1 About the Connector
This chapter introduces the CA ACF2 connector.
Introduction to the Connector
Oracle Identity Manager connectors are used to integrate Oracle Identity Manager with external, identity-aware applications.
Oracle Identity Manager automates access rights management, security, and provisioning of IT resources. This guide discusses the connector that enables you to use CA ACF2 as a managed (target) resource of identity data for Oracle Identity Manager.
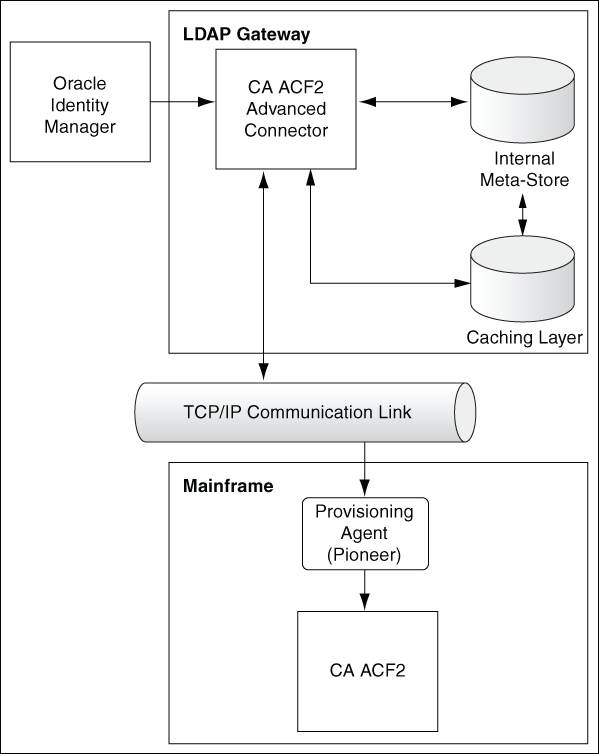
The advanced connector for CA ACF2 provides a native interface between Oracle Identity Manager and CA ACF2 installed on an IBM z/OS mainframe.
In the account management (target resource) mode of the connector, information about users created or modified directly on the target system can be reconciled into Oracle Identity Manager. In addition, you can use Oracle Identity Manager to perform provisioning operations on the target system.
If you configure CA ACF2 as a target resource, then user profiles on CA ACF2 correspond to accounts or resources assigned to OIM users.
Certified Components
These are the software components and their versions required for installing and using the CA ACF2 connector.
Table 1-1 Certified Components
| Component | Requirement |
|---|---|
|
Oracle Identity Governance or Oracle Identity Manager |
You can use one of the following releases:
|
|
Target system |
CA ACF2 R15 or R16 running on IBM z/OS 2.2, 2.3, 2.4, or 2.5 |
|
JDK |
The JDK version can be one of the following:
|
| LDAP Gateway |
The computer hosting the LDAP Gateway must run the following software:
|
|
Infrastructure Requirements: Message transport layer between the Oracle Identity Manager and the mainframe environment |
TCP/IP |
Certified Languages
These are the languages that the connector supports.
-
Arabic
-
Chinese (Simplified)
-
Chinese (Traditional)
-
Danish
-
English
-
French
-
German
-
Italian
-
Japanese
-
Korean
-
Portuguese
-
Spanish
Connector Architecture
Connector Components
-
LDAP Gateway: The LDAP Gateway receives instructions from Oracle Identity Manager in the same way as any LDAP version 3 identity store. These LDAP commands are converted into native commands for CA ACF2, encrypted using AES-128 encryption, and then sent to the Provisioning Agent. The response, which is also native to CA ACF2, is parsed into an LDAP-format response and returned to Oracle Identity Manager.
During reconciliation, the LDAP Gateway receives event notification, converts the events to LDAP format, and then forwards them to Oracle Identity Manager.
-
Provisioning Agent (Pioneer): The Provisioning Agent, running as an IBM z/OS STC (Started Task), is a mainframe component. It receives native mainframe CA ACF2 provisioning commands from the LDAP Gateway. These requests are decrypted, converted from ASCII to EBCDIC, passed to CA ACF2 through the standard RACF Sub System Interface API, and then posted to the CA ACF2 database. The response is parsed and returned to the LDAP Gateway.
Note:
At some places in the guide, the Provisioning Agent is referred to as Pioneer. -
Reconciliation Agent (Voyager): The Reconciliation Agent captures mainframe events by using exits, which are programs run after events in CA ACF2 are processed. These events include the ones generated at the TSO logins, the command prompt, batch jobs, and other native events. The Reconciliation Agent captures these events, transforms them into notification messages, and then sends them to Oracle Identity Manager through the LDAP Gateway.
Note:
At some places in this guide, the Reconciliation Agent is referred to as Voyager. -
Message Transport Layer: This connector supports a message transport layer by using the TCP/IP protocol, which is functionally similar to proprietary message transport layer protocols. In addition, the connector provides AES encryption for messages sent and received through the transport layer.
The AES encryption is performed using 128-bit cryptographic keys. In addition, Encryption and Decryption programs are supplied in the Distribution Load Library. The encryption or decryption does not require any network software or hardware.
Connector Operations
These are the operations that the connector performs.
This section provides an overview of the following processes:
Full Reconciliation Process
Full reconciliation involves fetching all existing user profile data from the mainframe to Oracle Identity Manager.
Note:
See Performing Full Reconciliation for detailed instructions of the full reconciliation process.-
You specify the full reconciliation configuration in the ACF2 Reconcile All Users scheduled task.
-
In the scheduled task form UsersList property, you enter a list of user IDs of the user profiles that you want to reconcile. If no users are specified, then all existing users on the target system will be reconciled.
-
You set a start time for the task and run the scheduled task. The task sends the list of user IDs to the LDAP Gateway.
-
The LDAP Gateway encrypts the list of user IDs and then sends it to the Provisioning Agent on the mainframe.
-
You run the scheduled task. The task sends a search request to the LDAP Gateway.
-
The LDAP Gateway encrypts the search request and then sends it to the Provisioning Agent on the mainframe.
-
The Provisioning Agent encrypts the user profile data received from ACF2 and then passes this data to the LDAP Gateway.
-
The LDAP Gateway decrypts the user profile data and passes it to Oracle Identity Manager.
-
If you configure the target system as a target resource, then this user profile data is converted into accounts or resources for OIM Users.
Incremental Reconciliation Process
In incremental reconciliation, only records that are added or modified after the last reconciliation run are fetched into Oracle Identity Manager.
Incremental reconciliation is initiated by one of the exits that work in conjunction with the Reconciliation Agent. Figure 1-1 shows the flow of data during this form of reconciliation.
Figure 1-1 Incremental Reconciliation Process
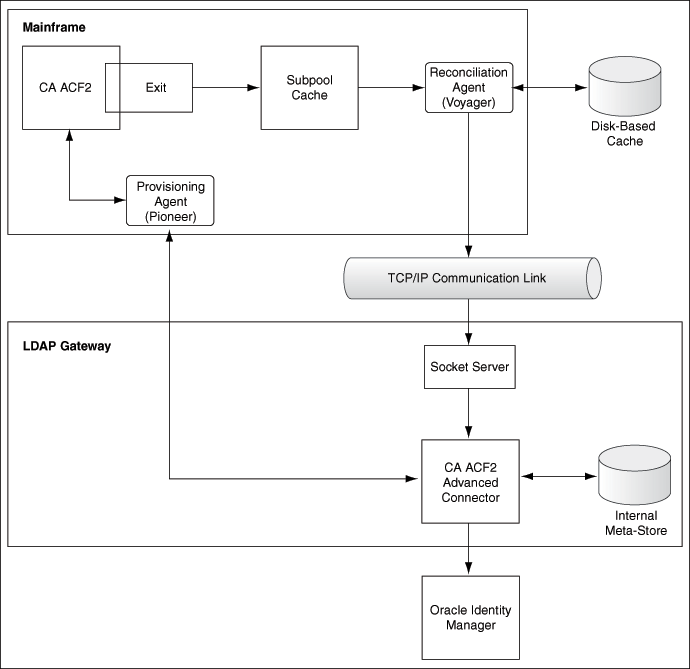
Description of "Figure 1-1 Incremental Reconciliation Process"
-
Incremental reconciliation begins when a user is created, updated, or deleted on CA ACF2. This event might take place either directly on the mainframe or in response to a provisioning operation on Oracle Identity Manager.
-
The Reconciliation Agent gathers data captured by one of three CA ACF2 exits: LIDPOST, NEWPXIT, or EXPPXIT. The exit detects the event and sends a message containing user data to Subpool 231 (cache). This message contains the minimum number of data items, such as the user ID and password, required to reconcile the event.
-
The Reconciliation Agent polls Subpool 231. When it finds a message in the subpool, it reads the message into its buffer. This frees up the subpool entry.
-
The Reconciliation Agent opens up a connection with the LDAP Gateway, and then sends the message to the gateway over TCP/IP.
Note:
- Messages sent to the LDAP Gateway are encrypted using AES-128 encryption.
- As mentioned in Step 2, the message sent by the Reconciliation Agent contains only a minimum amount of data. The LDAP Gateway sends a request to the Provisioning Agent to fetch the remaining user data from the target system.
Note:
Messages sent to the LDAP Gateway are encrypted using AES-128 encryption. -
The LDAP Gateway stores the events received from Reconciliation Agent (Voyager) in its backend, also known as persistent storage, if
_internalEnt_is set totruein the connector properties file in the Gateway. -
OIM then fetches these incremental events using
ACF2 Reconcile All Ldap Usersscheduled task which is communicated to LDAP's backend.
Provisioning Process
Provisioning involves creating or modifying a user's data on the target system through Oracle Identity Manager.
Figure 1-2 shows the flow of data during provisioning.
-
Provisioning data is sent from Oracle Identity Manager to the LDAP Gateway.
-
The LDAP Gateway converts the provisioning data into mainframe commands, encrypts the commands, and then sends them to the mainframe over TCP/IP
-
The Provisioning Agent installed on the mainframe decrypts the commands and then runs them on the mainframe.
-
The Provisioning Agent sends the output of the commands back to the LDAP Gateway.
-
The outcome of the operation on the mainframe is displayed on the Oracle Identity Manager console. A more detailed message is recorded in the connector log file.
Use Cases Supported by the CA ACF2 Connector
Large enterprises rely on mainframe systems for critical applications. The CA ACF2 security system is used to secure these mainframe systems. The following are some of the most common scenarios in which this connector can be used:
-
User Management
Creating and managing CA ACF2 users is traditionally done by the mainframe security team using native command line tools. Using the Oracle Identity Manager CA ACF2 connector, you can perform the CA ACF2 user management operations from Oracle Identity Manager. Joiner, mover, and leaver processes can be automated, and a user's ACF2 LID can be created by the Oracle Identity Manager team with little or minimal knowledge of underlying CA ACF2 commands. The following are some use cases for user management:- Creat user
- Update user
- Reset password
- Enable or disable user
- Add or remove a user from the ACF2 Access Rule
- Add or remove a user from the ACF2 Resource Rule
-
Password Management
Password reset requests are the highest contributors to helpdesk tickets where employees forget their password and call helpdesk. Using the Oracle Identity Manager CA ACF2 connector, employees can login to Oracle Identity Manager and perform a self-service password reset. This saves time and cost for the helpdesk team. Some enterprises also have password reset policies which can be automated using this connector through Oracle Identity Manager.
-
Access to mainframe datasets
Mainframe datasets are like files and folders on an operating system. CA ACF2 users need access to these datasets to perform their job. Enterprises using CA ACF2 use CA ACF2 Access Rules to protect these datasets. Using Oracle Identity Manager CA ACF2 connector, users can request for Access Rules, and, if approved by their manager, the Oracle Identity Manager CA ACF2 connector will provision the user's access to the access rule. This increases employee productivity.
-
Access to mainframe resources
In addition to datasets, mainframe system has generic resources, for example TSO, CICS. These resources are protected using CA ACF2 Resource Rules. Using the Oracle Identity Manager CA ACF2 connector, users can request for resource rules, and, if approved by their manager, the Oracle Identity Manager CA ACF2 connector will provision user's access to the resource rule.
-
LOGON ID Reconciliation
Oracle Identity Manager CA ACF2 connector supports full reconciliation of ACF2 LOGON IDs. The LOGIN ID attributes are reconciled based on their configuration.
-
Real time reconciliation for users
Oracle Identity Manager CA ACF2 connector also supports real-time reconciliation for users. If any CA ACF2 LID is created or updated natively in CA ACF2, then that change is detected by the Voyager component of the connector, and the changed user event is sent to the gateway persistence backend (dc=system,dc=backend). This can further be reconciled in Oracle Identity Manager using the CA ACF2 Reconcile LDAP Users task. This task can be configured to run in pre-defined intervals.
Features of the Connector
The following are features of the connector:
Target Resource Reconciliation
Target resource reconciliation involves fetching data about newly created or modified users on the target system and using this data to add or modify resources assigned to OIM users.
You can use the connector to configure CA ACF2 as a target resource of Oracle Identity Manager.
Full and Incremental Reconciliation
Full reconciliation involves reconciling all existing user records from the target system into Oracle Identity Manager, while in incremental reconciliation, only the records created or modified after the latest date/timestamp the last reconciliation was run are considered for reconciliation.
ACF2 Reconcile All LDAP Users. See Reconciling Internal LDAP Users to Oracle Identity Manager and Performing Full Reconciliation for more details.
You can perform a full reconciliation run at any time.
Limited (Filtered) Reconciliation
You can reconcile records from the target system based on a specified filter criterion.
- Logon ID filtering - The Scheduled Task
ACF2 Reconcile All Usersprovides this feature with the parameterUserLists. For more information, see Performing Full Reconciliation. - Attribute level filtering - The scheduled task
ACF2 Reconcile All Usersprovides this feature. For more information, see Performing Filtered (Limited) Reconciliation. - Filtering at agent level - Pioneer and Voyager provide this additional filtering feature. For more information, see Table 2-4 and Table 2-5.
Encrypted Communication Between the Target System and Oracle Identity Manager
AES-128 encryption is used to encrypt data that is exchanged between the LDAP Gateway, and the Reconciliation and Provisioning Agents on the Mainframe. This encryption is taken care by the Mainframe agents.
High Availability
-
Scenario 1: The Reconciliation Agent is running and the LDAP Gateway stops responding
- The Reconciliation Agent stops sending messages (event data) to the LDAP Gateway.
- Messages that are not sent are stored in the subpool cache.
Note:
The subpool cache cannot grow beyond the allocated limit. If the LDAP Gateway does not start responding before the allocated limit is reached, then new messages that come in are lost. - When the LDAP Gateway is brought back online, the Reconciliation Agent reads data from the subpool cache and then sends messages to the LDAP Gateway.
-
Scenario 2: The LDAP Gateway is running and the Reconciliation Agent stops responding
- Event data is sent to the subpool cache.
- When the Reconciliation Agent is brought back online, it reads data from the subpool cache and then sends messages to the LDAP Gateway.
-
Scenario 3: The LDAP Gateway is running and the mainframe stops responding
- Messages that are in the subpool cache are written to disk.
- When the mainframe is brought back online, event data written to disk is again stored in the subpool cache.
- The Reconciliation Agent reads data from the subpool cache and then sends messages to the LDAP Gateway.
-
Scenario 4: The LDAP Gateway is running and the Provisioning Agent or mainframe stops responding
The process task that sends provisioning data to the LDAP Gateway retries the task.
-
Scenario 5: The subpool is stopped by an administrator
If the subpool is stopped by an administrator, then it shuts down the Reconciliation Agent, thereby destroying any messages that are not transmitted. However, messages in the AES-encrypted file are not affected and can be recovered.
Connector Objects Used During Reconciliation and Provisioning
As discussed in one of the earlier sections, target resource reconciliation involves fetching data about newly created or modified users on the target system and using this data to add or modify resources assigned to OIM Users. Provisioning involves creating or modifying account data on the target system through Oracle Identity Manager.
The following sections provide information about connector objects used during reconciliation and provisioning:
Supported Functions for Reconciliation
These are the list of operations that the connector supports for your mainframe.
-
Create user
-
Modify user
-
Change password
-
Disable user
-
Delete user
-
Enable user
-
Grant user access to priviliges
Supported Functions for Provisioning
These are the list of operations that the connector supports for your target system.
Table 1-2 lists the provisioning functions supported by the connector.
Table 1-2 Supported Functions for Provisioning
| Function | Description | Mainframe Command |
|---|---|---|
|
Create user |
Adds new login ID record on CA ACF2 |
INSERT |
|
Modify user |
Modifies login ID record information on CA ACF2 |
CHANGE |
|
Change password |
Changes user password on CA ACF2 in response to password changes made on Oracle Identity Manager through user self-service. |
CHANGE |
|
Reset password |
Resets user password on CA ACF2 The passwords are reset by the administrator. |
CHANGE |
|
Disable user |
Disables user on CA ACF2 |
CHANGE |
|
Enable user |
Enables user on CA ACF2 |
CHANGE |
|
Delete user |
Removes user from CA ACF2 |
DELETE |
|
Grant user access to rule |
Creates or modifies a CA ACF2 resource or access rule for the CA ACF2 user |
SET RULE |
|
Grant user access to privileges (TSO) |
Provides user access to CA ACF2 security fields (including custom fields) |
CHANGE |
|
Grant user access to privileges (CICS) |
Provides user access to CA ACF2 CICS login ID record fields |
CHANGE |
User Attributes for Target Resource Reconciliation and Provisioning
Table 1-3 lists attribute mappings between CA ACF2 and Oracle Identity Manager for target resource reconciliation and provisioning. The OnBoardAcf2User and ModifyAcf2User adapters are used for the Create User and Modify User provisioning operations, respectively.
Table 1-3 User Attributes for Target Resource Reconciliation and Provisioning
| OIM Form | ACF2 Attribute | LDAP Attribute | Attribute Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| USER_ID | UID | uid | 24 characters | User login ID |
| FULL_NAME | NAME | cn | 20 characters | User full name |
| DEFAULT_GROUP | GROUP | group | 8 characters | Restriction group |
| USER_PASSWORD | PASSWORD | userPassword | 8 to 128 characters | Password used to login |
| PWD_EXPIRE | PSWD-EXP | passwordExpire | bit field | Date the user password expires |
| ACTIVE_DATE | ACTIVE | activeDate | 4-byte binary | Active date privilege |
| EXPIRE_DATE | EXPIRE | expireDate | 4-byte binary | Expire date privilege |
| TSO_DFTPFX | DFT-PFX | omvUid | 8 characters. however, the last character is reserved | OMV UID tsoDftPfx DFT-PFX TSO DFT-PFX |
| TSO_ACCTNUM | TSOACCT | tsoAcctNum | 40 characters | Default TSO account number on the TSO/E logon panel |
| TSO_PROC | TSOPROC | tsoProc | 8 characters | Default logon procedure on the TSO/E logon panel |
| TSO_SIZE | TSORGN | tsoSize | 2-byte binary | Minimum region size if not requested at logon |
| TSO_UNIT | TSOUNIT | tsoUnit | 8 characters | Default UNIT name for allocations |
| TSO_MAXSIZE | TSOSIZE | tsoMaxSize | 2-byte binary | The maximum region size the user can request at logon |
| TSO_PERF | TSOPERF | tsoPerf | 1-byte binary | Indicates the user's default TSO performance group (1-255). Zero indicates no performance group was specified. |
| TSO_COMMAND | TSOCMDS | tsoCommand | 8 characters | Command to be run during TSO/E logon |
| TSO_DEST | DFT-DEST | tsoDest | 8 characters | Default SYSOUT destination |
| TSO_HOLDCLASS | DFT-SUBH | tsoHoldclass | 1 character | Default hold class tsoSumitclass DFTSUBM Default submit class |
| TSO_MSGCLASS | DFT-SUBM | tsoMsgclass | 1 character | Default message class |
| TSO_SYSOUTCLASS | DFT-SOUT | tsoSysoutclass | 1 character | Default SYSOUT class. |
| TSO_SUBMITCLASS | DFT-SUBC | 1 character | Default TSO submit class. | |
| TSO_RBA | TSORBA | tsoRba | 3 hexadecimal bytes | Revoke NA Value 'Y' if user is suspended or 'N' if the user is not suspended |
| TSO_ACCTPRIV | ACCTPRIV | tsoAcctPriv | bit field | Indicates user has TSO accounting privileges (for UADS updates with the TSO ACCOUNT command). |
| TSO_ALLCMDS | ALLCMDS | tsoAllCmds | bit field | Indicates the ability to bypass the CA ACF2 restricted command lists by entering a special prefix character. |
| TSO_MAIL | tsoMail | bit field | Indicates that a user can receive mail messages from TSO at logon time. | |
| TSO_JCL | JCL | tsoJcl | bit field | Indicates the ability to submit batch jobs from TSO and to use SUBMIT, STATUS, CANCEL, and OUTPUT commands (for example, use TSO SUBMIT). |
| TSO_WTP | WTP | tsoWtp | bit field | Indicates that CA ACF2 displays write-to-programmer messages. CA ACF2 issues all violation and warning messages as WTPs. Specify this field for all TSO user logonid records so that they can receive CA ACF2 messages. |
| TSO_FSCRN | FSCRN | tsoFScrn | bit field | Indicates that a user can use the full-screen logon display. |
| TSO_MOUNT | MOUNT | tsoMount | bit field | Indicates permission to issue mounts for devices. |
| TSO_NOTICES | NOTICES | tsoNotices | bit field | Indicates a user can receive TSO notices at logon time. |
| TSO_OPERATOR | OPERATOR | tsoOperator | bit field | Indicates that a user has TSO operator privileges. |
| TSO_PROMPT | PROMPT | tsoPrompt | bit field | Indicates that CA ACF2 prompts a user for missing or incorrect parameters. |
| TSO_INTERCOM | INTERCOM | tsoIntercom | bit field | Indicates this user is willing to accept messages from other users through the TSO SEND command. |
| TSO_LGNACCT | LGN-ACCT | tsoLgnAcct | bit field | Indicates permission to specify an account number at logon time. |
| TSO_LGNMSG | LGN-MSG | tsoLgnMsg | bit field | Indicates this user has permission to specify a message class at logon time. |
| TSO_LGNPERF | LGN-PERF | LGNPERF | bit field | Indicates permission to specify a performance group at logon time. |
| TSO_LGNPROC | LGN-PROC | bit field | Indicates permission to specify the TSO procedure name at logon time. | |
| TSO_LGNRCVR | LGN-RCVR | tsoLgnRcvr | bit field | Indicates permission to use the recover option of the TSO or TSO/E Command Package. If not specified, the user cannot enter the PROFILE RECOVER command. |
| TSO_LGNSIZE | LGN-SIZE | tsoLgnSoze | bit field | Indicates that this user is authorized to specify any region size at logon time (overriding TSOSIZE). A user can specify size at logon time without this field, but is restricted to a maximum size based on the TSOSIZE unless the LGN-SIZE field is in the logonid record. |
| TSO_LGNTIME | LGN-TIME | tsoLgnTime | bit field | Indicates permission to specify the TSO session time limit at logon time. |
| TSO_LGNUNIT | LGN-UNIT | tsoLgnUnit | bit field | Indicates permission to specify the TSO unit name at logon time. |
| TSO_TIME | TSOTIME | tsoTime | 2-byte binary | Indicates a user’s default TSO time parameter, which is the CPU time limit (in minutes) associated with the TSO session. The maximum value is 1440. Zero indicates no default TSO time parameter was specified. |
| ACCESS_CNT | ACC-CNT | accessCnt | READONLY | The count of the number of system accesses made by this logonid since it was created. |
| TSO_LGNDEST | LGN-DEST | tsoLgnDest | bit field | Indicates permission to specify a remote output destination at TSO logon that overrides the value specified in the DFT-DEST field. |
| TSO_CONSOLE | CONSOLE | bit field | Permits you to access the TSO/E CONSOLE facility. | |
| ACCESS_DATE | ACC-DATE | accessDate | READONLY | ACCESS DATE |
| ACCESS_SRC | ACC-SRCE | accessSrc | READONLY | ACCESS SOURCE |
| ACCESS_TIME | ACC-TIME | accessTime | READONLY | ACCESS TIME |
| KERB_VIO | KERB-VIO | kerbVio | READONLY | PASSWORD KERB-VIO |
| KERB_CURV | KERBCURV | kerbCurv | READONLY | PASSWORD KERB-CURV |
| PASSWORD_DATE | PSWD-DAT | pswdDate | READONLY | PASSWORD DATE |
| PASSWORD_INV | PSWD-INV | pswdInv | READONLY | PASSWORD INTERVAL |
| PASSWORD_TOD | PSWD-TOD | pswdTod | READONLY | PASSWORD TIME OF DAY |
| PASSWORD_VIO | PSWD-VIO | pswdVio | READONLY | PASSWORD VIO |
| STAT_SECVIO | SEC-VIO | secVio | READONLY | STATISTICS |
| STAT_UPDTOD | UPD-TOD | updTod | READONLY | STATISTICS |
| CICS_ACF2CICS | ACF2CICS | cicsacf2cics | bit field | CICSACF2CICS |
| CICS_CL | CICSCL | cicscl | 3 hexadecimal bytes | cicscl |
| CICS_ID | CICSID | cicsid | 3 characters | CICS ID |
| CICS_IDLE | CICSIDLE | cicsidle | 1-byte binary | cicsidle |
| CICS_OPT | CICSOPT | cicsopt | eight-characters | cicsopt |
| CICS_PRI | CICSPRI | cicspri | 1-byte binary | cicspri |
| CICS_RSL | CICSRSL | 3 hexadecimal bytes | Indicates CICS resource access key. For CICS support only. | |
| MIN_DAYS | MINDAYS | minDays | 1-byte binary | PASSWORD MIN DAYS |
| MAX_DAYS | MAXDAYS | maxDays | 1-byte binary | PASSWORD MAX DAYS |
Resource Rule Attributes for Target Resource Provisioning
Table 1-4 lists resource rule attribute mappings between CA ACF2 and Oracle Identity Manager. The AssignUserToResourceRule and RemoveUserFromResourceRule adapters are used for resource rule provisioning operations.
Table 1-4 Resource Rule Attribute Mappings
| Child Form Field | CA ACF2 Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
RULE KEY |
KEY |
The high-level index of the data set name for which this rule is being written |
|
TYPE |
TYPE |
The type of resource rule |
|
ACCESS |
ACCESS |
System mode CA ACF2 should take when it validates access for this rule |
Access Rule Attributes for Target Resource Provisioning
Table 1-5 Access Rule Attribute Mappings
| Child Form Field | CA ACF2 Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
DATASET ID |
dsnmask |
The name of the data set or a mask |
|
RULE KEY |
$KEY |
The high-level index of the data set name for which this rule is being written, or the VSM key of the rule set. |
|
ACCESS READ |
Read |
Specifies read access and the action CA ACF2 should take when the environment matches |
|
ACCESS WRITE |
Write |
Specifies write access and the action CA ACF2 should take when the environment matches |
|
ACCESS EXECUTE |
Execute |
Specifies execute access and the action CA ACF2 should take when the environment matches |
|
ACCESS ALLOCATE |
Allocate |
Specifies allocate access and the action CA ACF2 should take when the environment matches |
Privilege Attribute for Target Resource Reconciliation and Provisioning
Table 1-6 Privilege Attribute Mapping
| Child Form Field | CA ACF2 Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PRIVILEGE_NAME | privileges | Logong ID privileges |
Reconciliation Rule
Reconciliation rules are used by the reconciliation engine to determine the identity to which Oracle Identity Manager must assign a newly discovered account on the target system.
See Also::
Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Oracle Identity Manager for generic information about reconciliation matching and action rulesDuring target resource reconciliation, Oracle Identity Manager tries to match each user profile fetched from CA ACF2 with existing CA ACF2 resources provisioned to OIM Users. This is known as process matching. A reconciliation rule is applied for process matching. If a process match is found, then changes made to the user profile on the target system are copied to the resource on Oracle Identity Manager. If no match is found, then Oracle Identity Manager tries to match the user profile against existing OIM Users. This is known as entity matching. The same reconciliation rule is applied during this process. If an entity match is found, then a CA ACF2 resource is provisioned to the OIM User. Data for the newly provisioned resource is copied from the user.
The following is the reconciliation rule for target resource reconciliation:
Rule name: IdfReconUserRule
Rule element: User Login Equals uid
-
User Login is the User ID field on the process form and the OIM User form.
-
uid is the USER attribute on CA ACF2.
-
On the Design Console, expand Development Tools and then double-click Reconciliation Rules.
-
Search for and open the IdfReconUserRule rule.
Reconciliation Action Rules
Reconciliation action rules specify actions that must be taken depending on whether or not matching CA ACF2 resources or OIM Users are found on Oracle Identity Manager when the reconciliation rule is applied.
Table 1-7 lists the reconciliation action rules.
Table 1-7 Reconciliation Action Rules
| Rule Condition | Action |
|---|---|
|
No Matches Found |
Assign to Administrator With Least Load |
|
One Entity Match Found |
Establish Link |
|
One Process Match Found |
Establish Link |
Note:
No action is performed for rule conditions that are not predefined for this connector. You can define your own action rule for such rule conditions. See Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Oracle Identity Manager for information about modifying or creating reconciliation action rules.-
On the Design Console, expand Resource Management and then double-click Resource Objects.
-
Search for and open the OIMAcf2ResourceObject resource object.
-
Click the Object Reconciliation tab, and then click the Reconciliation Action Rules tab. The Reconciliation Action Rules tab displays the action rules defined for this connector.
Lookup Definitions Used for Provisioning and Reconciliation
These are the lookup definitions that are created when you install the connector or import the connector xml into Oracle Identity Manager.
Table 1-8 Lookup Definition and Descriptions
| Lookup Definitions | Description |
|---|---|
| AtMap.ACF2 | Used during attribute mapping for provisioning. Code Key is the ACF2 Process form attribute name. Decode Key is the corresponding LDAP Attribute. |
| ACF2.AccessLevels | Used while granting a user a resource rule for pre-population of values allowed for attributes. |
| ACF2.AccessMods | Used while granting user an access rule for pre-population of values allowed for attributes. |
| Lookup.AccessRuleNames | Contains the list of access rule keys reconciled using ACF2 Find All Access Rules Task. Used while granting user an access rule for pre-population of Access Rule Key. |
| Lookup.ResourceNames | Contains the list of resource rule keys reconciled using ACF2 Find All Resource Rules Task. Used while granting a user a resource rule for pre-population of Resource Rule Key. |