|
Siebel Customer-Centric Enterprise Warehouse Installation and Configuration Guide > Storing, Extracting, and Loading Additional Data > About Integrating Data from Source Systems Without Prepackaged Business Adapters >
Load Process for Universal Source Data
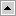
All universal source data goes through a similar load mapping that is made up of a staging table, Source Adapter mapplet, ADI mapplet, and data warehouse table. The basic load mapping for universal source flat files is shown in Figure 46.
Figure 46. Basic Load Mapping for Universal Source Data
|
Each of the load mapping components perform as follows: - Staging Table. The staging table serves as the source table for the load mapping. Each staging table mirrors its corresponding load control table structure. However, it does not have control columns, such as CURR_KEY, IA_INSERT_DT, IA_UPDATE_DT, and other CURR_* columns. If a load control table is not available, the staging table mirrors the IA table, except that instead of *_KEY and *_DT columns, it uses *_ID and *_DT columns.
- OD Table. The load control table determines if the source records loaded in the staging table are new, updated, or unchanged. New records are inserted into the data warehouse table. Updates to existing records overwrite the existing records if Type I Slowly Changing Dimensions are enabled. Updates to existing records are inserted if Type II Slowly Changing Dimensions are enabled. Unchanged records are rejected from the data warehouse because they already exist.
- Source Qualifier. The Source Qualifier joins the staging table and load control table and provides the Source ID and Key ID.
- Source Adapter. The Source Adapter mapplet adds the Type II Flag to the sourced data. If you want to incorporate additional data transformation logic, add it within this object.
- ADI. The ADI mapplet creates values for the INSERT_DT and UPDATE_DT columns. In addition, the ADI also performs the update strategy that either inserts new records, updates existing records, or rejects records from the load.
- Data Warehouse Table. The resulting data warehouse table (IA) stores the data for end user querying purposes. Although not illustrated in Figure 46, each time the IA table is loaded, the ADI also reloads the OD table after truncating it. Only the most recent snapshot of all column values are stored in OD tables; they do not store historical information.
|