This chapter describes how to integrate with SAP Remote Function Calls (RFCs) in the BEA eLink Adapter for R/3 environment. It includes the following sections:
For information about setting up RFC processing, see Configuring
for RFC Integration in the BEA eLink Adapter for R/3 Installation and
Configuration Guide.
About RFC Integration
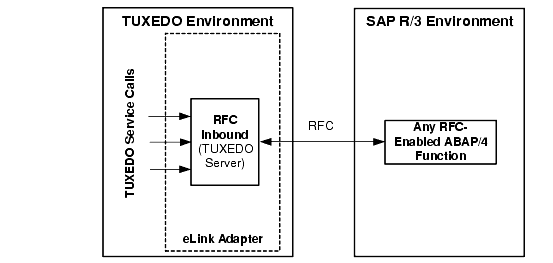
Figure 2-1 provides an overview of the information flow for RFC Inbound:
Figure 2-1 Overview of Information Flow for RFC Processing

RFC Inbound is a TUXEDO server that allows TUXEDO applications to invoke any ABAP/4 functions that have been RFC-enabled in R/3. See Invoking ABAP/4 Functions for more information.
Invoking ABAP/4 Functions
This section describes how to invoke RFC-enabled ABAP/4 functions in the TUXEDO environment using RFC Inbound, a TUXEDO server, via synchronous RFC. It includes the following topics:
For information about setting up RFC processing, see the following chapters in the BEA eLink Adapter for R/3 Installation and Configuration Guide:
RFC Inbound is a component of the BEA eLink Adapter for R/3 product that allows TUXEDO applications and other non-R/3 applications to invoke any ABAP/4 functions that have been RFC-enabled. RFC Inbound is a TUXEDO server that has a generic service, CR3_RFC_IN, which invokes any ABAP/4 function. The CR3_RFC_IN service is aliased to unique services corresponding to ABAP/4 functions. RFC Inbound advertises the ABAP/4 functions that it can invoke as TUXEDO services and aliases them to the CR3_RFC_IN service. Developers can configure which ABAP/4 functions can be invoked and the service names by which they are advertised.
Information Flow
RFC Inbound allows a TUXEDO application to act as a client to R/3. Figure 2-2 shows the information flow for invoking RFC-enabled ABAP/4 functions:
Figure 2-2 Information Flow for Invoking ABAP/4 Functions
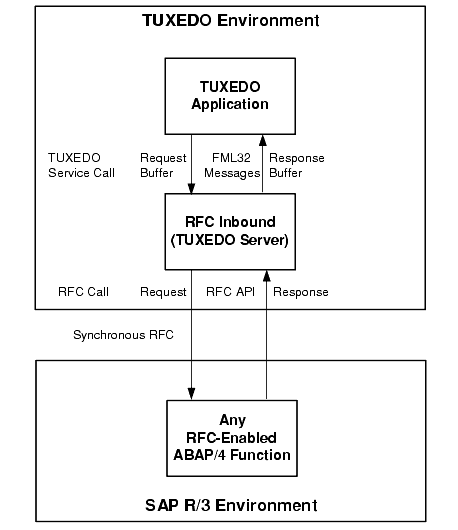
The information flow for invoking ABAP/4 functions is as follows:
It is the developer's responsibility to ensure that the names of import parameters and import tables are spelled exactly as they appear in the ABAP/4 function signature.
R/3-level errors. RFC Inbound populates the ELINK_APP_ERR field with the message text returned from R/3. RFC Inbound returns the FML32 response buffer to the calling application, as well as TPFAILwith the tpurcode set to 0.
Adapter-level errors. RFC Inbound populates the ELINK_ADAPTER_ERR_CODE and ELINK_ADAPTER_ERR fields with the appropriate adapter-level error code and BEA eLink Adapter for R/3-specific error code and message. RFC Inbound returns the FML32 response buffer to the calling application, as well as TPFAIL with the tpurcode set to -1. Alternatively, for uncorrectable errors such as a memory corruption problem, RFC Inbound returns TPEXIT (which causes the service to shut down) with the tpurcode set to -1.
ABAP/4 functions use the following types of parameters:
The exact parameters vary with each ABAP/4 function and are defined in the function's ABAP/4 function signature. Listing 2-1 defines a generic ABAP/4 function:
Listing 2-1
ABAP/4 Function Signature
FUNCTION FUNCTION_NAME
IMPORT
IMPORT_PARAM_1
IMPORT_PARAM_2
EXPORT
EXPORT_PARAM_1
EXPORT_PARAM_2
TABLE
TABLE_IN
TABLE_OUT
TABLE_IN_OUT
EXCEPTION
EXCEPTION_1
EXCEPTION_2
This function signature includes two import parameters and one import table that it reads as input, two export parameters and one export table that it writes as output, one table (TABLE_IN_OUT) that it reads on input and writes as output, and two exceptions that it can raise if an R/3 error occurs.
FML32 Field Definitions for RFC Inbound
In TUXEDO messages, import parameters, export parameters, table, and exceptions are represented as named fields in FML32 buffers. A calling application uses two kinds of buffers:
The calling application constructs a request buffer containing import parameters and import tables. RFC Inbound allocates a response buffer and populates it with data returned from the ABAP/4 function according to the settings of the CR3_EXPORT_PARAMS and CR3_EXPORT_TABLES environment variables in the configuration file.
Request Buffers
Before invoking a service associated with an RFC call, a calling application prepares an FML32 request buffer that contains the following information:
The calling application passes this request buffer when it invokes the service associated with the RFC.
For example, for the function signature shown in Listing
2-1, "ABAP/4 Function Signature " a calling application might construct
the following FML32 request buffer:
| FML32 Field Name | Field Value | Data Type |
|---|---|---|
|
IMPORT_PARAM_1 |
ParameterValue |
String |
|
IMPORT_PARAM_2 |
ParameterValue |
String |
|
TABLE_IN |
TableRowValue |
String |
|
TABLE_IN |
TableRowValue |
String |
|
TABLE_IN |
TableRowValue |
String |
|
.. |
.. |
String |
|
TABLE_IN_OUT |
TableRowValue |
String |
|
TABLE_IN_OUT |
TableRowValue |
String |
|
TABLE_IN_OUT |
TableRowValue |
String |
|
.. |
.. |
String |
In this example, the TABLE_IN_OUT table is both an import and export table. Therefore, the request buffer contains table rows to be passed into the ABAP/4 function. In addition, TABLE_IN_OUT is specified in the CR3_EXPORT_TABLES environment variable in the configuration file so that data from this table is returned in the response buffer.
Note:
It is the responsibility of the calling application to ensure that the names of import parameters and import tables are spelled exactly as they appear in the ABAP/4 function signature.
Response Buffers
The RFC Inbound allocates an FML32 response buffer. After executing the ABAP/4 function, RFC Inbound populates the response buffer with the results, which include:
For example, for the function signature specified in Listing
2-1, "ABAP/4 Function Signature " RFC Inbound might return the following
FML32 response buffer:
| FML32 Field Name | Field Value | Data Type |
|---|---|---|
|
EXPORT_PARAM_1 |
ParameterValue |
String |
|
EXPORT_PARAM_2 |
ParameterValue |
String |
|
TABLE_OUT |
TableRowValue |
String |
|
TABLE_OUT |
TableRowValue |
String |
|
TABLE_OUT |
TableRowValue |
String |
|
.. |
.. |
String |
|
TABLE_IN_OUT |
TableRowValue |
String |
|
TABLE_IN_OUT |
TableRowValue |
String |
|
TABLE_IN_OUT |
TableRowValue |
String |
|
.. |
.. |
String |
Note:
Error fields (ELINK_APP_ERR, ELINK_ADAPTER_ERR_CODE, and ELINK_ADAPTER_ERR) appear in the response buffer only if an R/3 error or adapter error occurs.
Configuring Export Parameters and Export Tables
Two environment variables control which export parameters and export tables are included in the response buffer:
After the ABAP/4 function is executed, RFC Inbound populates the response buffer
with these values. If an export parameter or export table is not specified in
this list, RFC Inbound discards it even if it is returned from the ABAP/4 function.
See Configuring RFC Integration in the BEA
eLink Adapter for R/3 Installation and Configuration Guide.
Handling Problems with RFCs
Two kinds of problems can arise when executing RFCs:
It is the responsibility of the calling application to retrieve and process exception and error information accordingly.
Handling R/3 Errors
If an exception is raised when executing the ABAP/4 function on R/3, RFC Inbound:
After making the service call, the calling application should check the return value and tpurcode. If TPFAIL is returned with tpurcode set to zero (0), it should parse the text in the ELINK_APP_ERR field in the response buffer and respond appropriately.
Handling Adapter Errors
If an adapter error occurs when executing an ABAP/4 function, RFC Inbound:
After making the service call, the calling application should check the return value and tpurcode. If TPFAIL or TPEXIT is returned and tpurcode is –1, it should parse the text in the ELINK_APP_ERR field in the response buffer and respond appropriately.
Checking the Error Log
If RFC Inbound encounters an adapter level error, it logs the following information to the TUXEDO userlog:
Refer to your TUXEDO documentation for more information about the TUXEDO userlog.