- 8.1. User Object Association
- 8.2. Configuration Properties
- 8.3. Transaction Association
- 8.4. FetchPlan Association
- 8.5. Persistence-Capable Lifecycle Management
- 8.6. Lifecycle Examples
- 8.7. Detach and Attach Functionality
- 8.8. JDO Identity Management
- 8.9. Cache Management
- 8.10. Extent Factory
- 8.11. Query Factory
- 8.12. Sequence Factory
- 8.13. Connection Access
- 8.14. Closing
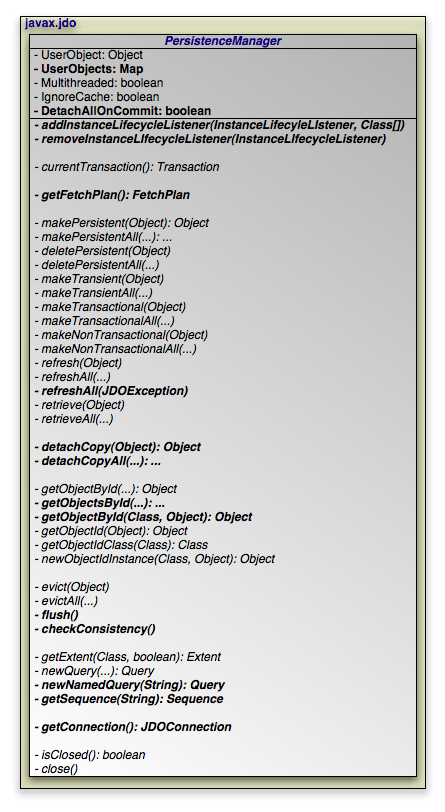
The diagram above presents an overview of the
PersistenceManager interface. For a complete
treatment of the PersistenceManager API, see the
Javadoc documentation. Methods whose parameter signatures consist
of an ellipsis (...) are overloaded to take multiple parameter types.
![[Note]](img/note.gif) | Note |
|---|---|
Kodo extends the standard |
The PersistenceManager is the primary interface
to the JDO runtime.
Each PersistenceManager manages a cache of
persistent and transactional objects, and has an association with
a single Transaction.
We divide the methods of the PersistenceManager
into the following functional categories:
User object association.
Configuration properties.
Transactionassociation.FetchPlanassociation.Persistence-capable lifecycle management.
Detach and attach functionality.
JDO identity management.
Cache management.
Extent,Query, andSequencefactory.Connection access.
Closing.
public Object getUserObject (); public void setUserObject (Object obj); public Object putUserObject (Object key, Object obj); public Object getUserObject (Object key); public Object removeUserObject (Object key);
The PersistenceManager's user objects
allow you to associate arbitrary objects with each
PersistenceManager. The given objects are not
used in any way by the JDO implementation.
The getUserObject and setUserObject
methods associate a primary user object with the
PersistenceManager. The
putUserObject, getUserObject, and
removeUserObject methods, on the other hand,
delegate to an internal map of secondary user objects. As in the
java.util.Map APIs, the put
and remove operations return
the object formerly stored under the given key.