Tutorials
|
|
Introduction to the BEA AquaLogic Service Bus Tutorials
What is BEA AquaLogic Service Bus?
BEA AquaLogic Service BusTM is a configuration-based, policy-driven Enterprise Service Bus (ESB). It is targeted for service-oriented integration, managing Web Services, and providing traditional message brokering across heterogeneous IT environments. AquaLogic Service Bus manages the routing and transformation of messages in an enterprise system to promote seamless application integration. The AquaLogic Service Bus Console enables you to configure a proxy service specific to your needs and to manage your Web services by controlling the service and policy configurations and by monitoring system and operations tasks. AquaLogic Service Bus relies on WebLogic Server® run-time facilities. To learn more, see BEA AquaLogic Service Bus Concepts and Architecture.
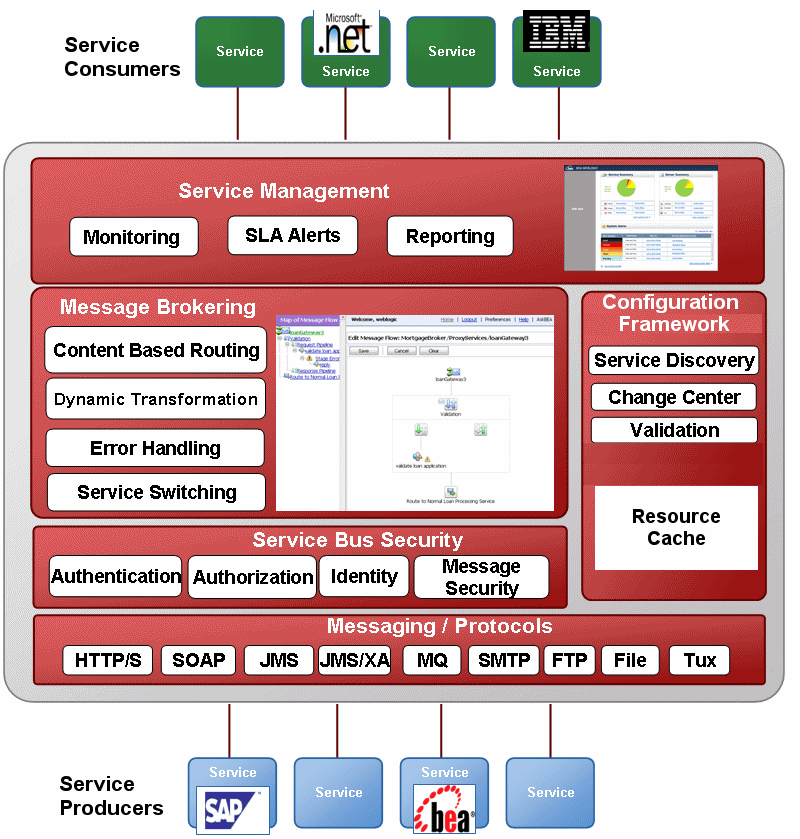
The following figure illustrates the intermediary function of AquaLogic Service Bus, and shows the servers on which it relies.
Figure 1-1 AquaLogic Service Bus Architecture
AquaLogic Service Bus Basic Concepts
AquaLogic Service Bus allows you to manage your Web services and deliver true message brokering through the configuration of proxy services in the AquaLogic Service Bus Console. It is used to resolve differences in requirements between business services and service clients. The basic concepts underlying AquaLogic Service Bus are described in this section. For more information about AquaLogic Service Bus, see BEA AquaLogic Service Bus Concepts and Architecture.
In this tutorial, you will see the benefits of using AquaLogic Service Bus acting as an intermediary between clients and business services. This tutorial focuses on the configuration of the proxy service. AquaLogic Service Bus is also used to manage your Web services. The configuration functions are separated from the management functions in the AquaLogic Service Bus Console. This separation allows implementations to evolve independently and dynamically, as driven by the needs of the business without requiring costly infrastructure development efforts.
AquaLogic Service Bus provides intelligent message brokering between business services (such as enterprise services and databases) and service clients (such as presentation applications or other business services) through proxy services that you configure using the AquaLogic Service Bus Console. Proxy services are AquaLogic Service Bus definitions of intermediary Web services that AquaLogic Service Bus implements locally on WebLogic Server. With AquaLogic Service Bus message brokering, service clients exchange messages with an intermediary proxy service rather than working directly with a business service.
A proxy service can route messages to multiple business services; you can choose to configure a proxy service with an interface that is independent of the business services with which the proxy service communicates. In such cases, you would configure a message flow definition to route a message to the appropriate business service and map the message data into the format required by the business service's interface.
Business services are remote services or external endpoints that are typically not implemented by the AquaLogic Service Bus server. They are definitions of the enterprise services with which you want to exchange messages. For more information on business services, see Business Services in Using the AquaLogic Service Bus Console.
In AquaLogic Service Bus, a Message Flow is the implementation of a proxy service. You configure the logic for the manipulation of messages in proxy service message flow definitions. This logic includes such activities as transformation, publishing, and reporting, which are implemented as individual actions within the stages of a pipeline. Pipelines are one-way processing paths that include no branching.
Each pipeline is a sequence of stages containing actions. A stage is a user-configured processing step. Messages fed into the pipelines are accompanied by a set of message context variables that contain the message contents and can be accessed or modified by actions in the pipeline stages.
Pipeline pairs are request and response pipelines.The request pipeline definition specifies the actions that AquaLogic Service Bus performs on request messages to the proxy service before invoking a business service or another proxy service. The response pipeline definition specifies the processing that AquaLogic Service Bus performs on responses from the service invoked by the proxy service before the proxy service returns a response to a client.
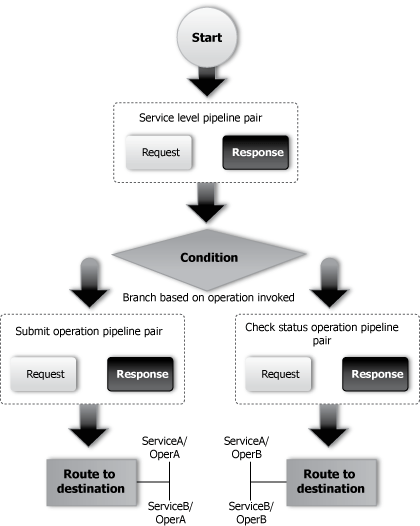
Each pipeline consists of a sequence of stages containing actions. However, a single service level request pipeline might optionally branch out into operational pipelines (at most one per operation and optionally a default operational pipeline). The determination of the operation is done through user-selected criteria. The response processing starts with the relevant operation pipeline which then joins into a single service-level response pipeline.
The following figure shows an example of operation pipelines in a proxy service:
Figure 1-2 Example of Operation Pipelines in a Proxy Service
For more information, see "Pipeline Pairs" in BEA AquaLogic Service Bus Concepts and Architecture. For information about how to use the WebLogic Service Bus Console to configure proxy services and other resources, see Using the AquaLogic Service Bus Console.
Overview of the Tutorials
These tutorials show how AquaLogic Service Bus is used to route a loan application to appropriate business services based on the configurations set in the proxy service. The AquaLogic Service Bus Console is comprised of JSP-based portlets that support the configuration and design of the proxy service message flows and the associated resources.
Focus of the Tutorials
These tutorial highlights specific features available in AquaLogic Service Bus. In the tutorials, you will use the console to create the proxy service that will interact with the service client and business services. Working through the tutorial you will:
- Learn how to configure the proxy services to process the input and output messages in a message flow.
- Create, read, and update configuration objects (such as proxy services, WSDLs, and so on).
- See how AquaLogic Service Bus handles session management to allow configuration changes to happen locally, and then when complete, to instantiate the changes in the core environment.
- Configure resources such as WSDLs, Service Callouts, XQueries, and business services.
- Route messages according to XQuery-based policies or callouts to external Web services.
- See how BEA AquaLogic Service Bus manages synchronous and asynchronous messages.
- Define a transformation on an XML message, based on XQuery, supporting a callout to a Web service to gather additional data for the transformation.
- See how message processing by AquaLogic Service Bus is driven by metadata specified as the message flow definition for a proxy service in the AquaLogic Service Bus Console.
How to Use the Tutorials
The tutorials represent typical use case scenarios for BEA AquaLogic Service Bus. You will learn how to configure and use BEA AquaLogic Service Bus to resolve the business scenarios presented in the specified use cases. Using the tutorials will:
- Provide you with a good understanding of the basic concepts underlying BEA AquaLogic Service Bus.
- Show you how to navigate the AquaLogic Service Bus Console and demonstrate the capabilities of the Console.
- Provide the basic steps that will help you to learn to configure more complicated scenarios.
Complete the first tutorial, Routing a loan application, to become familiar with BEA AquaLogic Service Bus, then proceed to the other tutorials provided as part of the tutorial suite:
- Tutorial 1. Routing a Loan Application is based on scenarios that demonstrate how AquaLogic Service Bus facilitates the routing of messages within an enterprise.
- Tutorial 2. Transforming a Loan Application describes how to configure your existing AquaLogic Service Bus configuration to address the new requirement of adding a transformation stage.
- Tutorial 3. Validating a Loan Application describes how a BEA AquaLogic Service Bus proxy service can be configured to validate a message passing from a client to a business service.
Document Conventions
The following conventions are used throughout this document:
- The instructions in the tutorial documentation are for Windows command shells. If you are using a UNIX-based shell, substitute / for \ in path names.
BEA_HOMErepresents the directory in which you installed your BEA product; for example, c:\bea.