


|

|
|
|
|
Administering the SNA Components
The topics in this section cover activities an administrator performs with the System Network Architecture Communications Resource Manager (SNACRM) to maintain BEA WebLogic Java Adapter for Mainframe (JAM) applications.
The interface to the stack administration and configuration is dependent on the stack provider and thus cannot be covered in this guide. Refer to vendor publications for the stack(s) used in your environment.
This section discusses the following topics:
Starting The SNACRM on Unix or Windows NT
The SNACRM is a server that communicates directly with the PU 2.1 server to provide SNA connectivity. These servers can be started manually. The PU 2.1 server must always be started before the SNACRM. Both servers must be started before starting the associated SNA domain gateway. Before you start the SNACRM or the PU 2.1 server, you must set several environment variables.
Setting Enviroment Variables
The following environment variables must be set in the environment where the SNACRM is started.
FLDTBLDIR32=JAM Installation Directory/lib
FIELDTBLS32=JAM Installation Directory/fmb.def
APPDIR=<wherever>
These environment variables can be added as `set' or `export' commands in a script file used to start a SNACRM. Or they can be added to the startweblogic script for use when a SNACRM is spawned on startup.
Starting the PU2.1 Server
Refer to the operational documentation provided by your SNA stack vendor for information about starting the PU2.1 server. The SNA stack must be running and active before you start the SNACRM.
Starting the SNACRM
To start the SNACRM on Unix:
When you start the SNACRM from the Unix command line, the SNACRM Command Line Console puts its prompt in a window, and if exited, shuts down all of the active links.
To start the SNACRM from a Command Prompt Window on Windows NT:
On Windows NT, the SNACRM can be started in its own window, however, no prompt is displayed and no console commands are available. Refer to Command Reference Pages, for more detailed information about the SNACRM command.
Starting the SNACRM on OS/390 MVS
The OS/390 MVS platform sets the environment and invokes the SNACRM through Job Control Language (JCL).
Refer to Sample JCL for the SNACRM Command and Command Reference Pages, for more information about sample SNACRM JCL and the SNACRM command.
Note: If the SNACRM is installed on an MVS platform, it does not have to be restarted if the JAM gateway goes down. Only the MVS version of the SNACRM has this persistent feature.
Using The SNACRM Monitor
You can use the SNACRM monitor to set trace levels for a selected SNACRM and the associated APPC stacks. You also can observe link activity and display trace status, link status, and link statistics.
Notes: The SNACRM monitor does not show trace data. This data is captured in a file under the APPDIR directory (where APPDIR is the variable name associated with the application directory). Please contact BEA Customer Support for help in locating the trace file(s) and interpreting them.
The JAM software includes a jsnacrm utility that launches and executes the SNACRM monitor. The jsnacrm utility is designed for Java platforms and supplies both a Java-based application and an applet.
Note: The jsnacrm utility cannot be run from an OS/390 mainframe platform. It must be run on a Unix or Windows NT platform to connect to an OS/390 SNACRM.
The following discussion relates to the Java-based SNACRM monitor only.
The BEA eLink Java Adapter for Mainframe software CDROM contains the following files associated with the jsnacrm utility:
Prerequisite for Running the JSNACRM Utility on an NT Platform
The jsnacrm utility is written in Java as both an application and an applet. The application launches and executes like any other Java application and can be set up so it is accessible from the Windows desktop. The applet launches and executes from a network browser.
Running the Java Applet Version
The following sections describe how to set up and run the Java applet version of the jsnacrm utility.
Prerequisites for Running the Java Applet Version
You must have either Netscape Communicator 4.x or Internet Explorer 4.x or 5.x installed on your NT Windows system. You also must have the Java plug-in installed on your system. You can download this plug-in from the following internet location:
http://java.sun.com/products/plugin
Note: If the Java plug-in is not already installed on your system, when you attempt to open the jsnacrm.html file, the program prompts you for an automatic download of the plug-in by the browser.
Next, you must set up your system to accept code signed by the identity moncrm. To do this, perform the following steps:
javakey -c moncrm true
javakey -ic moncrm %TUXDIR%\bin\moncrm.x509
Starting the Java Applet
To start the Java applet in an existing browser, open the file:
<tuxedo-path>\bin\jsnacrm.html
To build a shortcut to start the Java applet using a separate instance of your network browser, enter the following command:
<browser-pathname> %TUXDIR%\bin\jsnacrm.html
Running the Java Applet Version
Set up your applet version to monitor either a local or remote SNACRM. To do this, you make selections on the Java Plug-in Properties control panel. This control panel is automatically downloaded with the plug-in and is initiated from the Windows Start Programs pop-up menu. Refer to online documentation about the control panel at the following Internet location:
http://java.sun.com/products/plugin/1.1.1/docs
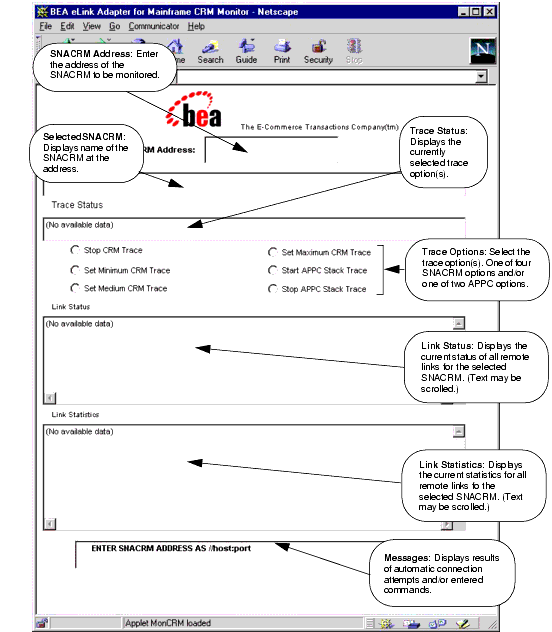
When the Monitor screen displays (Figure 3-1), enter the address of the SNACRM that you want to monitor in the field at the top of the screen.
To monitor a local SNACRM, select Applet Host from the Network Access drop-down menu. Type the following in the Enter SNACRM Address panel:
//localhost:port
where:
To monitor a remote SNACRM, select Unrestricted from the Network Access drop down menu. Type the following in the Enter SNACRM Address panel:
//remotehostname:address
where:
The GUI contains two screen areas that require user entry and four screen areas that display information about the SNACRM being monitored. Status messages are displayed at the bottom of the screen. The GUI screen functions are listed in Table 3-1 and shown in Figure 3-1.
|
Display Section |
Function |
|---|---|
|
SNACRM Address |
This is where you enter the address of the SNACRM to be monitored. |
|
Selected SNACRM |
Displays the name of the SNACRM at the address entered in the address field. |
|
Trace Status |
Displays the currently selected trace options. |
|
Trace Options |
|
|
Link Status |
Displays the current status of all remote links for the selected SNACRM. (Text may be scrolled.) |
|
Link Statistics |
Displays the current statistics for all remote links for the selected SNACRM. (Text may be scrolled.) |
|
Message Line |
Displays messages showing either the results of automatic connection attempts or commands issued to change the trace options. |
Figure 3-1 The SNACRM Monitor Running as an Applet on a Network Browser
Running the Java Application Version
The Java application version displays and operates identically to the applet version. Refer to screen definitions and functions discussed under "Running the Java Applet Version."
To build a shortcut for starting the Java application version, perform the following steps:
jrew -classpath %ClassPath%;jsnacrm.jar jsnacrm
To run from a command window, perform the following steps:
jrew -classpath %ClassPath%;jsnacrm.jar jsnacrm
Activating and De-Activating Links
The JAM gateway software provides a command line tool you can use to activate and de-activate links that have been defined in the JM_SNALINKS section of the jcrmgw.cfg file. This tool consists of two commands and their associated parameters: crmlkon and crmlkoff.
Note: If a link to a remote host is de-activated and re-activated by the host, the JAM software normally re-establishes the link automatically. If this does not occur, you can use the crmlkon command to re-establish the link.
Using the crmlkon Command
You can start one or more SNA links with this command. Use the following syntax:
crmlkon -n<hostname:port> [-v -i -h] <linkname> ...
where:
Notes: There is no notification that the link(s) started with the crmlkon command are activated. Use the SNACRM monitor to verify a link is active. Refer to Using The SNACRM Monitor for more information.
Refer to crmlkon in Appendix A, "Command Reference Pages" for more information on the crmlkon utility.
Using the crmlkoff Command
You can stop one or more SNA links with this command. Use the following syntax:
crmlkoff -n<hostname:port> [-v -i -h] <linkname> ...
where:
Notes: There is no notification that the link(s) stopped with the crmlkoff command are de-activated. Use the SNACRM monitor to verify a link is not active. Refer to Using The SNACRM Monitor for more information.
Refer to crmlkoff in Appendix A, "Command Reference Pages" for more information on the crmlkoff utility.
Stopping the SNACRM on Unix or Windows NT
To stop the SNACRM on Unix:
When you stop the SNACRM from the Unix command line, the SNACRM Command Line Console shuts down all of the active links.
To stop the SNACRM from a Command Prompt Window on Windows NT:
Stopping the SNACRM on OS/390 MVS
The OS/390 MVS platform stops the SNACRM through Job Control Language (JCL). When you are running the SNACRM on an OS/390 operating system, the persistent SNACRM feature allows the SNACRM to continue running , even if the JAM Gateway fails. You must explicitly shutdown the SNACRM if you need to shut it down.
Refer to Sample JCL for the CRMDOWN Command and Command Reference Pages, for more information about sample crmdown JCL and the crmdown command.
Note: If the SNACRM is installed on an MVS platform, it does not have to be stopped and restarted if the JAM gateway goes down. Only the MVS version of the SNACRM has this persistent feature.
Refer to crmdown in Appendix A, "Command Reference Pages" for more information on the crmdown utility.

|
|

|
|
|
|
Copyright © 2000 BEA Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
|