
|
AR_BUSINESS_UNITS |
M_P_BUSN_ORGS_COMPANY_HIERARCHY_EXTRACT |
S_M_P_BUSN_ORGS_COMPANY_HIERARCHY_EXTRACT |
|
DEPARTMENTS |
M_P_PROFIT_CNTRS_HIERARCHY_EXTRACT |
S_M_P_PROFIT_CNTRS_HIERARCHY_EXTRACT |
|
OPERUNIT |
M_P_COST_CENTERS_HIERARCHY_EXTRACT |
S_M_P_COST_CENTERS_HIERARCHY_EXTRACT |
The GL Account Dimension in the Oracle Business Analytics Warehouse is at a granularity of a combination of chartfields. PeopleSoft Financials provides several chartfields for GL Accounts, such as Account, Alternate Account, Operating Unit, Department etc. The ETL program extracts all possible combinations of these chartfields that you have used and stores each of these chartfields individually in the GL Account Dimension. It extracts the combinations of chartfields used from the following PeopleSoft account entry tables:
PS_VCHR_ACCTG_LINES (Accounts Payable)
PS_ITEM_DST (Accounts Receivable)
PS_BI_ACCT_ENTRY (Billings)
PS_CM_ACCTG_LINE (Costing)
PS_JRNL_LN (General Ledger)
The GL Account Dimension (W_GL_ACCOUNT_D) in the Oracle Business Analytics Warehouse provides a flexible and generic data model to accommodate up to 30 chartfields. These are stored in the generic columns named ACCOUNT_SEG1_CODE, ACCOUNT_SEG2_CODE and so on up to ACCOUNT_SEG30_CODE, henceforth referred to as segments. These columns store the actual chartfield value that is used in your PeopleSoft application.
Mapping PeopleSoft Chartfields
A CSV file has been provided to map the PeopleSoft Chartfields to the generic segments. Use this file to specify which PeopleSoft application chartfield should be populated in which segment. The file is called file_glacct_segment_config_psft.csv and is located in the <OracleBI>\dwrep\Informatica\SrcFiles folder.
The first row in the file is a header row; do not modify this line. The second row in the file is where you specify how to do the mapping. The value for the column ROW_ID is hard coded to "1"; there is no need to change this.
Note that the file contains 30 columns – SEG1, SEG2, up to SEG30. You will have to specify which chartfield needs to be populated in each of these columns by specifying one of the supported values for the chartfields. The chartfields currently supported for the PeopleSoft application are listed below.
|
Note: Values are case sensitive. You must specify the values exactly as shown below. |
Account
Alternate Account
Operating Unit
Fund Code
Department
Program Code
Class Field
Budget Reference
Product
Project
Affiliate
Fund Affiliate
Operating Unit Affiliate
ChartField 1
ChartField 2
ChartField 3
|
Note: You only need to include the chartfields in the CSV file that you want to map. |
Hierarchy
Oracle Business Intelligence Application supports hierarchy for all these segments. If you have created a "tree" in PeopleSoft for any of these chartfields, you can extract these trees into Oracle Business Analytics Warehouse's hierarchy to analyze your facts at any levels of the hierarchy. Information is provided in the sections that follow on how to extract these trees and how to setup the repository file (RPD) to use the Oracle Business Analytics Warehouse's hierarchy.
GL Balance Aggregate
The Oracle Business Analytics Warehouse data model has a fact table (W_GL_BALANCE_F) that stores GL Balance for all your GL Accounts. To compress this fact table for better performance, it also provides an aggregate table built on top of this fact table that stores GL Balances for up to 6 segments of your choice. The number of segments you want in the aggregate table and which ones, are totally configurable. This configuration is done at the third line of the file_glacct_segment_config_psft.csv file. Specify a value of "Y" under the segment column that you want to be included in the aggregate table.
|
Note: You can have only up to 6 "Y"s in the file. Also, it is not a requirement that you have to use all 6. If, for example you want only 3 segments in your aggregate, you need only to specify 3 'Y's. |
Example CSV File Configuration
As an example for the configuration of the file_glacct_segment_config_psft.csv file, consider the following scenario:
Your system uses 4 chartfields, Account, Alt Account, Operating Unit, and Dept. Assume that you are interested in analyzing your data by only 3 of the 4 chartfields: Account, Operating Unit, Department, and that you typically view your GL Balances at the combination of Account and Department. Only occasionally do you want to view your GL balances as the combination of all 3 chartfields. In this scenario, the CSV file should look like:
Table 10-9 Example CSV Chartfield Mapping Values
| ROW_ID | SEG1 | SEG2 | SEG3 |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Account |
Operating Unit |
Department |
|
AGGREGATION |
Y |
Y |
With this configuration, W_GL_ACCOUNT_D would store the "Account" chartfield value in SEGMENT1 column, "Operating Unit" chartfield value in SEGMENT2 column, and so forth. The GL Balance aggregate table, W_GL_BALANCE_A would store GL Balances for each unique combination of "Account" chartfield and "Department" chartfield.
You can categorize your PeopleSoft General Ledger accounts into specific group account numbers. The GROUP_ACCT_NUM field denotes the nature of the General Ledger accounts.
|
Note: It is critical that the General Ledger Account Numbers are mapped to the Group Account Numbers (or domain values) as the metrics in the General Ledger reporting layer uses these values. |
For example, Cash account, Payroll account, and so on. For a list of the Group Account Number domain values, see Oracle Business Analytics Warehouse Data Model Reference Version 7.9. The group account num configuration is used during data extraction as well as front-end reporting. For example the group account num configuration is used heavily in both Profitability Analysis (Income Statement) and General Ledger analysis. The logic for assigning the accounts is located in the file_group_acct_codes_psft.csv file. This file is located in the <OracleBI>\dwrep\Informatica\SrcFiles folder.
Table 10-10 Layout of file_group_acct_codes_psft.csv File
| BUSINESS_UNIT | FROM_ACCT | TO_ACCT | GROUP_ACCT_NUM |
|---|---|---|---|
|
AUS01 |
101010 |
101099 |
AP |
|
AUS01 |
131010 |
131939 |
AR |
|
AUS01 |
152121 |
152401 |
COGS |
|
AUS01 |
171101 |
173001 |
OTHER |
|
AUS01 |
240100 |
240120 |
REVENUE |
|
AUS01 |
251100 |
251120 |
TAX |
In the Table above, in the first row, all accounts within the account number range from 101010 to 101099 containing a Business Unit equal to AUS01 are assigned to AP. Each row maps all accounts within the specified account number range and with the given Business Unit. If you need to assign a new group of account numbers, you can then assign GL accounts to the new group of account numbers in the file_group_acct_codes_psft.csv file.
Oracle Business Intelligence Application provides a set of mechanism to support various tree structures in the PeopleSoft application. The following tables illustrate the supporting structure types and level types.
For any nodes in the tree, except for the bottom nodes, W_HIERARCHY_D will have one corresponding record. As the "E" node in above tree (the one with blue square), you will have the following record in the database.
Table 10-13 Example CSV Chartfield Mapping Values
| HIER1_CODE | HIER2_CODE | HIER3_CODE | HIER4_CODE | HIER5_CODE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
US |
E |
E |
E |
E |
If the actual hierarchy level in the tree ends earlier than the predefined level of W_HIERARCHY_D, then the lower hierarchy level in the table will repeat the same value as its next higher level. The predefined level is 20, which means if one path of the tree only has 5 level, so the level 6~20 will repeat the value of level 5's value.
For the leaf node in the detail tree shown above, W_HIERARCHY_D will have a record for every existing record within this detail range (The extraction process will find the single record in relevant table according to tree's structure). For example, in the CA node (the one with red square), the range is 2334-2434 and 3001-3001. The tree structure table (for example, State_TBL) contains 2340, 3001 two records. When generating CA node, the extraction process will extract these two records, put them into W_HIERARCH_D as following structure. NOTE: This is purely for W_HIERARCHY_D, for W_INT_ORG_DHS, the order of hierarchy is reversed.
Table 10-14 Example CSV Chartfield Mapping Values
| HIER1_CODE | HIER2_CODE | HIER3_CODE | HIER4_CODE | HIER5_CODE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
US |
W |
CA |
2340 |
2340 |
|
US |
W |
CA |
3001 |
3001 |
In both Summary Tree and Detail Tree, the lowest level node is always a node with specific value (as above example, the name and the code may be different). For the case of winter tree, the lowest level code would be the same as higher level.
The record "Kuo" is stored in the database as follows:
Table 10-15 Example CSV Chartfield Mapping Values
| HIER1_CODE | HIER2_CODE | HIER3_CODE | HIER4_CODE | HIER5_CODE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Smith |
Cheng |
Kuo |
Kuo |
Kuo |
Oracle BI Applications uses the following tables to handle the extraction and load process of the tree. They are standard and not tree or tree-structure specific.
The General Ledger Chartfield Hierarchy is shown in the table below.
Table 10-16 General Ledger Chartfield Hierarchy
| Sequence | Table Name |
|---|---|
|
1 |
W_PSFT_TREE_TMP |
|
1 |
W_PSFT_GLHIER_CF_DH_TMP |
|
2 |
W_PSFT_GLHIER_DTLRGE_DH_TMP |
|
2 |
W_PSFT_GLHIER_VERT_DH_TMP |
|
3 |
W_PSFT_GLHIER_FLAT_DH_TMP |
|
4 |
W_HIERARCHY_DS |
The Internal Organization Hierarchy is shown in the table below.
Table 10-17 Internal Organization Hierarchy
| Sequence | Table Name |
|---|---|
|
1 |
W_PSFT_INT_ORG_TREE_TMP |
|
1 |
W_PSFT_INT_ORG_GLBU_DH_TMP |
|
2 |
W_PSFT_INT_ORG_DTLRGE_DH_TMP |
|
2 |
W_PSFT_INT_ORG_VERT_DH_TMP |
|
3 |
W_PSFT_INT_ORG_FLAT_DH_TMP |
|
4 |
W_INT_ORG_DHS |
|
5 |
W_INT_ORG_DH |
|
Note: The hierarchy related extraction and load tasks are deactivated in the standard application. To activate the hierarchy extractions and load tasks, you need to activate certain Configuration Tags in Oracle Data Warehouse Administration Console (DAC). |
Configuration Tags is a DAC feature, which allows users to activate or deactivate a certain set of tasks in your ETL process. When deactivated, those set of tasks will not get executed when running the execution plan. When activated, those set of tasks will get executed when running the execution plan.
Oracle BI Applications includes two configuration tags for hierarchy extractions and load, as follows:
"PeopleSoft - Populate Non Business Unit Related Hierarchies", which contains all but business unit related hierarchies' extractions and load tasks.
"PeopleSoft - Populate Business Unit Related Hierarchies", which contains Business Unit related hierarchies' extractions and load tasks.
By simply activating and de-activating them in a Subject Area, you can control whether these hierarchy extraction and load tasks get executed in the execution plan.
To enable a set of tasks in your ETL process:
Open DAC, click "Design" button in navigation panel, and click "Configuration Tag".
De-select the "Inactive" checkbox of the specific hierarchy you want to enable.
For GL Chartfield, de-select the checkbox of "PeopleSoft - Populate Non Business Unit Related Hierarchies". For Business Unit, de-select the checkbox of "PeopleSoft – Populate Business Unit Related Hierarchies".
Save your changes
Click tab "Subject Area", check subject area one by one.
For every subject area, if the hierarchy-relevant item in its Configuration Tag (see the panel below subject area, there is a "Configuration Tag" tab) is inactive, de-select it, and save it.
As every tree in PeopleSoft is an identical item, each of them is extracted into data warehouse separately – that means it is required to create a new mapping if a new tree is to be extracted.
Oracle Business Intelligence Application provides a set of example mappings to extract Internal Organization Hierarchy and General Ledger Chartfield Hierarchy related trees. Users can customize their own extractions by simply copying some of those mappings and modifying one or two naming parameters.
This section includes an example set of mappings for General Ledger Chartfield extraction. This example extracts a GL Account tree named "ACCTROLLUP" with SETID "SHARE" from the PeopleSoft application. To get other GL Chartfield related trees to be extracted, you need to customize DE_PSFT_Stage_GLHierarchy_AccountHierarchy_Extract and SDE_PSFT_Stage_GLHierarchy_GetAccountChartField.
You do not need to change or copy the rest of the mappings. The example customization is provided as below.
Table 10-18 General Ledger Chartfield Hierarchy Mappings
| Exec Sequence | Mapping Name | Needs Customization? |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
SDE_PSFT_Stage_GLHierarchy_AccountHierarchy_Extract |
Y |
|
1 |
SDE_PSFT_Stage_GLHierarchy_GetAccountChartField |
Y |
|
2 |
SDE_PSFT_Stage_GLHierarchy_GetHierarchyLevel |
N |
|
2 |
SDE_PSFT_Stage_GLHierarchy_DeriveRange |
N |
|
3 |
SDE_PSFT_Stage_GLHierarchy_Flatten |
N |
|
4 |
SDE_PSFT_GLHierarchy_Derive |
N |
For example, if a user wants to extract a tree named "DEPARTMENT_HIERARCHY" with SETID "XYZ", which uses DEPT_TBL as its structure's Record Name, DEPTID as Field Name (that means it builds up the hierarchy for Department chartfield from General Ledger), the following customization steps are required:
Create new mappings by copying the existing SDE_PSFT_Stage_GLHierarchy_AccountHierarchy_Extract and SDE_PSFT_Stage_GLHierarchy_GetAccountChartField mappings.
Name the new mappings SDE_PSFT_Stage_GLHierarchy_DepartmentHierarchy_Extract and SDE_PSFT_Stage_GLHierarchy_GetDepartmentChartField.
Adjust Settings in SDE_PSFT_Stage_GLHierarchy_DepartmentHierarchy_Extract, as follows:
In SDE_PSFT_Stage_GLHierarchy_DepartmentHierarchy_Extract, open Source Definition PSFT_TREE_VERTICAL_FLATTENING.
Under the "Properties" tab, change the Tree Name to "DEPARTMENT_HIERARCHY", and Set ID to "XYZ".
Adjust Settings in SDE_PSFT_Stage_GLHierarchy_GetDepartmentChartField.
In the SDE_PSFT_Stage_GLHierarchy_GetDepartmentChartField mapping, change the source table to "DEPT_TBL" (also change the Source Qualifier). Connect SETID, DEPTID, EFFDT, EFF_STATUS, and DESCR from Source Qualifier to next Filter "Filter_GLACCT" corresponding fields (connect DEPTID to CHARTFIELD).
In the last Expression Transformation of this mapping ("Exp_TMPGLACCT"), change the expression field SOURCE_TABLE_NAME field to "DEPT_TBL" (the same name as the source table).
Save all your changes in the Informatica folder.
Add Corresponding Sessions and Workflows in Informatica Workflow Manager, as follows:
Open Informatica Workflow Manager
Locate folder "SDE_PSFT_88_adapter" (or "SDE_PSFT_84_adapter").
Open Task Developer and create a new task for the that mappings you just created.
Referring to the parameters in the original sample sessions (see table below, and leave other mappings set to the default value), modify these newly created sessions.
Parameter Configurations for SDE_PSFT_Stage_GLHierarchy_DepartmentHierarchy_Extract Session are shown in the table below:
Table 10-19 General Ledger Chartfield Hierarchy Mappings
| Tab Name | Parameter Name | Value |
|---|---|---|
|
Properties |
Parameter Filename |
$PMSourceFileDir\parameterfileOLTP.txt |
|
Properties |
$Source connection value |
$DBConnection_OLTP |
|
Properties |
$Target connection value |
$DBConnection_OLAP |
|
Properties |
DTM buffer size |
32000000 |
|
Config Object |
Default buffer block size |
128000 |
|
Config Object |
Stop on errors |
1 |
|
Config Object |
Override tracing |
Normal |
|
Mapping |
ConnectionW_PSFT_TREE_TMP - Rational |
$DBConnection_OLAP |
|
Mapping |
ConnectionSQ_PSFT_TREE_VERTICAL_FLATTENING - Application |
$DBConnection_OLTP |
|
Mapping |
ConnectionW_PSFT_TREE_TMP1 - Rational |
DBConnection_OLAP |
|
Mapping |
ConnectionLkp_Tree_ChartField - Rational |
$DBConnection_OLTP |
|
Mapping |
SDE_PSFT_Stage_GLHierarchy_DepartmentHierarchy_Extract – Session$Source Connection Value |
$DBConnection_OLTP |
|
Mapping |
SDE_PSFT_Stage_GLHierarchy_DepartmentHierarchy_Extract – Session$Target Connection Value |
$DBConnection_OLTP |
|
Note: The SDE_PSFT_Stage_GLHierarchy_GetDepartmentChartField parameters are similar to this. |
Save your changes
Open Workflow Designer.
Create a Workflow with the same name as Session.
Drag the newly created session to the panel.
Connect the start with the session.
Save and Check-in all your changes in Informatica Designer and Workflow Manager.
Re-configure the DAC settings, as follows:
Log in to the DAC and display the Task tab.
Add those two newly modified workflows as a task, right-click the task, and choose "synchronize" to update those newly added tasks.
Add your tasks into Configuration Tags: navigate to Configuration Tag panel (click "Design", choose "Configuration Tag"). Select "PeopleSoft - Populate Non Business Unit Related Hierarchies" item. Select "Tasks" tab in the panel below. Click "Add/Remove" button; query the new mappings you just entered into DAC. Select mappings; add them into the right panel. Click OK, then click Save.
Reassemble all the financial related areas: Click "Design" button at the top tool bar of DAC, select "Subject Areas" tab, for each of the financial-related subject areas (Cost of Goods Sold, General Ledger, Payables, Receivables, Revenue), right click on it, choose "assemble" item.
Re-build related execution plan: Click "Execute" button at the top tool bar of DAC, select "Execution Plans" tab, find the executing plan for your PeopleSoft Financial Application (for example Financials_PeopleSoft 8.8), right click on it, choose "build" item.
Internal Organization Hierarchy follows a similar logic to the previous section. But since it only extracts the hierarchy related to Business Unit (unlike GL Chartfield, there are many different types of trees), only the Tree Name and SETID are required to change.
Table 10-20 General Ledger Chartfield Hierarchy Mappings
| Exec Sequence | Mapping Name | Needs Customization? |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
SDE_PSFT_Stage_InternalOrganizationDimension_CompanyHierarchy_Extract |
Y |
|
1 |
SDE_PSFT_Stage_InternalOrganizationDimension_CompanyHierarchy_GetGLBU |
N |
|
2 |
SDE_PSFT_Stage_InternalOrganizationDimension_CompanyHierarchy_GetHierarchyLevels |
N |
|
2 |
SDE_PSFT_Stage_InternalOrganizationDimension_CompanyHierarchy_DeriveRange |
N |
|
3 |
SDE_PSFT_Stage_InternalOrganizationDimension_CompanyHierarchy_Flatten |
N |
|
4 |
SDE_PSFT_InternalOrganizationDimension_CompanyHierarchy_Derive |
N |
As the above table illustrates, only the SDE_PSFT_Stage_InternalOrganizationDimension_CompanyHierarchy_Extract mapping needs to be modified (that is, there is no need to change or copy the rest mappings). For example, if you want to extract a tree named "BIZ_UNIT_HIER" with SETID "XYZ", which uses BU_GL_UPDAT2_VW as its structure's Record Name, and BUSINESS_UNIT as its field name (that means it builds up hierarchy for BUSINESS_UNIT), do the following:
Create a new mapping by copying the existing SDE_PSFT_Stage_InternalOrganizationDimension_CompanyHierarchy_Extract mapping.
Name the new mappings SDE_PSFT_Stage_InternalOrganizationDimension_CompanyHierarchy2_Extract.
Adjust Settings in SDE_PSFT_Stage_InternalOrganizationDimension_CompanyHierarchy2_Extract, as follows:
In SDE_PSFT_Stage_InternalOrganizationDimension_CompanyHierarchy2_Extract, open Source Definition PSFT_TREE_VERTICAL_FLATTENING.
Under the "Properties" tab, change the Tree Name to "BIZ_UNIT_HIER", and Set ID to "XYZ".
Add Corresponding Sessions and Workflows in Informatica Workflow Manager.
Save your changes in the Informatica Folder.
Add Corresponding Sessions and Workflows in Informatica Workflow Manager, as follows:
Open Informatica Workflow Manager, find folder "SDE_PSFT_88_adapter" (or "SDE_PSFT_84_adapter")
Open Task Developer, and create new task for the mappings that you just created.
Using the parameters in the original sample sessions as a guide (refer to the parameter settings for SDE_PSFT_Stage_GLHierarchy_DepartmentHierarchy_Extract), modify these newly created session.
Save your changes.
Open Workflow Designer and create Workflow with the same name as the Session.
Drag the newly created session to the panel and connect the start with the session.
Save and Check-in all your changes in Informatica Designer and Workflow Manager.
Re-configure the DAC settings, as follows:
Log in to the DAC and display the Task tab.
Add those two newly modified workflows as a task, right-click the task, and choose "synchronize" to update those newly added tasks.
Add your tasks into Configuration Tags: navigate to Configuration Tag panel (click "Design", choose "Configuration Tag"). Select "PeopleSoft - Populate Non Business Unit Related Hierarchies" item. Select "Tasks" tab in the panel below. Click "Add/Remove" button; query the new mappings you just entered into DAC. Select mappings; add them into the right panel. Click OK, then click Save.
Reassemble all the financial related areas: Click "Design" button at the top tool bar of DAC, select "Subject Areas" tab, for each of the financial-related subject areas (Cost of Goods Sold, General Ledger, Payables, Receivables, Revenue), right click on it, choose "assemble" item.
Re-build related execution plan: Click "Execute" button at the top tool bar of DAC, select "Execution Plans" tab, find the executing plan for your PeopleSoft Financial Application (for example Financials_PeopleSoft 8.8), right click on it, choose "build" item.
This section contains additional configuration steps that apply to Universal, and contains the following topics:
This configuration is required only if you are implementing Oracle Profitability Analytics and you want to allocate your expenses by product or by customer dimensions. The out-of-the-box adapter of Oracle BI Applications does not capture the miscellaneous cost and expenses associated with generating revenue from a customer or from a product (for example, expenses such as marketing campaign expenses). Since the way that these miscellaneous expenses are allocated across products or customers can be very different between different companies, we do not perform this type of allocations out of box; we require customers to feed us the result of the allocations through Universal Adapter.
The Customer Costs Lines (W_CUSTOMER_COST_LINE_F) table stores cost details by customers. The total cost by customers include both direct cost that is captured in the financial system by products, and the allocated costs that are captured in the costing system. The table also stores the source of allocations. For example, the Sales and Marketing costs are not be captured as direct costs by customers. However, at a later point in time, the costs could be allocated from a combination of General Ledger accounts or Cost Centers into various customers. This table stores the source cost centers and General Ledger accounts as well. The Customer Costs can be categorized by Sales, Marketing, Service, and Operating costs. These could be further broken down to Salaries, Events, and Promotions. Oracle Business Analytics Warehouse provides a set of categories, and these can be changed depending on the user needs and cost components by which customers are tracked. The actual cost lines are also tracked in this table. Apart from Customers, there are number of other dimensions by which the costs can be tracked such as Sales Region, Sales Geography, Company, Business Area and the associated hierarchies. The different cost lines such as Sales, Marketing, and Operating costs, have different details and many dimensions are included in this table. Some of the dimension keys are not be applicable to certain cost components. It is important that an organization identifies the dimensional keys that are used for Product Cost Analysis for various components.
The Product Costs Lines (W_PRODUCT_COST_LINE_F) table stores cost details by products. The total cost by products include both direct cost that is captured in the financial system by products, and the allocated costs that are captured in the costing system. The table also stores the source of allocations. For example, the Sales and Marketing costs are not captured as direct costs by products. However, at a later point in time, the costs are allocated from a combination of General Ledger accounts and Cost Centers into various products. This table also stores the source cost centers and General Ledger accounts. The product costs can be categorized by Sales, Marketing, Service, and Operating costs. These could be further broken down into Salaries, Events, and Promotions. Oracle Business Analytics Warehouse provides a set of common categories, and these can be changed depending on the user needs and cost components by which products are tracked. The actual cost lines are also tracked in this table. Apart from products, there are number of other dimensions by which the costs are tracked such as Sales Region, Sales Geography, Company, Business Area, and the associated hierarchies. The different cost lines such as Sales, Marketing, and Operating costs, have different details and many dimensions are included in this table. Some of the dimension keys are not applicable to certain cost components. It is important that an organization identifies the dimensional keys that is used for Product Cost Analysis for various components.
In Oracle's Profitability Analytics, the Customer Costs Lines and Product Costs Lines fact tables store the costing and expenses for the Profitability functional area. You need to use these tables with General Ledger Revenue and General Ledger COGS fact tables.
The General Ledger Revenue and General Ledger COGS fact tables are populated by the or Oracle 11i source system, but the Customer Costs Lines and Product Costs Lines fact tables are populated by the universal source system.
To load the Customer Costs Lines and Product Costs Lines tables
Open the customer_cost_line.csv file in the $pmserver\Sample Universal Source Files folder.
Insert a record into the file for each customer costing transaction you want to load into the Customer Cost fact table.
For the DATASOURCE_NUM_ID column, you need to provide the same source identifier value as in the file_parameters_ora11i.csv file.
Save the file in the $pmserver\srcfiles directory, then close the file.
Repeat steps 1 to 3 for the file_product_cost.csv file.