


|

|
|
|
|
Understanding the BEA WebLogic Java Adapter for Mainframe Solution
Businesses around the world are using BEA WebLogic Server as the deployment platform for Java-based e-commerce applications. These applications support a wide range of business transactions, from simply displaying the content of a web page to processing secure, online financial transactions. As the complexity of web-based applications evolve, the business transactions supported by these applications may require direct integration with IBM mainframe applications in order to complete. Storing up transactions for the mainframe and executing them periodically in batch mode is not sufficient. To meet the rigorous demands for fast and flawless execution of customer service requests, the business transactions must integrate with mainframe applications in real-time. BEA WebLogic Java Adapter for Mainframe (JAM) built on WebLogic Server meets these demands.
This section discusses the following topics:
The BEA WebLogicTM Enterprise Application Integration Solution
Corporations have become increasingly dependent on technology, investing heavily in applications and business models to meet their specific business needs. As more complex and disparate technology is added to the business environment, the need for a method of integrating these applications into a unified set of business processes has become increasingly important. Companies have invested millions of dollars in "best-of-breed" business models that are unable to work together as a unified system: The company's inventory control business application, human resources application and sales automation applications operate in unique ways and cannot communicate with each other without complex and often tenuous connections.
Instead of developing new applications that may or may not function as well as top-of-the-line prepackaged business applications, business managers are demanding that seamless bridges be built between existing business applications to bind them into a single, unified enterprise application. Enterprise application integration (EAI) provides the solution to this problem by allowing the unrestricted sharing of data and business processes among any connection applications and data sources in the enterprise without the necessity of changing the original applications or data structures.
Enterprise Application Integration (EAI): A Step Beyond the Middleware Solution
The need for integration between various enterprise applications has historically been solved with middleware, which provides only point-to-point linkage that requires complex links and significant alterations to source code and target systems. An EAI solution is a platform that allows all transaction information to be immediately available in any form and from any location in the enterprise and makes every application, database, transaction table, method available at any time. It is implemented by providing a set of integration-level application semantics that provide a common way for business processes and data to communicate across applications.
This solution focuses on the integration, reuse, and distribution of both business-level processes and data, and it seeks to mask the underlying configuration and functional complexities from users so that they need only an understanding of the applications they are integrating, not the integration system itself. A new generation of application servers allow developers to build and reuse business processes
The BEA EAI Solution on WebLogic Server
Integration requires an open, business-level view of the data and processes in an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system in which the integration points are based on business objects, such as invoice, employee, customer, sales order, and purchase order. Leveraging various interfaces in an integration solution requires complex middleware technology and target application expertise. Figure 1-1 provides a graphic overview of the components of the BEA EAI Solution on WebLogic Server.
Figure 1-1 The BEA EAI Solution on WebLogic Server
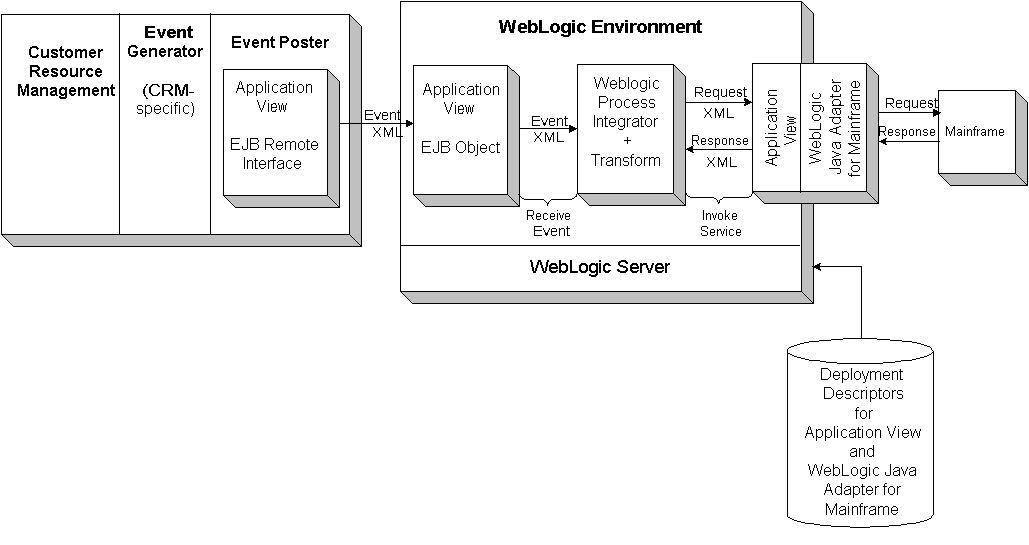
Currently, most advanced middleware vendors provide adapters to one or more of these interfaces. However, these offerings typically solve only a particular type of integration problem and usually introduce more proprietary technology into the integration solution. Consequently, the ideal integration solution is an industry standards-based abstraction layer that hides the complexities of the various interfaces and provides an open, business-level view of your third party applications. The BEA EAI leverages the strength, flexibility, and scalability of BEA WebLogic ServerTM. Figure 1-1 provides a visual over view of the BEA EAI Solution on WebLogic Server.
Understanding the WebLogic Sever Integration Environment
BEA WebLogic SeverTM is an open, extensible, standards-based application server platform that is used for assembling, deploying, and managing distributed applications. The BEA WebLogicTM product group includes application servers and related products that are designed to solve the urgent IT challenges of e-commerce and Web-ready applications. BEA WebLogic products provide the maximum flexibility in component-based application development, deployment, and management, while protecting IT investments through their unmatched adherence to industry standards. WebLogic is a rich, high-performance, fully integrated Java platform for enterprise applications. With WebLogic, you can:
Note: Refer to the BEA WebLogicTM product documentation on the Product Documentation page at http://www.oracle.com/technology/documentation/index.html for the most up-to-date information on WebLogic solutions.
Accelerate Your Development Time
WebLogic isolates your developers and applications from disparities among Java platforms and database interfaces, and from low-level programming complexities like sockets and thread management. These kinds of resources belong in the server infrastructure, not in your application. WebLogic helps you get your application in users' hands quickly in the following ways:
You want to build applications that last. You want to build them fast, and you want to leverage your existing databases, applications, systems, and infrastructure. To accomplish these goals, BEA WebLogic helps you:
Standard Java Servlets can isolate the presentation logic from the EJB business logic for the HTML client so that desktop applications written in Java, Visual Basic, PowerBuilder, and other IDEs can access EJB components directly, providing identical business logic to these clients. Combining EJB with the multiple client models supported by WebLogic gives you complete flexibility in choosing and mixing application models.
WebLogic offers a variety of load-balancing and failover models that can be configured to meet the needs of the application. WebLogic's intelligent "SmartStubs" for RMI and EJB objects can select any one of the servers in a cluster during a name binding. Servlet session management is handled through the standard Java Session Management API rather than a proprietary solution.
Similarly, Enterprise JavaBeans can access existing databases directly or through legacy transaction systems to provide data and processing to new applications in a component-centric paradigm. As you migrate your legacy applications to Java or to new systems, the Enterprise JavaBeans insulate client applications from changes.
The same Enterprise JavaBeans can be used in many variants of the application. And because business process information has been abstracted away from the specifics of a single application interface, those business components can be reused over and over again in new applications, to significantly reduce cost over the life cycle of your enterprise applications.
Scale and Manage as Your Needs Grow
Scale and manage WebLogic as your needs grow with the following features:
An application server is the engine that runs the applications that drive e-commerce. Application servers are software programs deployed on high-performance computers that act as go-betweens and service enablers, connecting browsers on desktops with the back-end systems and databases of e-businesses over the Internet. As companies increasingly leverage intranets and extranets as well as the Internet as new business environments, their networked applications need to be dynamically linked to other applications and data sources, and easily deployed and managed across machines and networks that are themselves in flux.
With the industry's most comprehensive suite of transaction and application servers, BEA provides an end-to-end transaction platform for building a solid, easy-to-manage e-commerce system engineered for rapidly launching high-value services to increase competitive advantage.
BEA's transaction and application server family provides development and deployment solutions for e-commerce that stretch from front-end, simple HTML-based Web sites to mainframe-class systems. The marriage of BEA's application server and transaction processing server is a perfect combination of capabilities for the Internet Economy. BEA WebLogic ServerTM focuses on Web-based Java applications, while BEA eLink Platform and BEA WebLogic EnterpriseTM focus on managing high-volume, heterogeneous transactions. Together, they drive end-to-end e-business with unfailing reliability that both consumers and companies can count on.
The BEA WebLogic family of application servers includes:
Figure 1-2 WebLogic Family of Application Servers
The award-winning BEA WebLogic ServerTM provides the performance, scalability, and high-availability required to power e-commerce and Internet business solutions. The server of choice for many e-businesses, it offers the following features:
For e-commerce solutions that require the greatest choice of development and deployment options and unlimited scalability, BEA WebLogic EnterpriseTM delivers a proven and scalable transaction platform that brings together the top industry standards with the power of component-based programming to create complete production-ready e-commerce solutions.
WebLogic Express
BEA WebLogic ExpressTM provides a solution for developing simple HTML front-end applications to a database for companies who want to develop new business logic in Java but not EJBs or components.
BEA WebLogic Java Adapter for Mainframe Overview
BEA WebLogic Java Adapter for Mainframe (JAM) is a set of software components that provides seamless bidirectional interactions between Java applications running on a WebLogic Server platform and either Customer Information Control System (CICS) applications, or Information Management System (IMS) applications running on a mainframe. With CICS, the Java application request/response operations interact using Distributed Program Links (DPL). With IMS, the Java application request/response operations interact using IMS implicit Application Program-to-Program Communication (APPC) support.
JAM Architecture
BEA WebLogic Java Adapter for Mainframe enables bidirectional connectivity between Java applications running on the WebLogic Application Server and Mainframe COBOL applications running in the CICS or IMS environments.
The JAM product provides the following features:
The eGen COBOL Copybook utility translates COBOL copybooks to JAVA source that can be used as the basis for application development and data transformation.
The Java Communications Resource Manager Gateway (JCRMGW) runs in a WebLogic Server instance and an SNA Communications Resource Manager (SNACRM) can run in the native UNIX/NT environment or distributed to the mainframe as an MVS APPC application. The SNACRM may also be distributed to another UNIX/NT system, separate from the WebLogic Server platform.
Note: WebLogic Server is required and a third-party SNA stack is required if the SNACRM is not installed on a mainframe, but are sold separately.
In a typical scenario, existing mainframe COBOL applications are exposed to new or existing applications in the WebLogic Server environment. The development tools generate JAVA code from COBOL copybook source. The COBOL copybook contains the structure and size of the data that is passed between the WebLogic Server and mainframe applications. The source code generated from the copybook provides classes that can be extended by the application developer to perform discrete business operations. During runtime, the data passed between applications is stored in a data view object. This object provides set and access methods for all fields in the data buffer. The object also provides a method for converting the object to an XML document. The XML document can be used as input to other applications and, specifically, the WebLogic Process Integrator work flow engine. An XML schema can be generated from the original COBOL copybook for manipulation and transformation of XML documents.
The JAM architecture requires APPC-based communications with mainframe CICS and IMS. The product structure is flexible enough to allow TCP access to the mainframe, if certain product components are installed on the mainframe.
The JCRMGW runs in WebLogic Server and is an eGen client gateway that communicates over TCP/IP to the SNACRM. The SNACRM can run on the same or separate platform other than the JCRMGW. When the SNACRM is running in the UNIX/NT environment, a third party SNA stack is required to enable SNA communications with the mainframe. The SNACRM could alternatively be installed on the mainframe running as a UNIX application under OS/390 UNIX, or as a native MVS APPC application. When the SNACRM is running under OS/390 UNIX or MVS, it does not require a third party SNA stack, but directly accesses VTAM for communications with CICS or IMS. Figure 1-3 illustrates the JAM architecture.
Figure 1-3 JAM Architecture
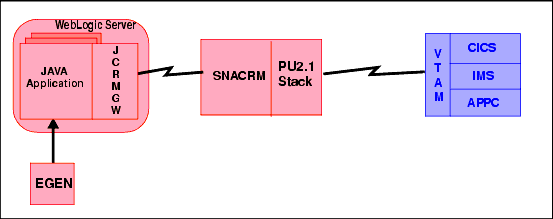
The eGen COBOL code generator is the utility that generates Java source code from a COBOL copybook. A base Java application is provided on the JAM product CD-ROM so you can modify it to create custom Java applications. The generated code is dependent on the generation model chosen:
The generated code provides for data accessors and conversions as well as miscellaneous functions. The generated servlet provides a basic form that matches the copybook. You can use this servlet for testing or proof of concept. For examples of using the eGen COBOL code generator, refer to Developing Java Applications and Programming Scenarios.
Java Communications Resource Manager Gateway
The Java Communications Resource Manager Gateway (JCRMGW) is the Java application that manages sessions providing access into and out of the Java environment. JCRMGW is an EJB component that runs on WebLogic Server Java Virtual Machine (JVM). JCRMGW processes Java-to-mainframe requests and responses in conjunction with the SNACRM. Requests coming from the mainframe are mapped to an EJB that services the request while requests going to the mainframe are mapped to a mainframe program that can be executed using a CICS DPL or started from an IMS queue.
JAM includes a utility that allows system managers to monitor the status of connections to the mainframe and to set traces on connections for diagnostic purposes.
System Network Architecture Communications Resource Manager
The SNACRM runs as a separate native process. It enables APPC conversations and DPL protocols to flow into and out of the Java environment and runs on the same platform as the SNA stack. The SNACRM obtains its configuration from the JCRMGW. If the Java gateway is running on a platform other than the one on which the SNACRM is running, the SNACRM should be started before WebLogic Server is started so it is monitoring the address specified in the JCRMGW configuration.
The SNACRM supports non-transactional IMS programs using the implicit APPC support for IMS. Implicit APPC is similar to the CICS/ESA DPL. Any IMS program that sends and receives messages to and from the IMS message queue can be used without change as either a client or a server.
In order for the SNACRM to properly operate within the JAM environment, the CICS remote domain must be prepared to conduct operations with the local domain. This includes:
For more detailed information, refer to the BEA SNACRM Administration Guide accessible from the JAM online documentation in both HTML and PDF formats.
Supported Third-Party SNA Stack
A properly configured SNA protocol stack is required for the SNACRM to communicate with a mainframe if your SNACRM is not installed on the mainframe. (Refer to the BEA WebLogic Java Adapter for Mainframe Release Notes for a complete list of supported stacks.) The JCRMGW requires the following parameters from the SNA stack configuration:
The local name of the SNACRM that is used by the mainframe CICS region.
An alias representing the mainframe partner application to be used by the SNACRM.
SNA mode definitions provide session characteristics for given local/remote LU pair.
Sessions are required for connections to be made between two LU. MAX sessions should be high enough to handled the expected gateway traffic.
This parameter is optional and determines priority of session activation.
|
|
|
Copyright © 2000 BEA Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
|