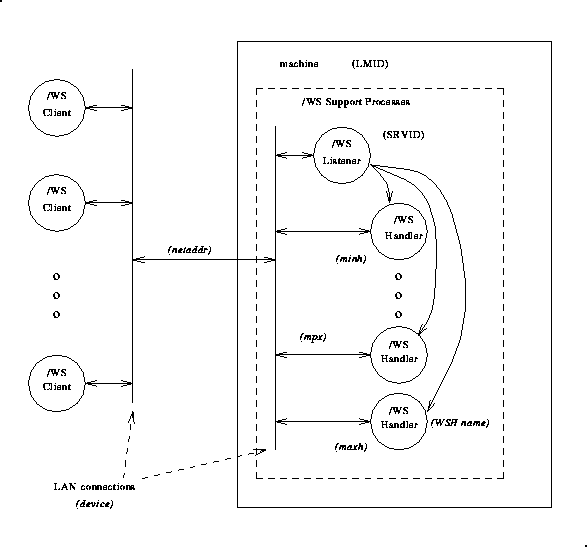
Figure 2-1 illustrates the relationship between Workstation clients and the support processes on the machine serving as the administrative domain. The words in parentheses are substitutables in the command line options of the WSL or server entry parameters.
Figure 2-1 BEA TUXEDO Workstation Feature: Support Processes
The format of the CLOPT parameter is as follows:
CLOPT="[-A] [servopts options] - - -nnetaddr[-ddevice] \
[-wWSHname] [-ttimeout-factor] [-Tclient-timeout] \
[-mminh] [-Mmaxh] [-xmpx-factor] \
[-pminwshport] [-Pmaxwshport] \
[-Iinit-timeout] [-ccompression-threshold] [-kcompression-threshold] \
[-zbits] [-Zbits] [-Hexternal_netaddr] [-K {client|handler|both|none}]"
As noted above, the -A value indicates that the WSL is to be booted offering all its services. This is a default, but it is shown in the example to emphasize the distinction between system-supplied servers and application servers. The latter may be booted offering only a subset of their available services.
The -- syntax marks the beginning of parameters that are passed to the WSL after it has been booted.
The -n netaddr Option
This is required. netaddr is the network address used by Workstation clients to connect to your application. The Workstation listener process uses this address to listen for clients attempting to connect at this address.
The -d device Option
The value of device is the device name used by the Workstation listener to access the network. In the past this option was required if the transport provider was TCP/IP. As of BEA TUXEDO Release 6.4, this option is no longer required.
The -w WSHname Option
WSHname is the name of the Workstation handler process started by the Workstation listener. You should specify the name of the executable created by buildwsh(1). The default name assumed for that a.out is WSH, the Workstation handler that is delivered with Workstation. That name is used if the -w option is omitted. If you customize a Workstation handler, make certain that it resides in either $APPDIR or $TUXDIR/bin. If your customized Workstation handler is used by only one application, we recommend putting the handler in the directory specified by the APPDIR environment variable. If the handler is used by many applications, we recommend putting it in the bin directory under $TUXDIR.
The -t timeout-factor Option
When a large number of workstation clients attempt to connect simultaneously, some of the requests may time out due to a blocking condition. The -t timeout-factor is provided to guard against this possibility. The value of timeout-factor is a number that, when multiplied by SCANUNIT, specifies the amount of time in seconds that should be allowed for a workstation client to complete initialization processing through the WSH before being timed out by the WSL. The default for this parameter is 3 in a non-security application, and 6 in a security application.
The -T client-timeout Option
Client-timeout is the amount of time (in minutes) that a client is allowed to stay idle. If a client does not make any requests within this time period, the WSH disconnects the client. If this argument is not given or is set to 0, then the timeout is infinite.
The -m minh Option
The minh value is the minimum number of Workstation handler processes to be started by this Workstation listener when the listener is booted. If specified, the -m option takes a value from 0 to 255. The default is 0.
The -M maxh Option
maxh is the maximum number of Workstation handler processes to be started by this Workstation listener. If specified, the -M option takes a value from 1 to 32,767. The default is MAXWSCLIENTS for the machine divided by the multiplexing factor MPX. For example, let's say you specify MAXWSCLIENTS=100 in the MACHINES section and -x10 for the CLOPT of the listener. The default for -M maxh is 100/10 or 10. maxh must be greater than or equal to minh.
The -x mpx-factor Option
The mpx-factor value specifies the number of Workstation clients you want each Workstation handler to support simultaneously. If specified, the -x option takes a value from 1 to 32,767. The default is 10.
The -K { client | handler | both | none } Option
Use -K to turn on the network keep-alive operation for the client, the handler, or both. You can turn off this option for both the client and handler by specifying none.
Example
The entries related to Workstation as specified in the configuration file for the bankapp application are shown in Listing 2-1.
Listing 2-1 Excerpts from bankapp configuration file
#
# ubbconfig file for Workstation example, SHM mode
#
"mach1" LMID="SITE1"
TUXCONFIG="/tuxroot/tuxapp/tuxconfig"
TUXDIR="/tuxroot"
APPDIR="/tuxroot/tuxapp"
TLOGDEVICE="/tuxroot/tuxapp/TLOG"
TLOGNAME="TLOG"
TLOGSIZE=100
MAXACCESSERS=100
MAXWSCLIENTS=50
#
*GROUPS
"GRP1" LMID="SITE1" GRPNO=4
#
*SERVERS
"WSL" SRVGRP="GRP1" SRVID=2
CLOPT=" - -n //wsl.beasys.com:3107 -d /dev/tcp"
RQPERM=0660 REPLYQ=Y RPPERM=0660
MIN=1 MAX=1 CONV=N
SYSTEM_ACCESS=FASTPATH
MAXGEN=5 GRACE=86400 RESTART=Y
#