







|
Most portals incorporate content into their applications. Content can be anything from advertisements (graphic files), documents (text files), or animation files. Portal content is typically stored in a content repository that is part of a content management system connected to the portal. Developers and administrators then have access to content and can determine how it is viewed by portal visitors.
This chapter includes the following sections:
The content management system in WebLogic Portal allows you to store and access content, track its progress, and incorporate content in your portal applications. It provides an easy integration between creating content and delivering that content to your users. Content contributors use repositories in WebLogic Portal to store and access content. If WebDAV is enabled, content contributors can also access content through applications such as Microsoft Word. For more information, see Using WebDAV with Your BEA Repository.
For information about tracking the content retrieved from the virtual content repository, see Setting Up Events and Behavior Tracking. in the Interaction Management Guide.
Content repositories are connected to your portal with the Virtual Content Repository. Portal developers use the content API and JSP tools to access the Virtual Content Repository and deliver content to portal visitors. For more information about the Virtual Content Repository, see Connecting Repositories to the Virtual Content Repository.
Content repositories are connected to WebLogic Portal using the Virtual Content Repository. When a content repository is connected to the Virtual Content Repository, portal developers and content contributors can access content using WebLogic Portal content tools, including the Portal Administration Console, the content API, JSP tags, content selectors, placeholders and WebDAV-enabled applications.
You can also integrate third-party content management systems (including JSR 170-compliant repositories) with WebLogic Portal by connecting them to the Virtual Content Repository. For information about using a third-party repository, see Connecting to a Third-Party Repository. Once connected to the Virtual Content Repository, content within a third-party repository can be searched and utilized by WebLogic Portal.
Typically, you access the Virtual Content Repository through the Portal Administration Console, as shown in Figure 1-1.
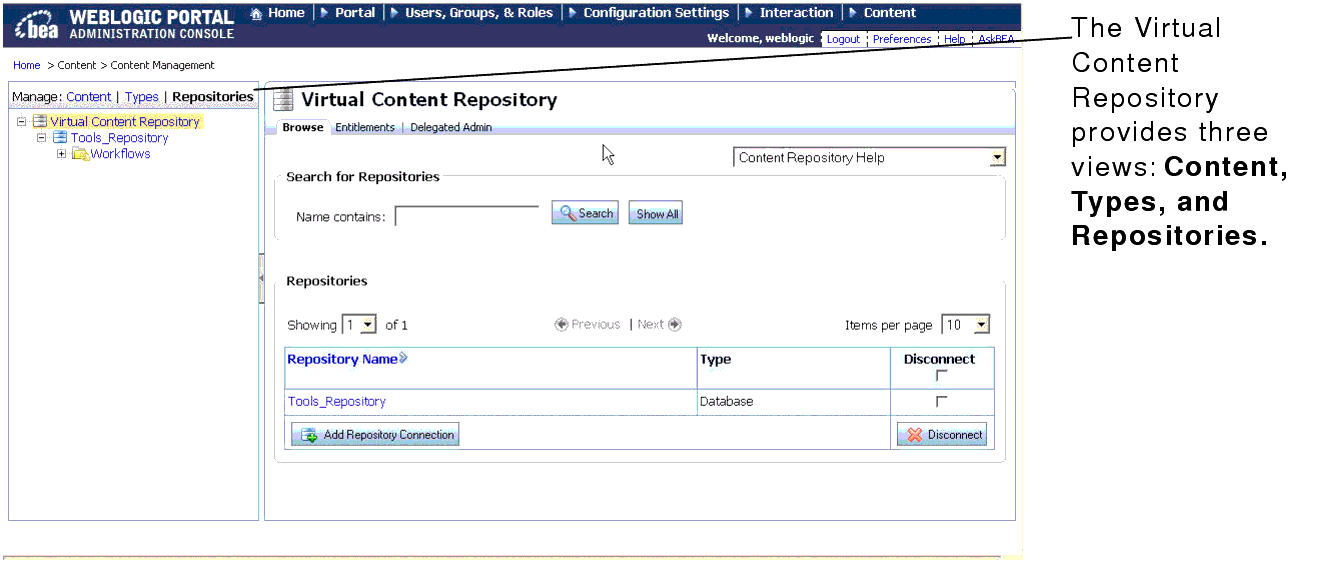
The Virtual Content Repository provides three views of your content repositories: Content, Types, and Repositories.Table 1-1 lists each view and the tasks you accomplish in each one.
|
|
By default, portal applications are configured to use a single BEA content repository to store your content. BEA repositories use your portal database to store content in reserved tables. However, you can use multiple BEA repositories and configure them to use file system to store your content.
Within a BEA repository, you can:
You can also enable BEA repositories to take advantage of BEA's library services. Library services allow users to track versions of content and use content workflows to enforce processes that you want content contributors to use, such as getting approval and retiring outdated content. For more information about library services, see Adding Content to a BEA Repository. Library-services content is referred to as versioned content.
If you are using a library services-enabled BEA repository, you can also:
Typically, content contributors add content to a BEA repository through the Portal Administration Console, which provides access to your content repositories. Content users can also add content using Windows Explorer, providing the repository is configured to use WebDAV. For more information, see Using WebDAV with Your BEA Repository.
When users add content to a repository, they create metadata for the content file by associating the content with a content type and assigning property values such as date, author, color, and so on. Portal developers use this metadata to retrieve and display content within your portal application. By using content types, portal developers can easily retrieve content from your repository and create content relationships. For example, retrieve all content created by a certain author.
Figure 1-3 shows an example of adding content to a repository.
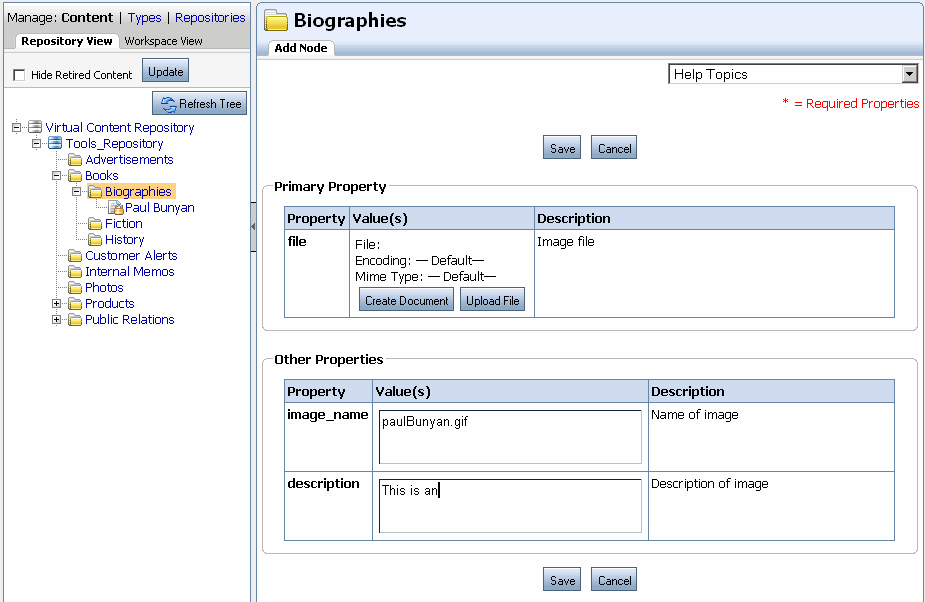
For more information about adding content, see Adding Content to a BEA Repository.
When a content repository is connected to the Virtual Content Repository, portal developers can deliver that content to your portal users using a variety of WebLogic Portal development tools. These include the content API, JSP tags, and personalization tools. For more information about delivering content in your portal, see Delivering Content Within Your Portal.
The content management system in WebLogic Portal allows developers to:
You can ensure the security of your portal content using Delegated Administration and Visitor Entitlements in the Portal Administration Console.
You can use Delegated Administration to determine which users can add or modify content. For example, you can allow only certain users, such as editors, to approve content for publishing, or disallow users from deleting content from your repository. Visitor entitlements allow you to define who can access a portal and what they can do within the portal. For more information about security, see the WebLogic Portal Security Guide.
The tasks in this guide are organized according to the portal life cycle. For more information about the portal life cycle, see the WebLogic Portal Overview Guide. The portal life cycle contains four phases:
Figure 1-4 shows how content management fits into the portal life cycle.
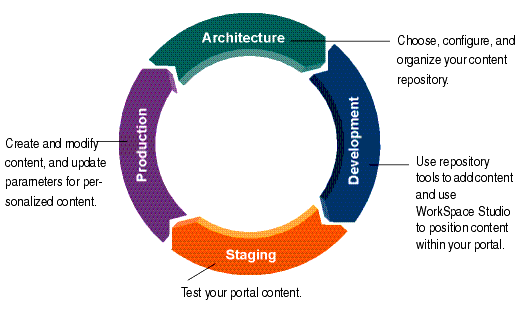
During the architecture phase, you choose the type of content repository and set it up to match your business needs. This includes creating content types to store content, creating content workflows, and creating content folders to organize your repository. You also plan propagation strategies and determine which content tools you will use.
During the development phase, content contributors add content and developers determine how to present that content within your portal. Content contributors use the Portal Administration Console to add and manage content. Using WorkSpace Studio, portal developers use content selectors, placeholders, JSP tags, HTML, and the content API to retrieve and display content.
The staging phase is when you test your portal and verify that developed content is appearing correctly. You might move iteratively between developing and testing what you created. If you return to the development phase and make changes, you must redeploy your portal application to see the changes in the staging phase.
This is the phase where you manage your production environment. During the production phase, you use the Portal Administration Console to adjust settings, add content, modify content selectors, and create ad campaigns.


|